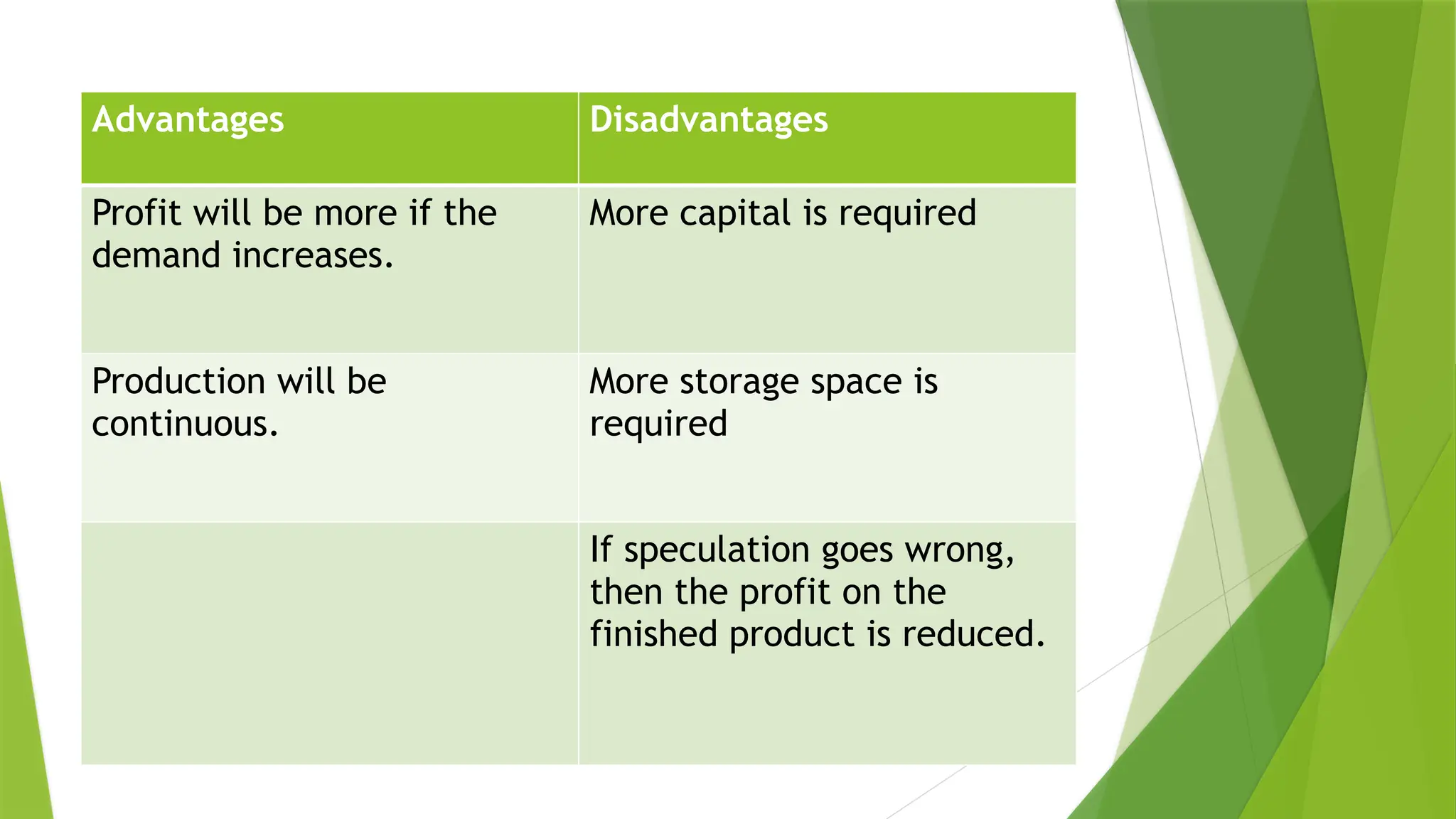
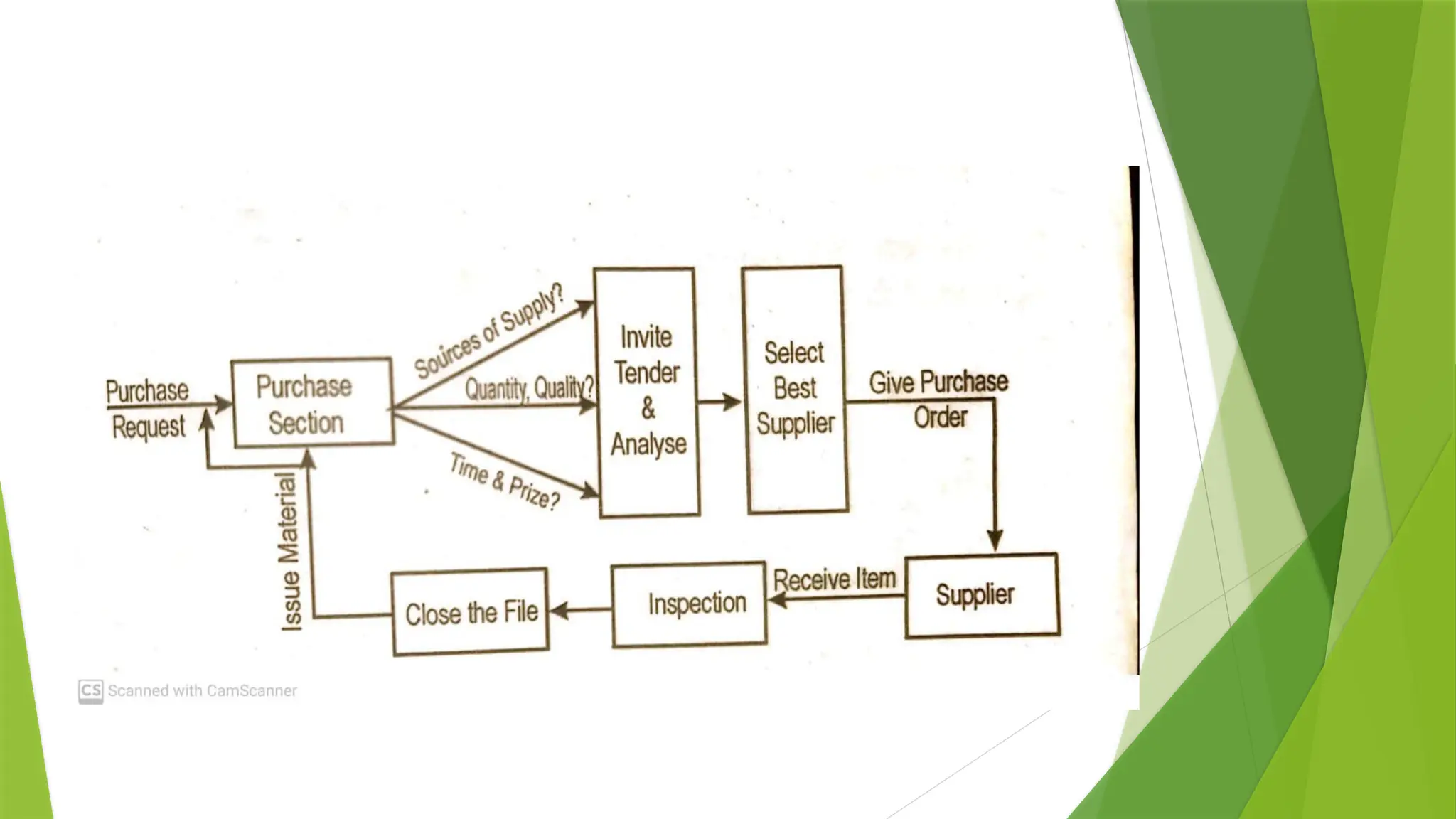
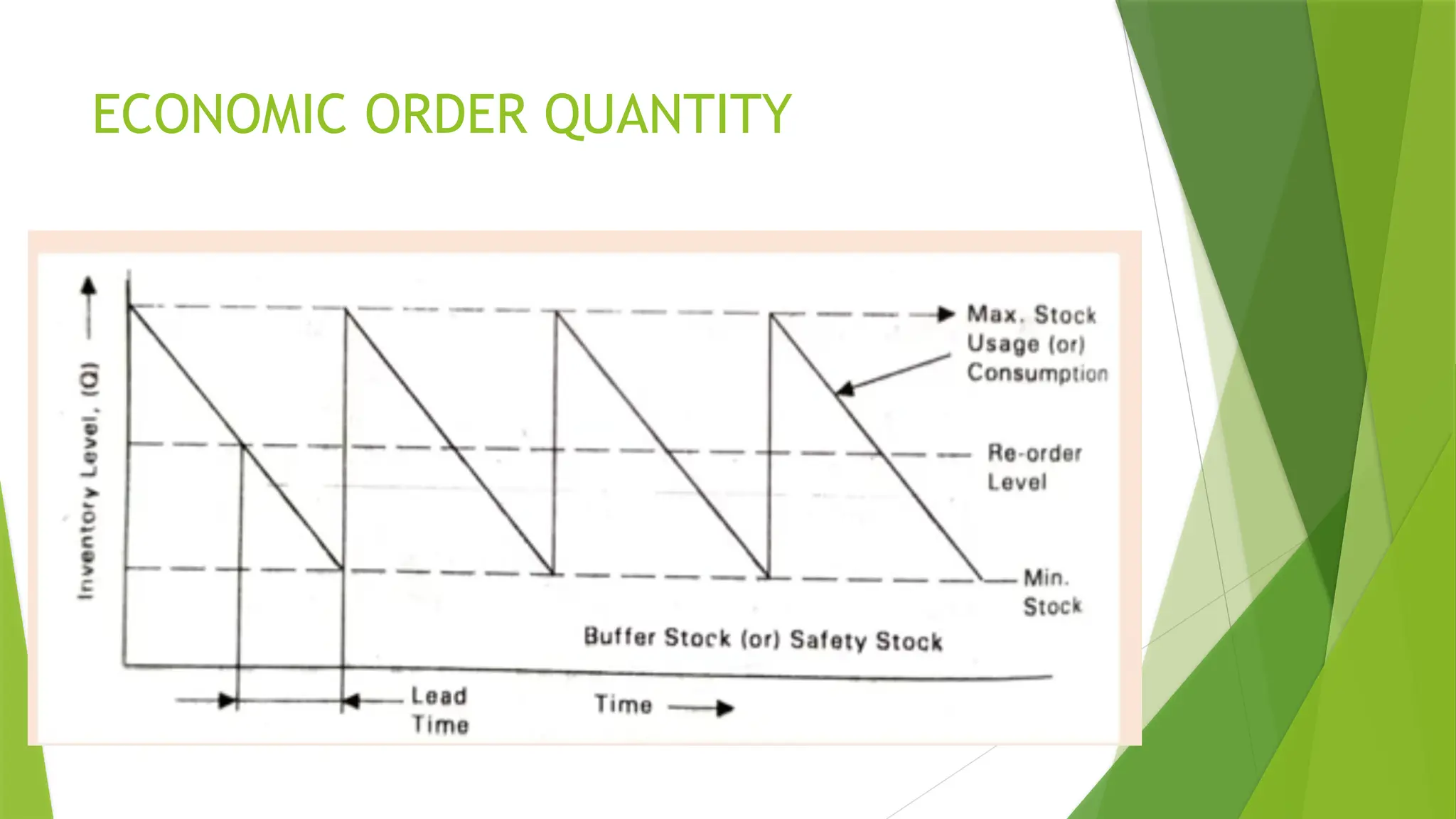
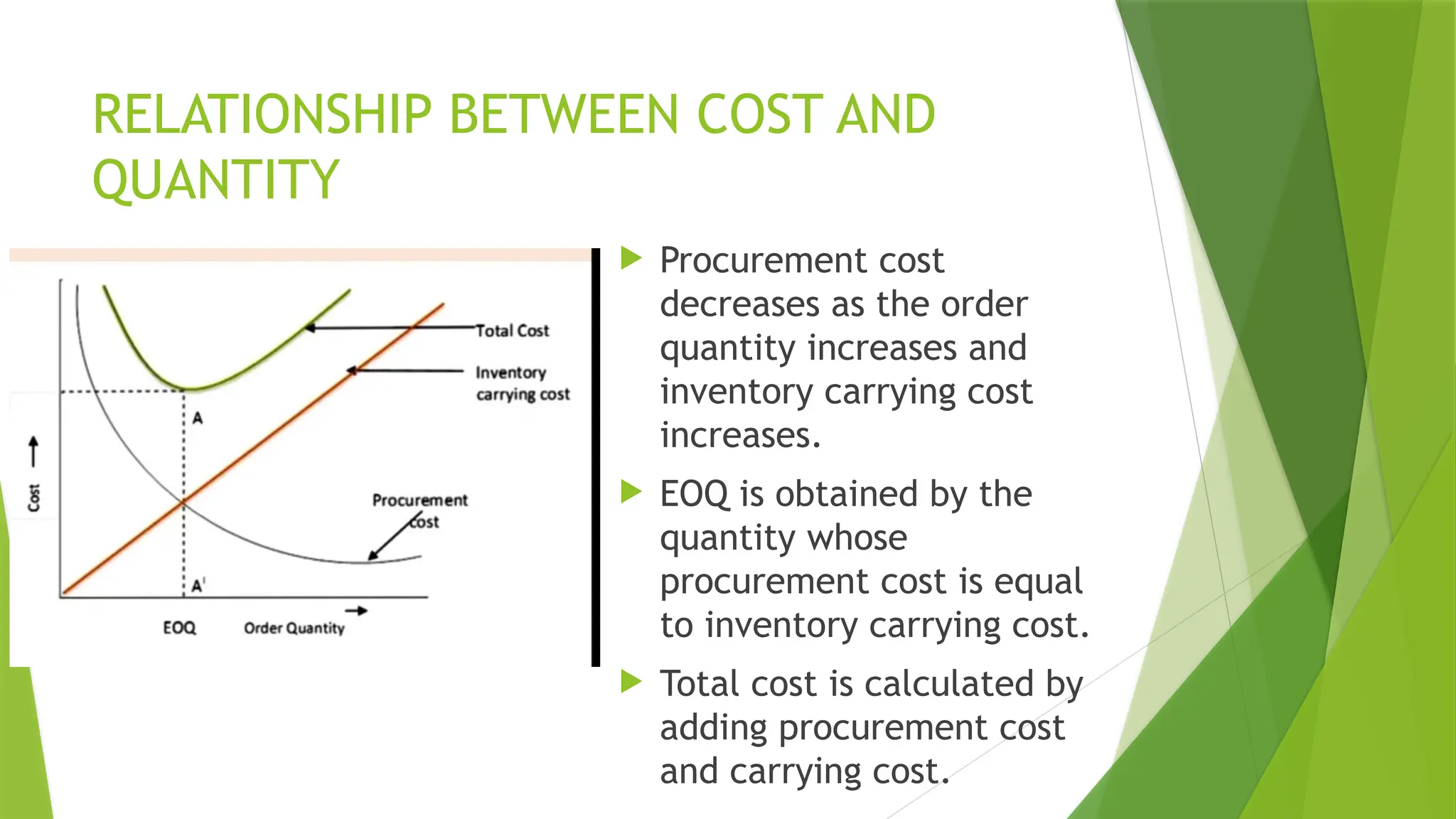
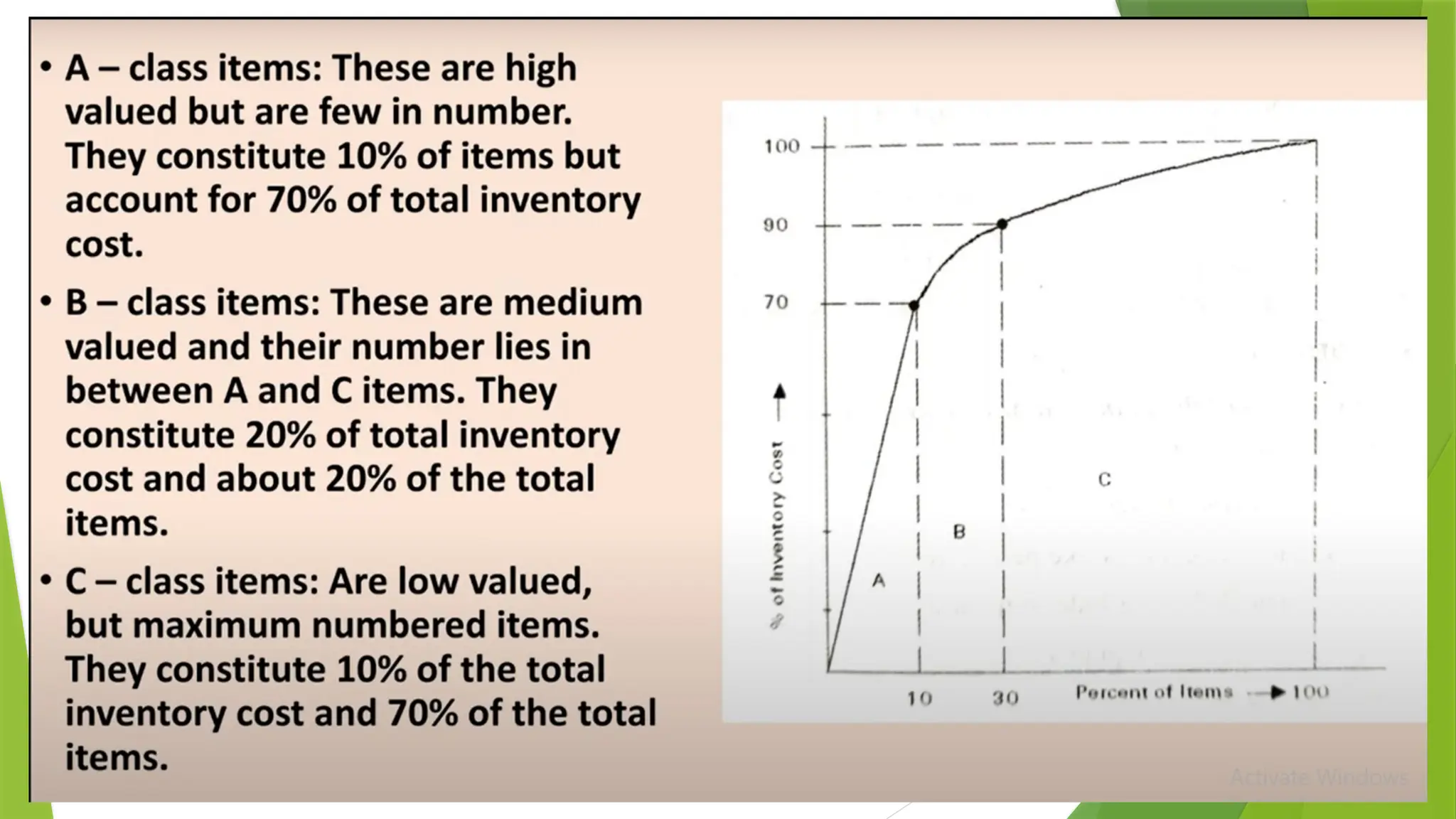
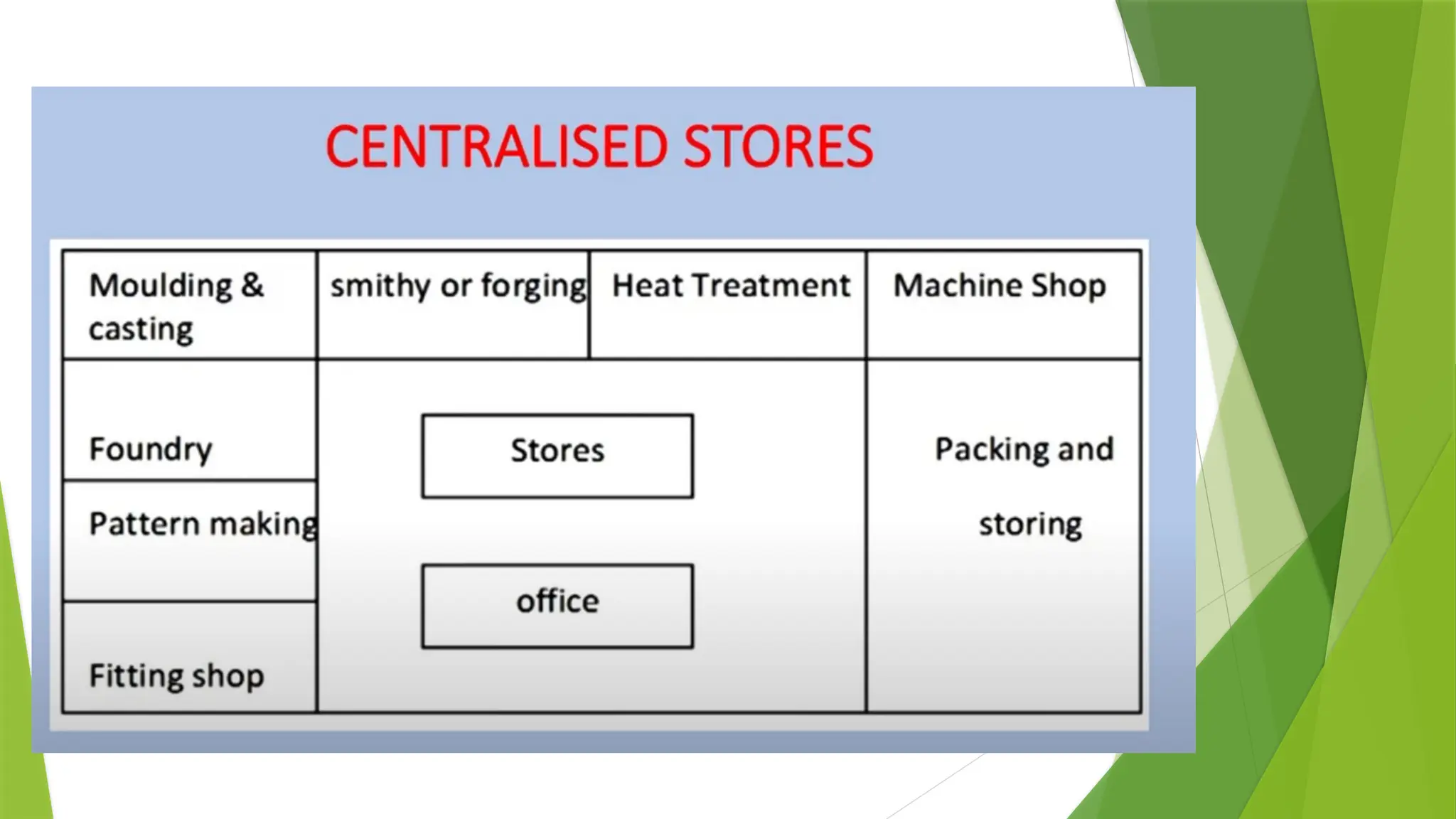
The document covers quality management principles emphasizing the importance of quality in manufacturing, including concepts like ISO 9000 and Total Quality Management (TQM). It outlines the processes for quality planning, the roles of various departments, and the benefits of adopting quality standards to improve customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Additionally, it details materials management and purchasing methods to ensure the effective flow of resources in an organization.