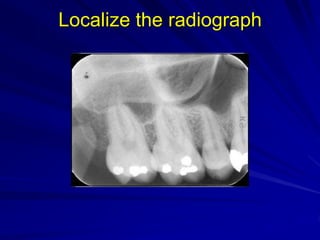
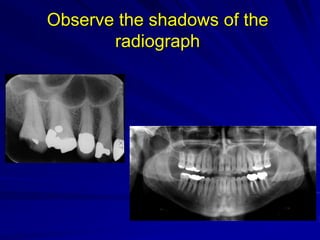
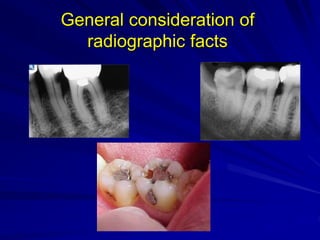
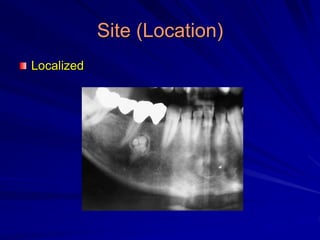
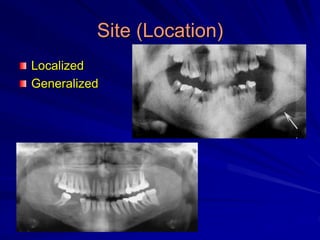
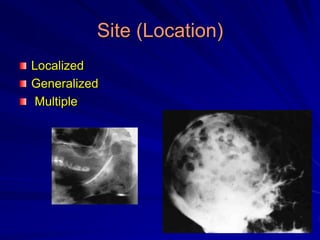
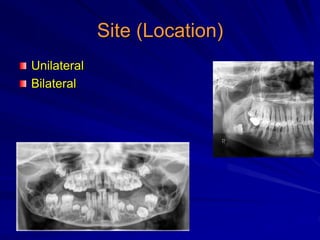
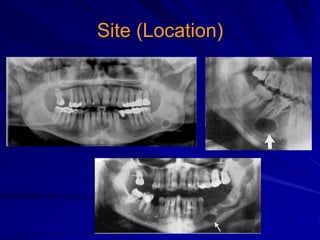
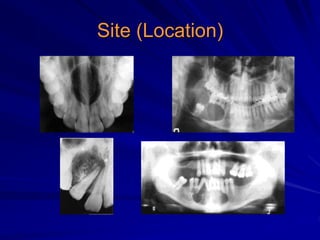
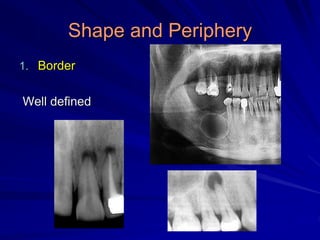
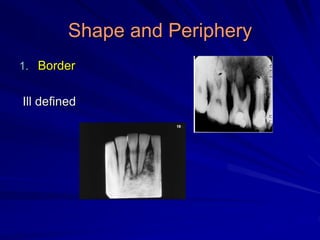
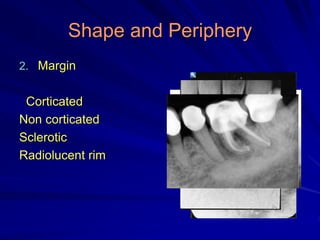
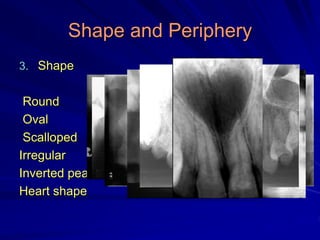
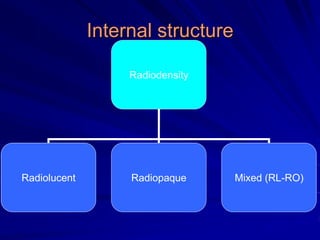
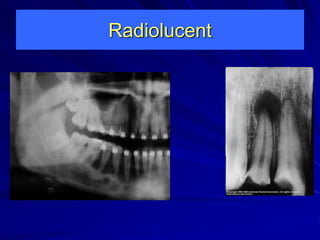
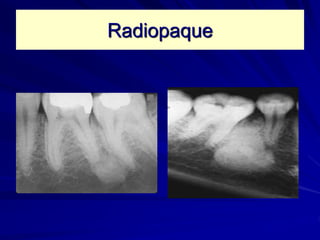
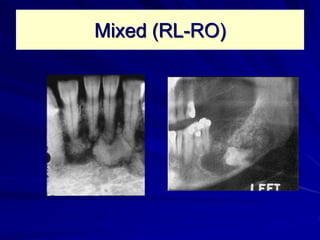
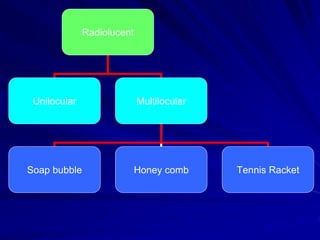
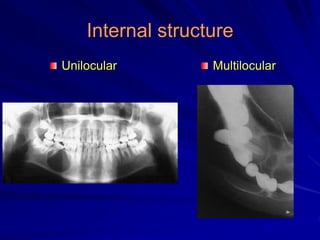
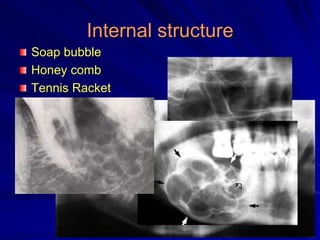
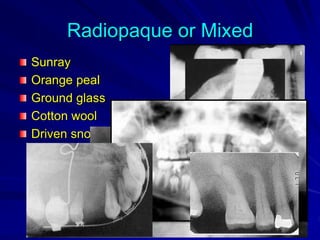
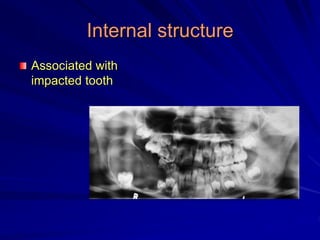
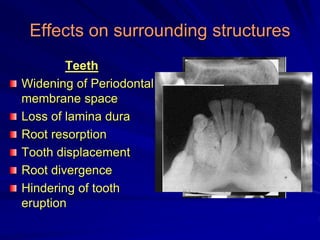
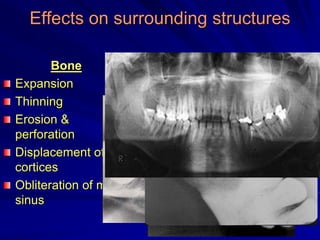
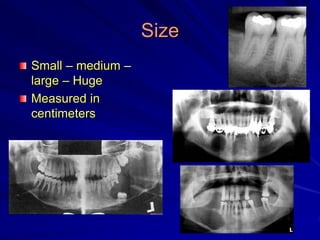
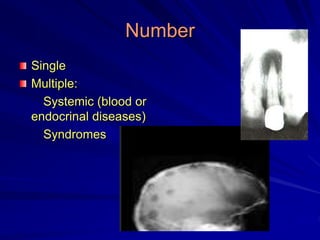
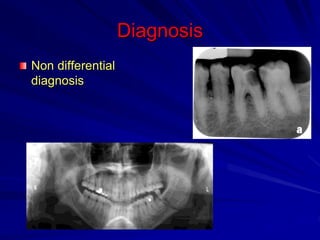
This document discusses principles of radiographic interpretation in dentistry. It describes interpretation as explaining what is seen on dental radiographs based on the ability to read what is revealed. The objectives of interpretation are detection, description, and differentiation of diseases using a systematic LOGIC method of localizing images, observing shadows, considering radiographic facts, formulating interpretations, and correlating findings with history and exam. Essential requirements include knowledge of normal anatomy, variations, and pathological appearances as well as optimal viewing conditions.