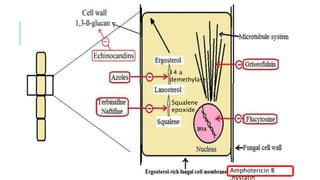
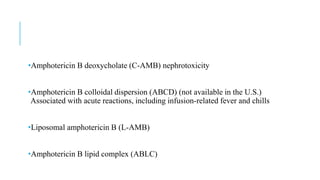
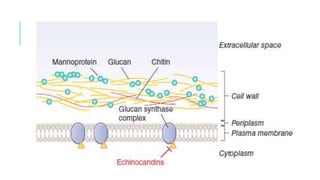
This document discusses various classes of antifungal drugs including polyenes, echinocandins, azoles, and allylamines. It provides details on specific drugs in each class like amphotericin B, fluconazole, terbinafine, and caspofungin. It also covers the mechanisms of action, indications, dosing considerations, toxicities and interactions for many of these antifungal agents. Finally, it discusses several topical antifungal drugs and their uses in treating superficial fungal infections.