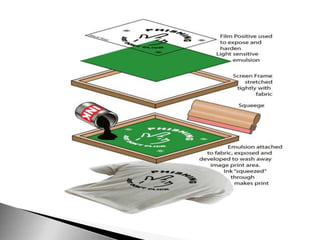
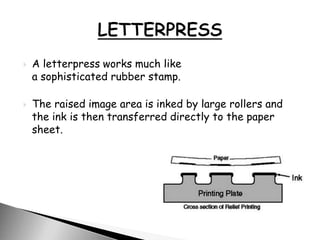
The document details various types of printing inks and methods, including gravure, inkjet, offset lithography, letterpress, and silk screen, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. Gravure is noted for its high print quality and longevity but is expensive, while inkjet printing is recognized for its affordability and color capabilities. It also discusses mesh counts, color theory in printing, and the principles behind different printing techniques.