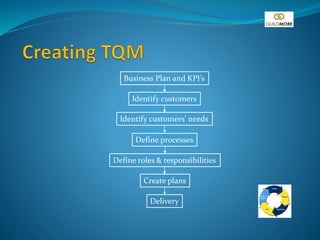
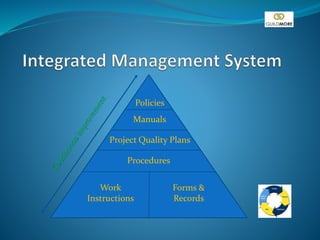
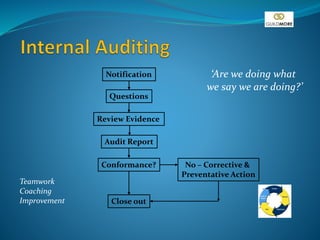
This document discusses the concept of Total Quality Management (TQM) at Guildmore. It outlines how quality was viewed in the past versus the present, focusing more on prevention and continuous improvement rather than inspection. TQM involves customer satisfaction, quality management systems, and strategic improvement across the entire company. The document provides details on policies, procedures, auditing, documentation, and standards to establish an integrated quality management system.