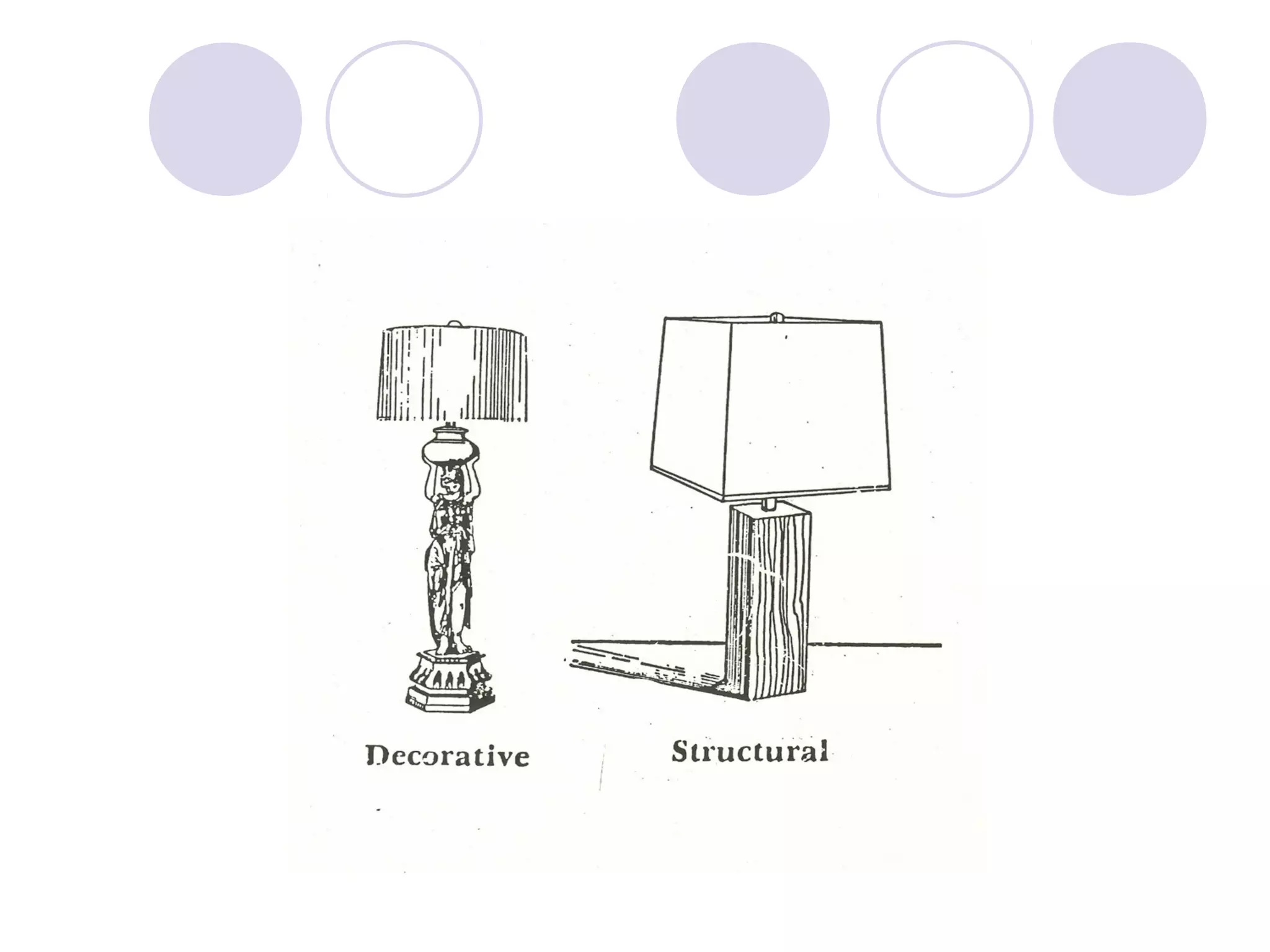
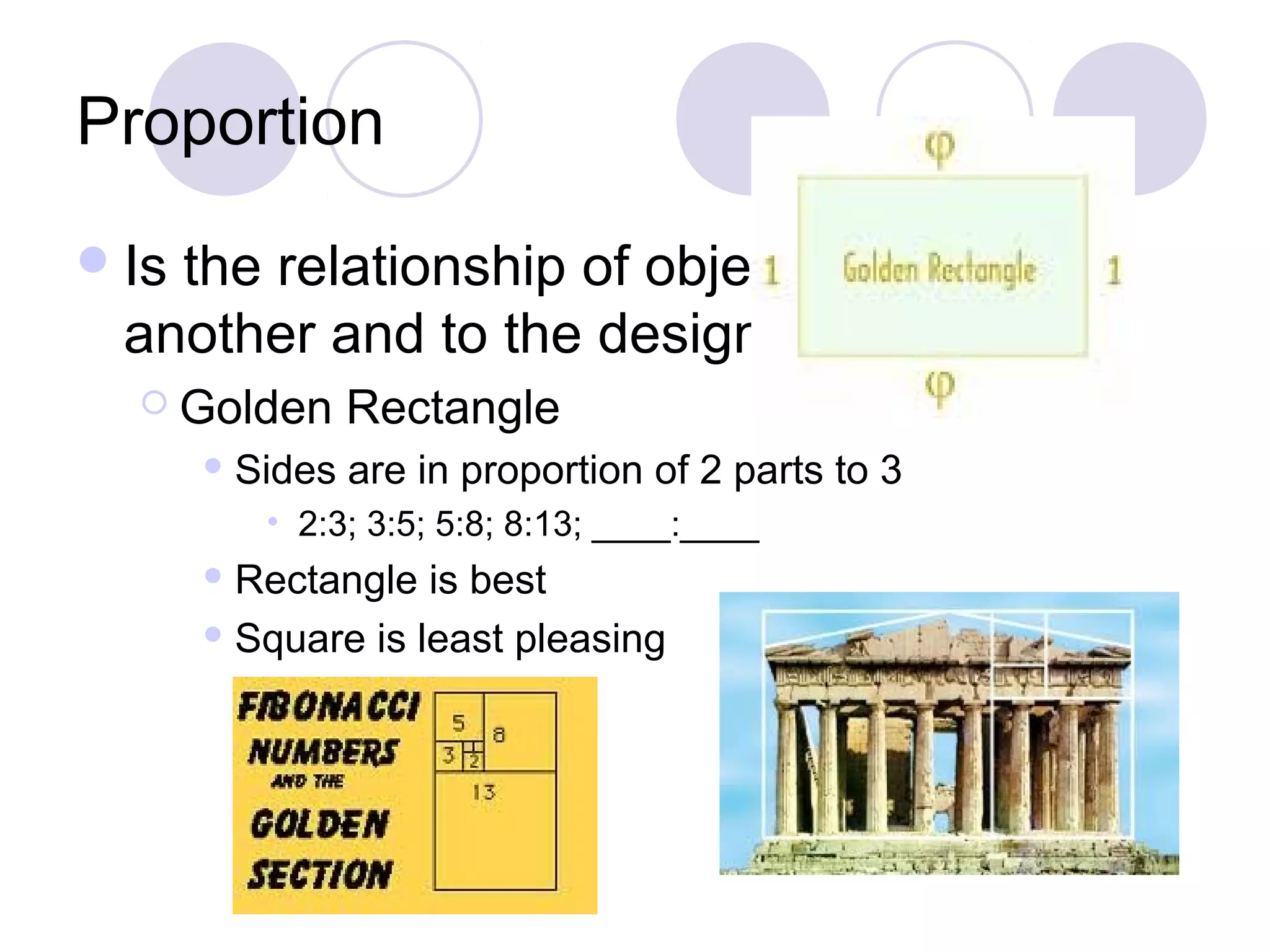
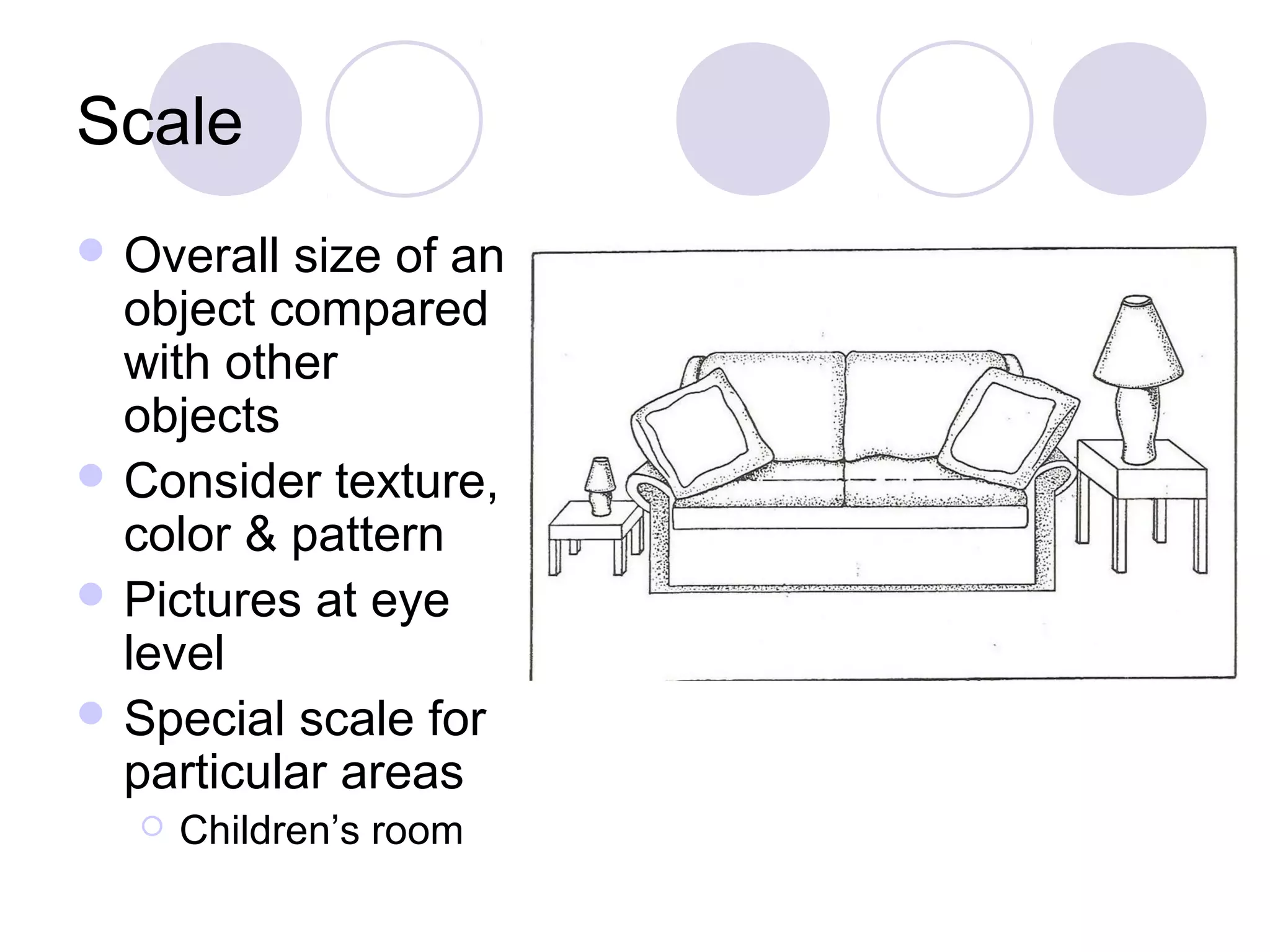
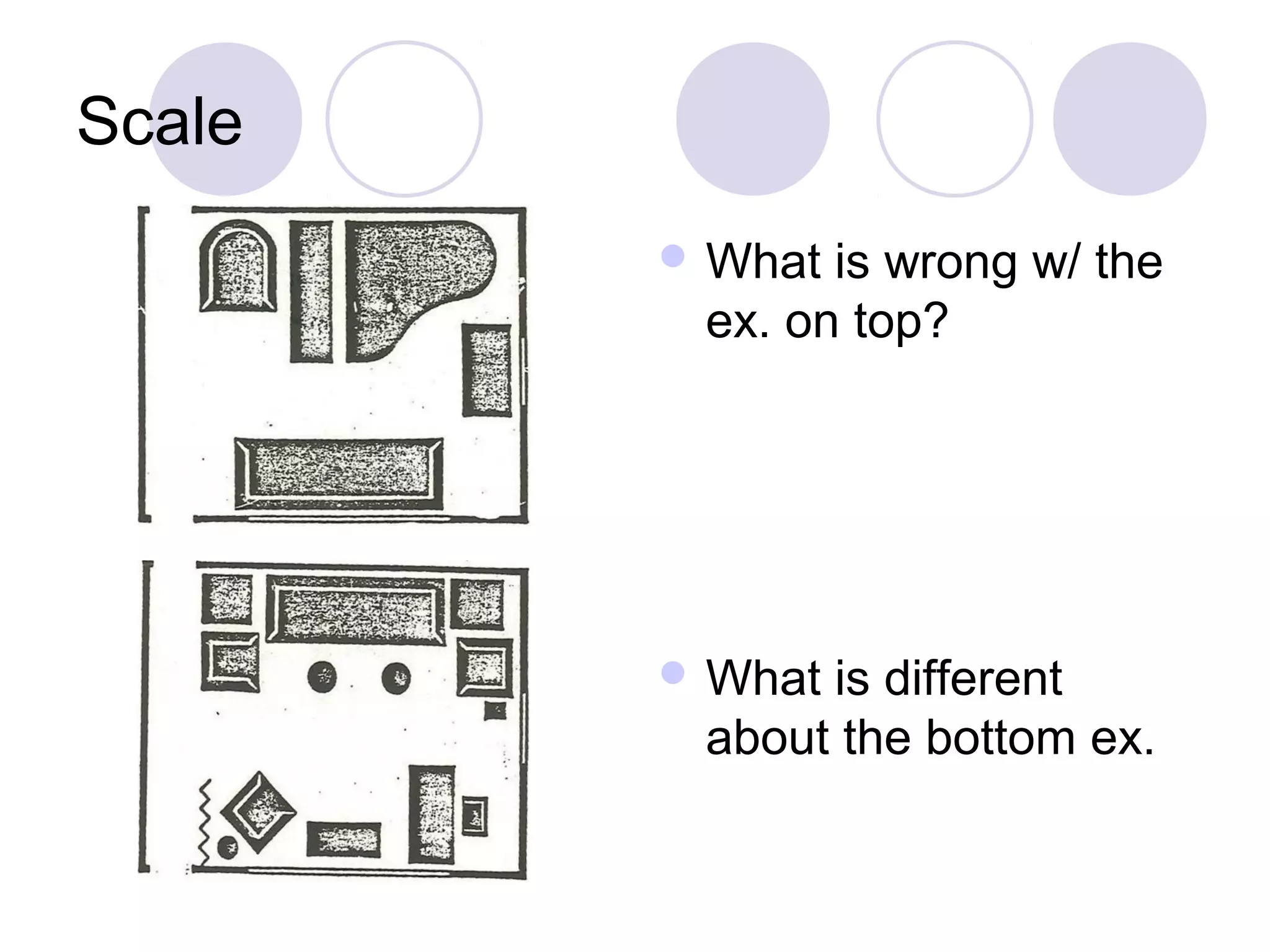
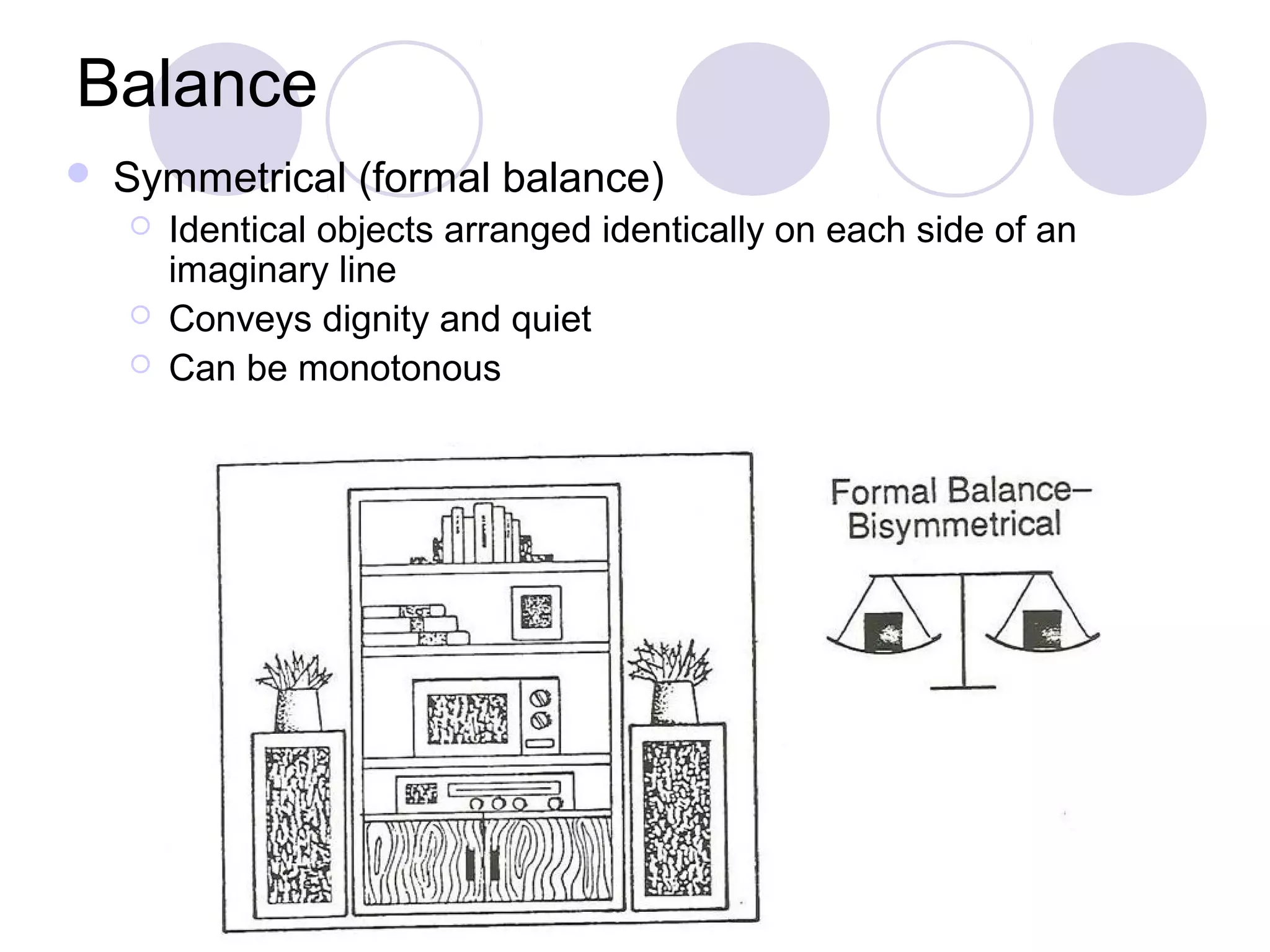
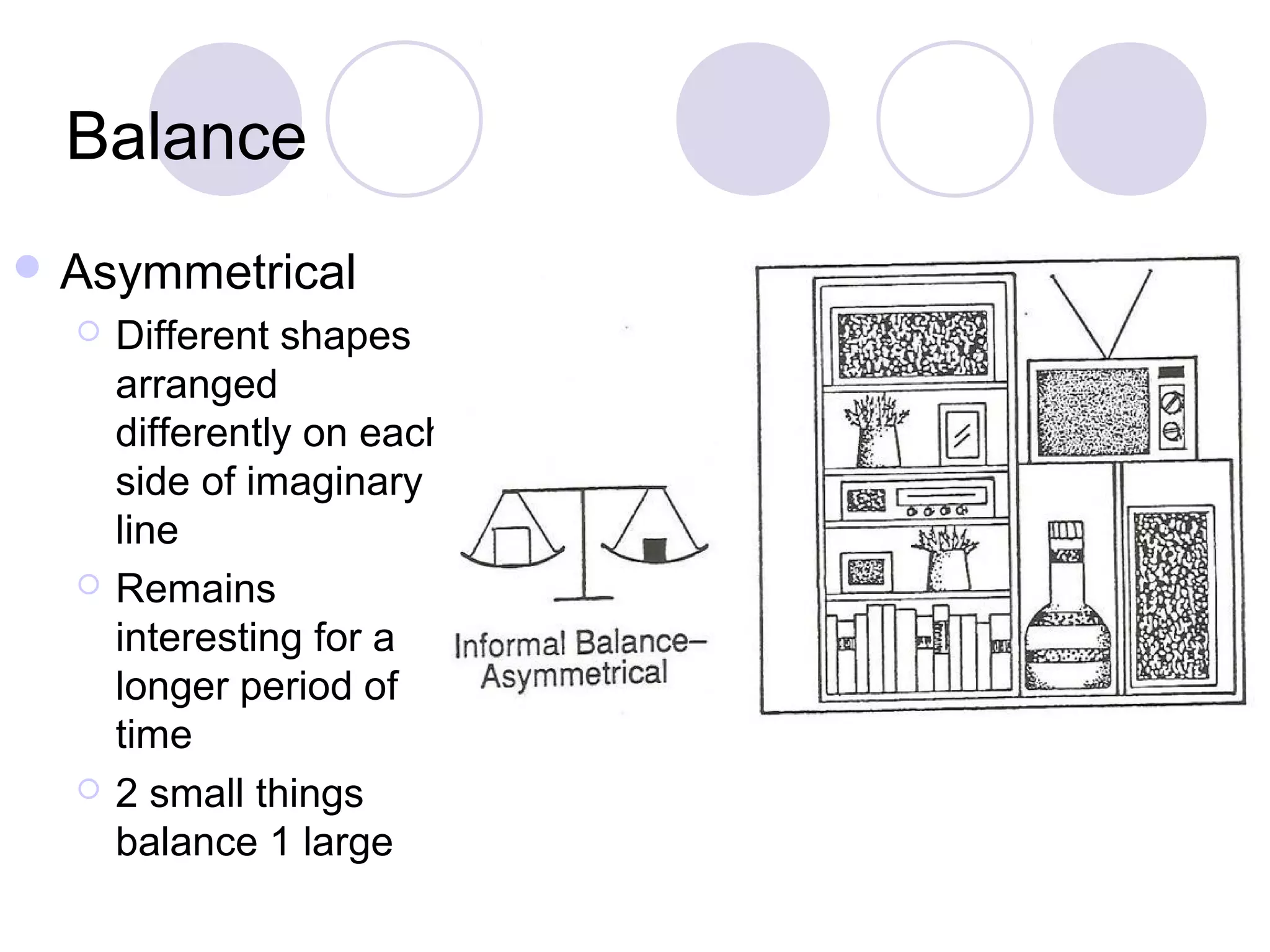
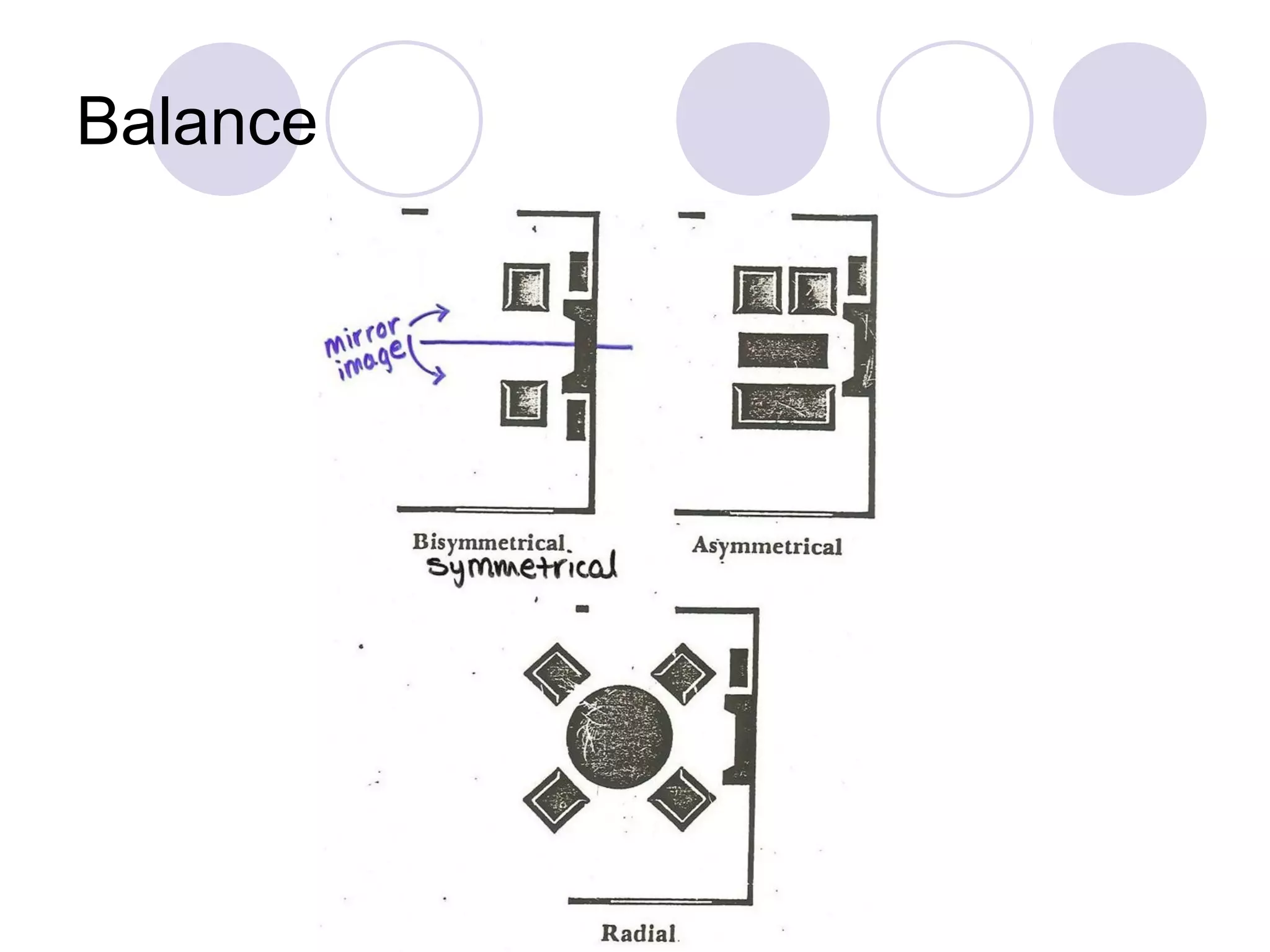
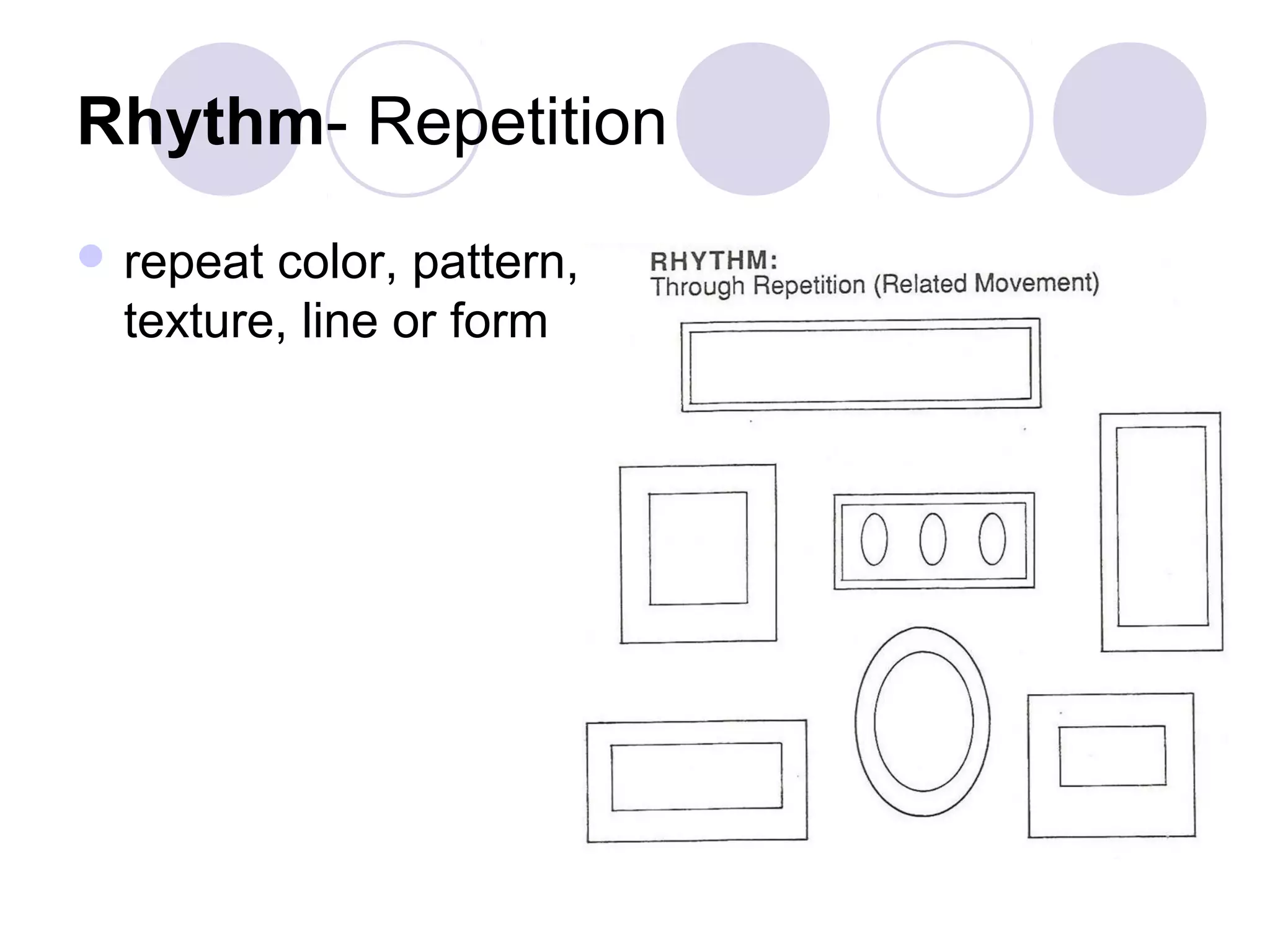
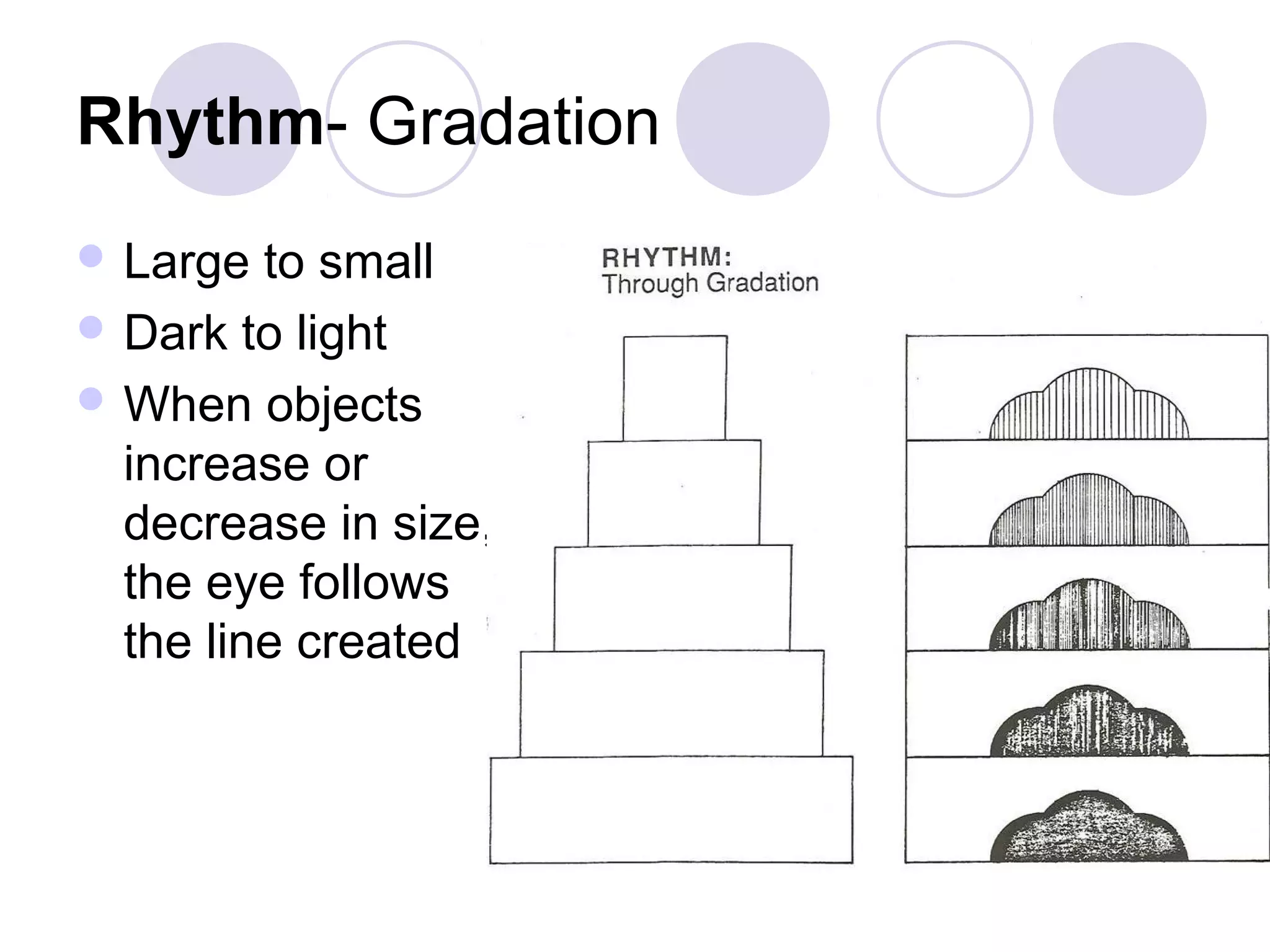
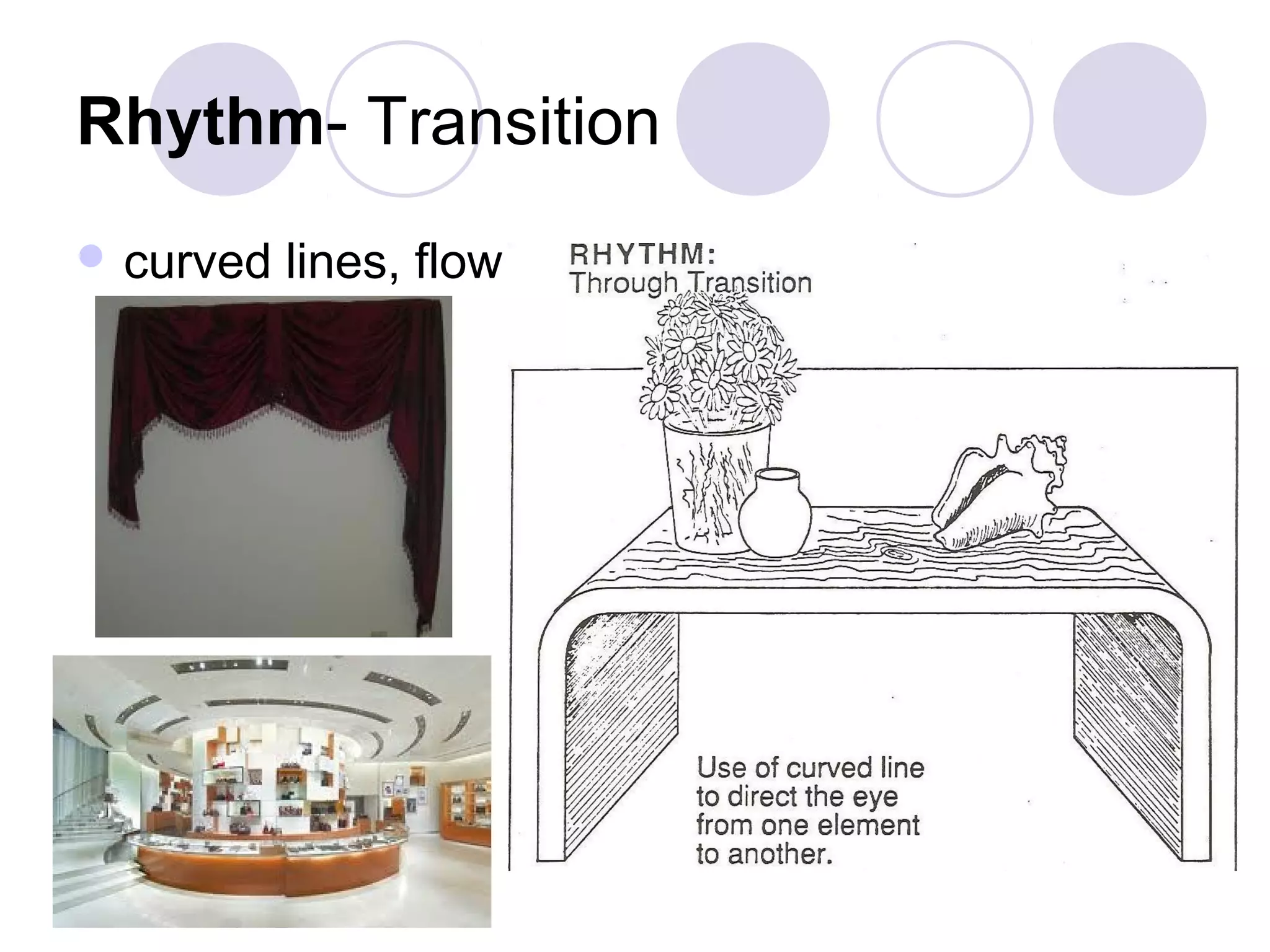
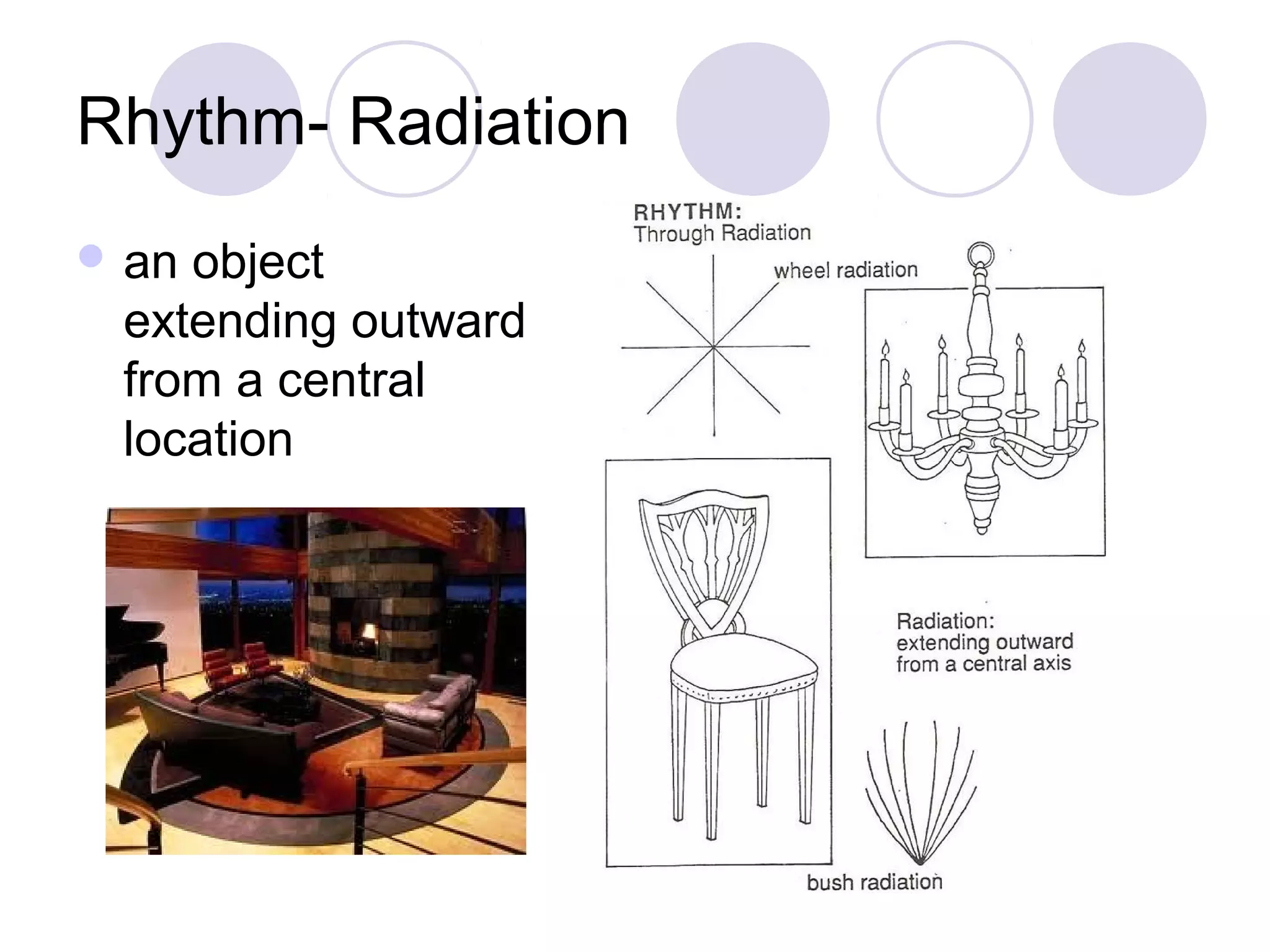
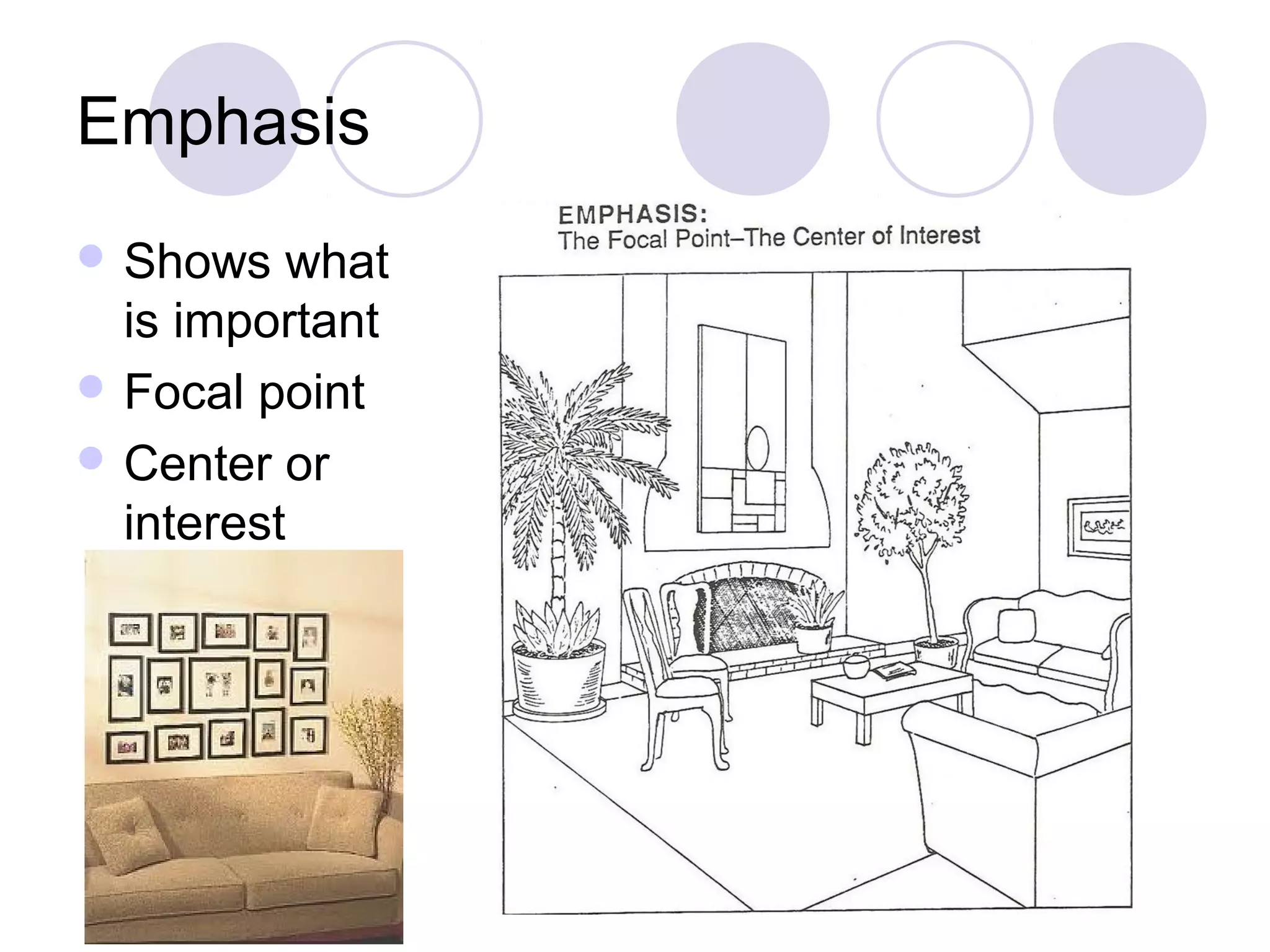
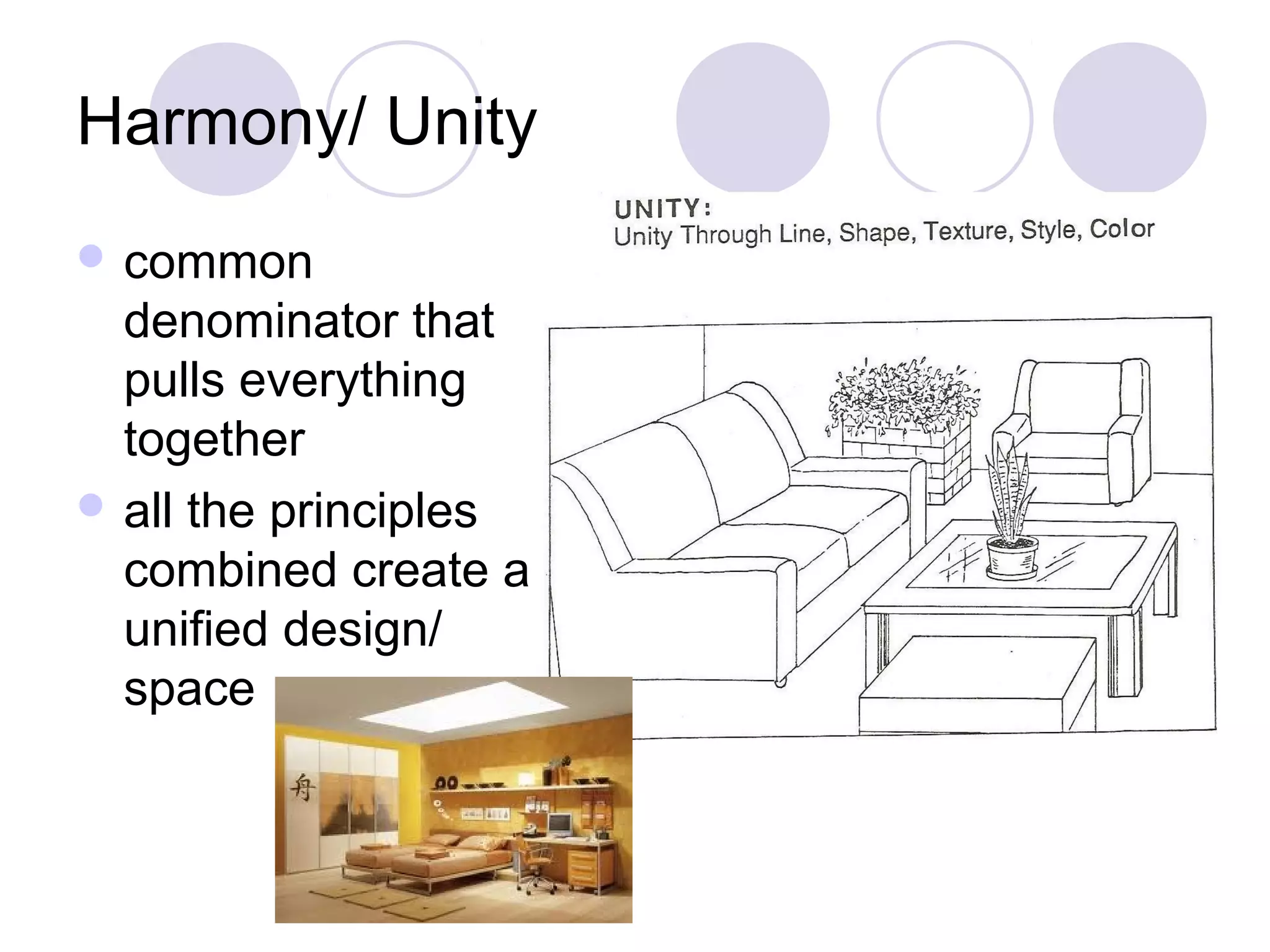
This document discusses principles of design, including structural design, decorative design, and five key principles: proportion/scale, balance, rhythm, emphasis, and harmony/unity. It provides examples and explanations of each principle. Proportion relates to the relationship between objects and the design as a whole. Balance can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. Rhythm helps move the eye through repetition, gradation, transition, or radiation. Emphasis shows what is important. Harmony/unity creates a unified design by combining all the principles.