1. The document discusses good documentation practices for quality assurance and quality systems. It outlines the key elements of quality systems and 10 commandments for good manufacturing practices.
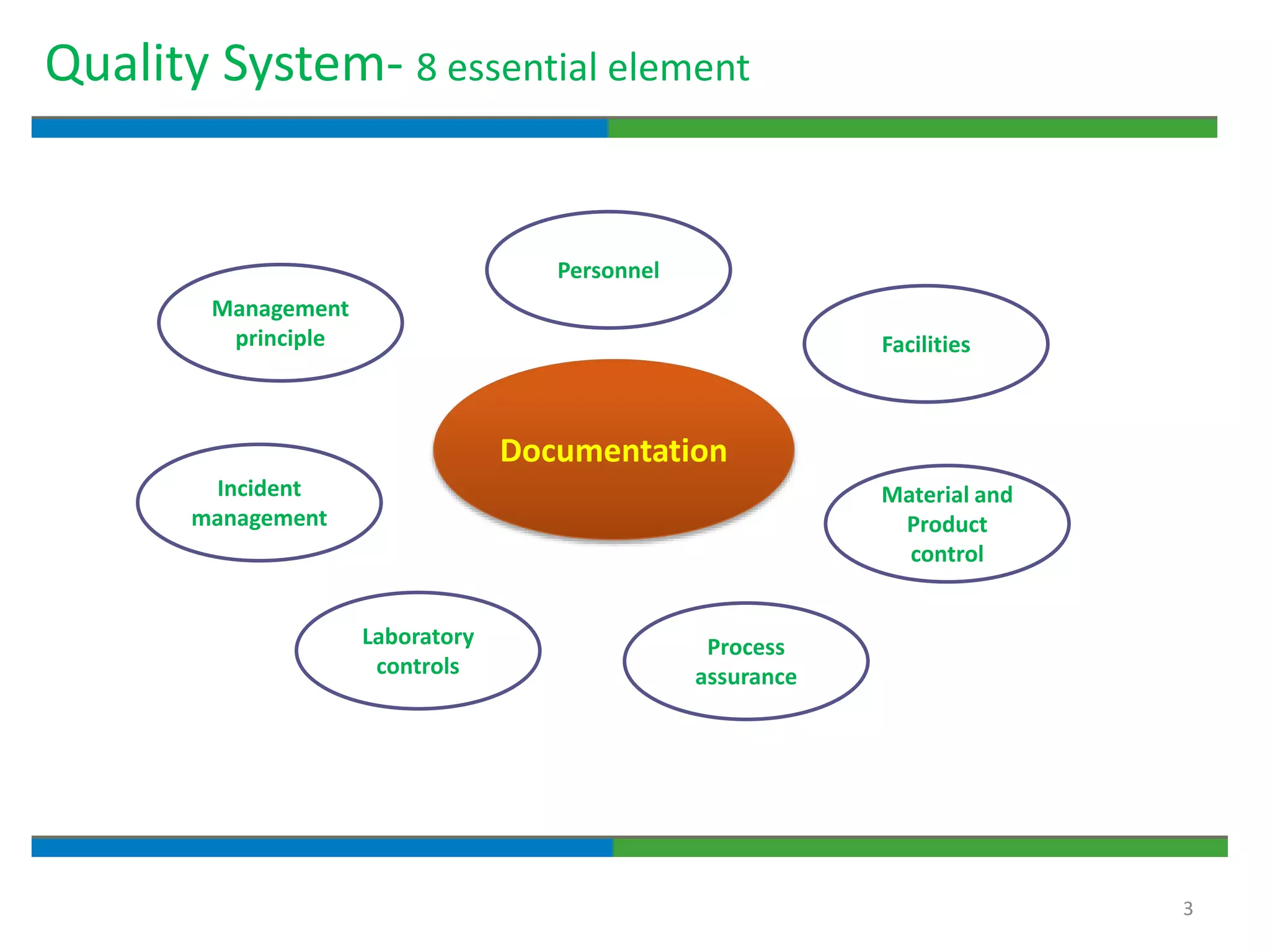
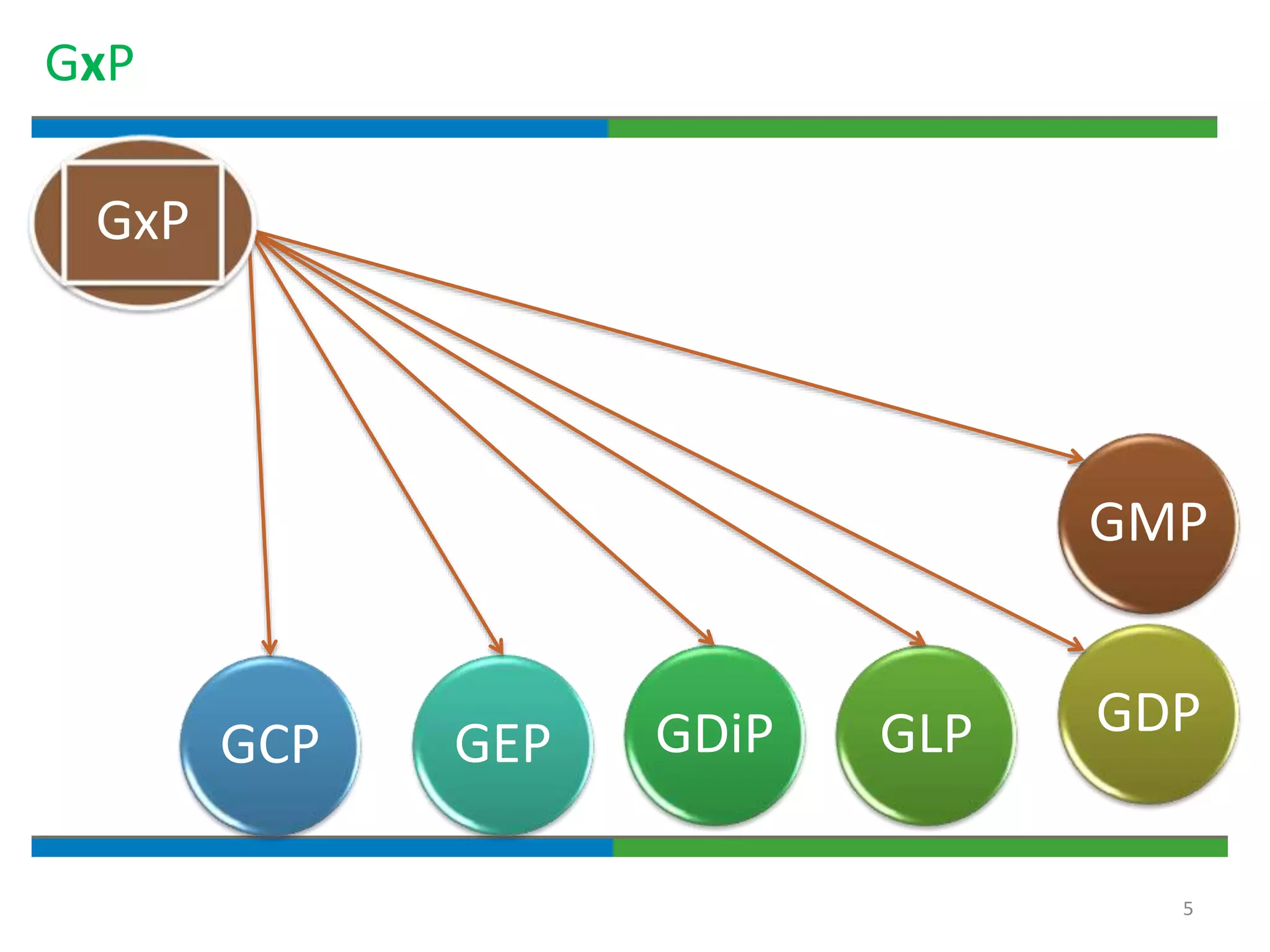
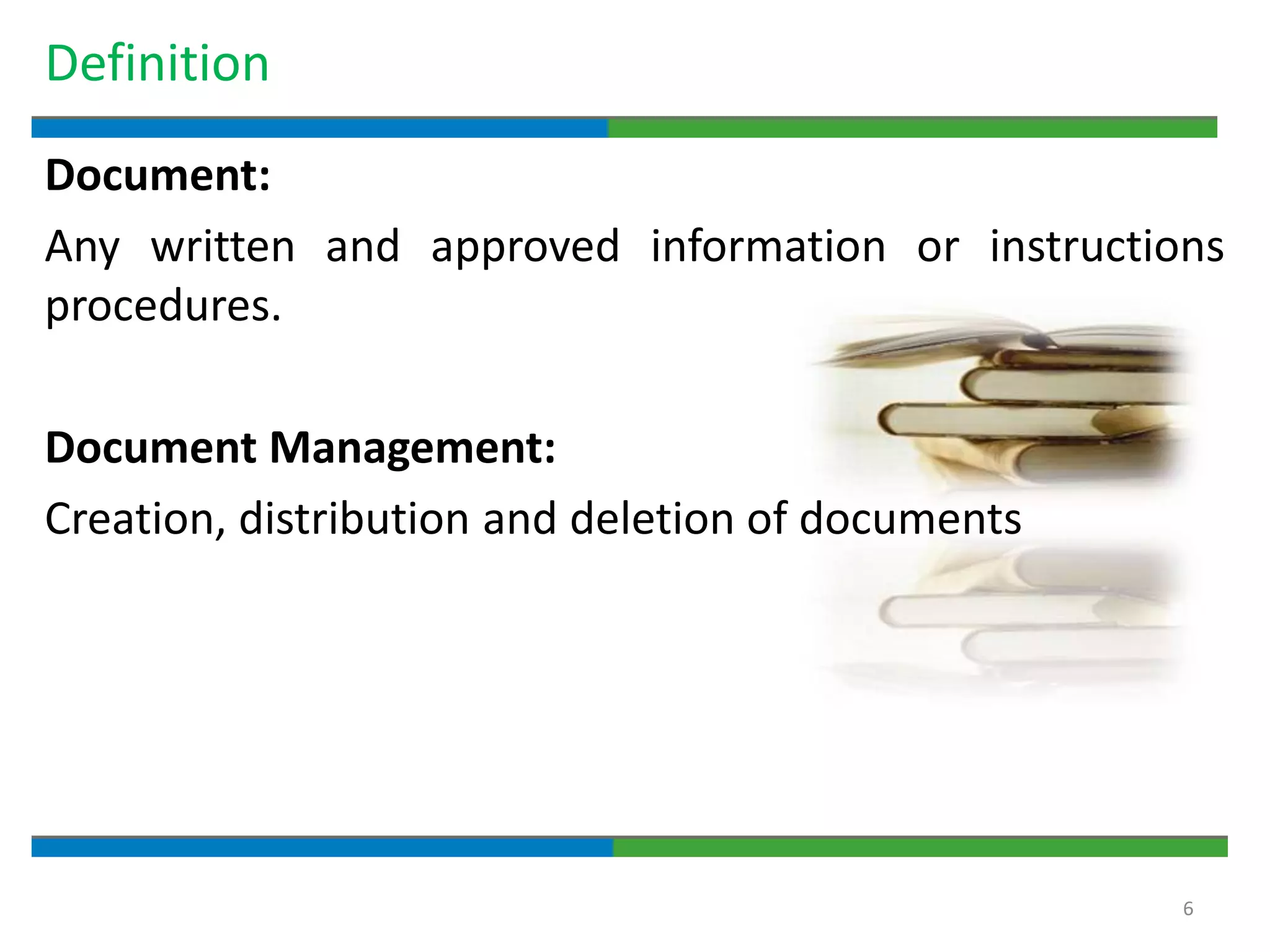
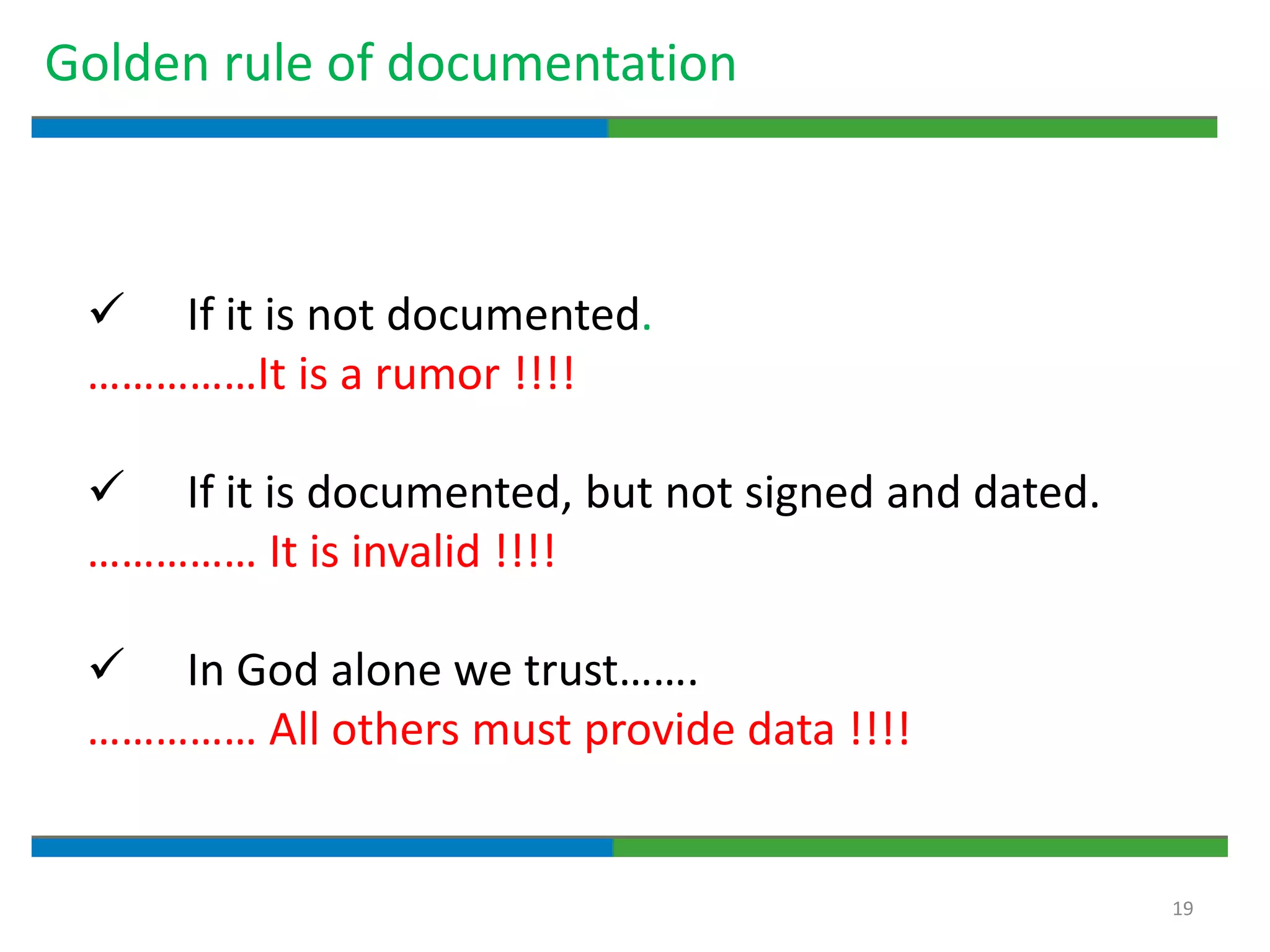
2. It defines key quality terms like GxP, defines what a document is, and explains the regulatory expectations around documentation being concise, legible, accurate and traceable.
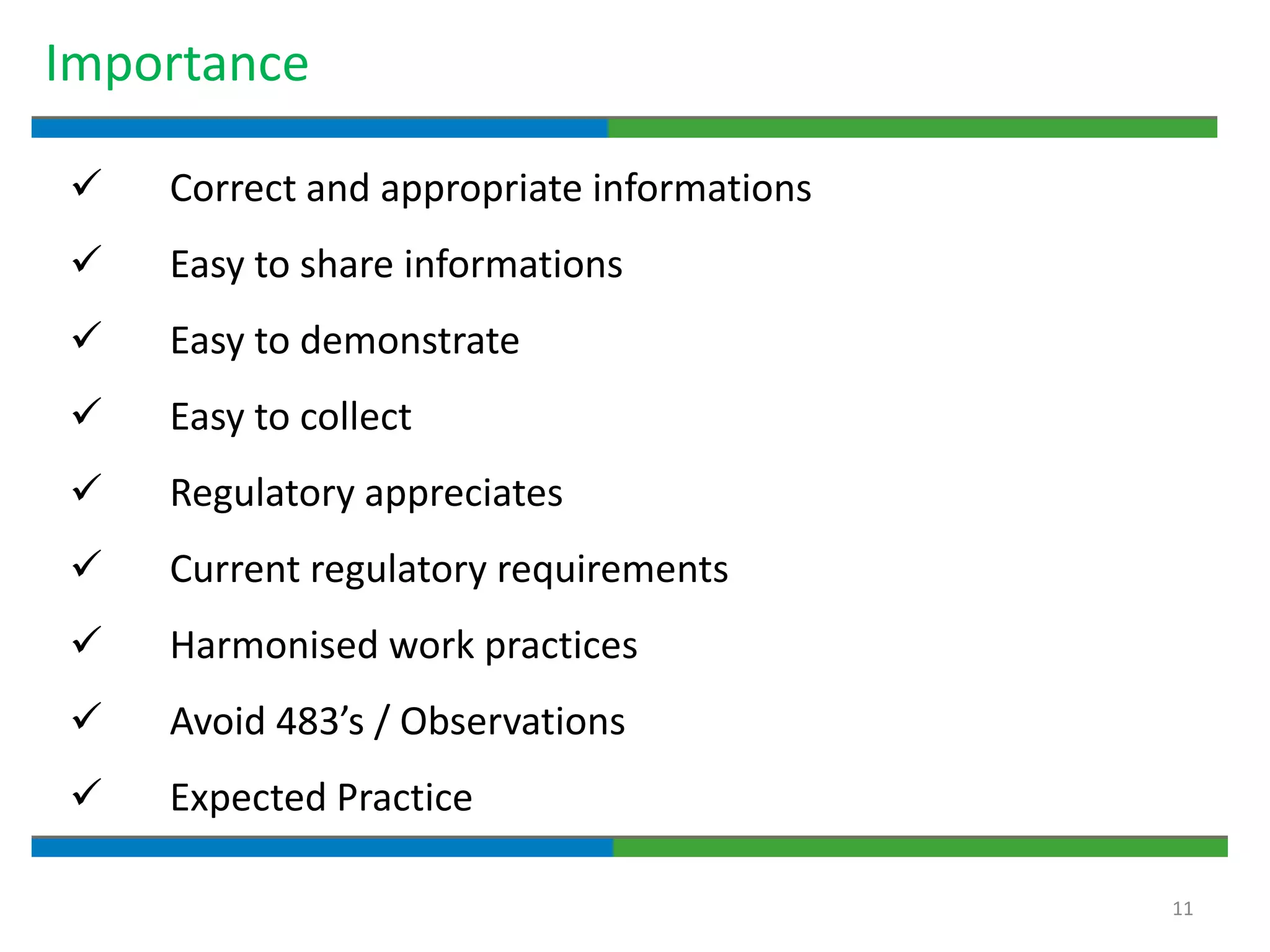
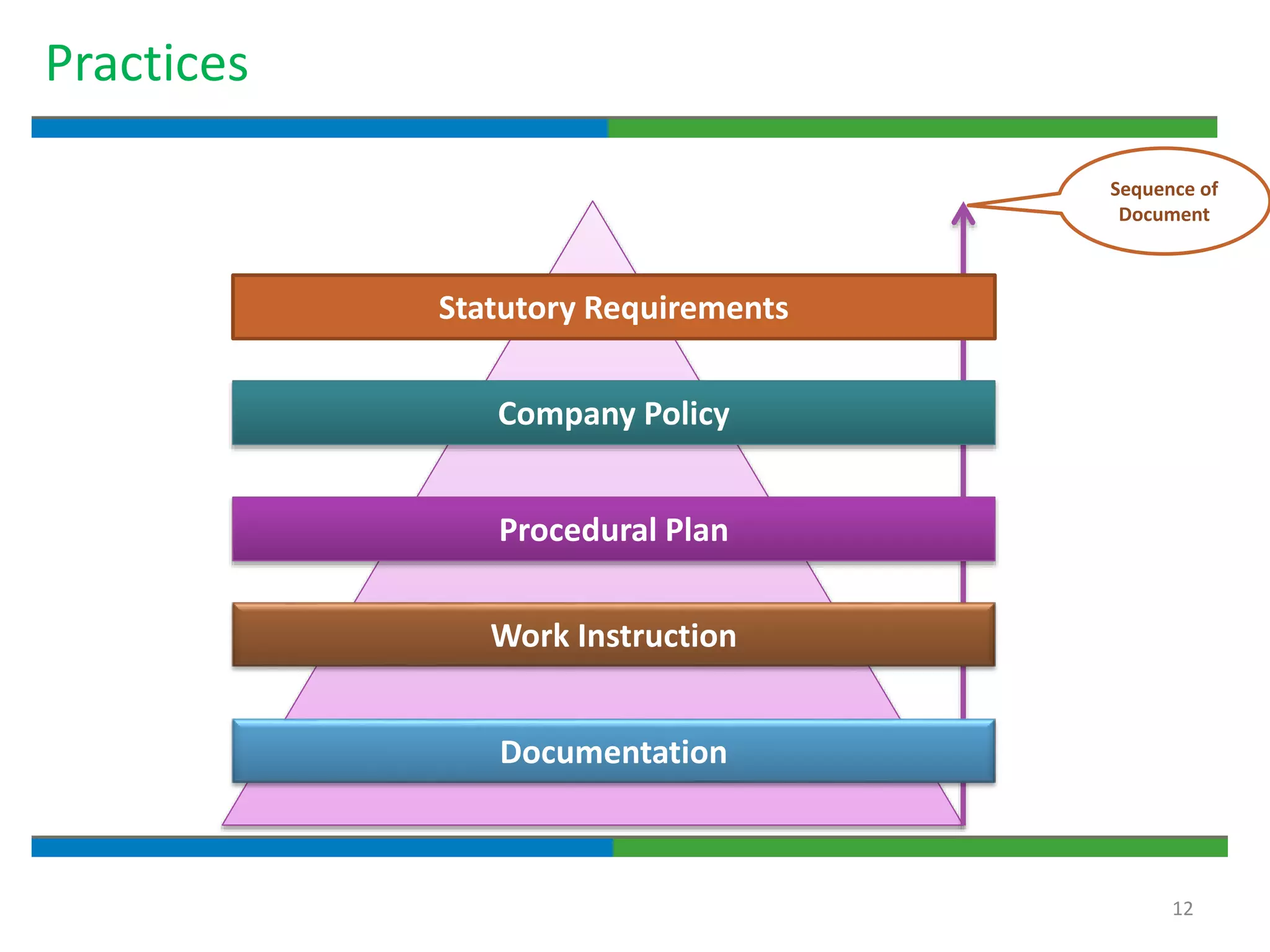
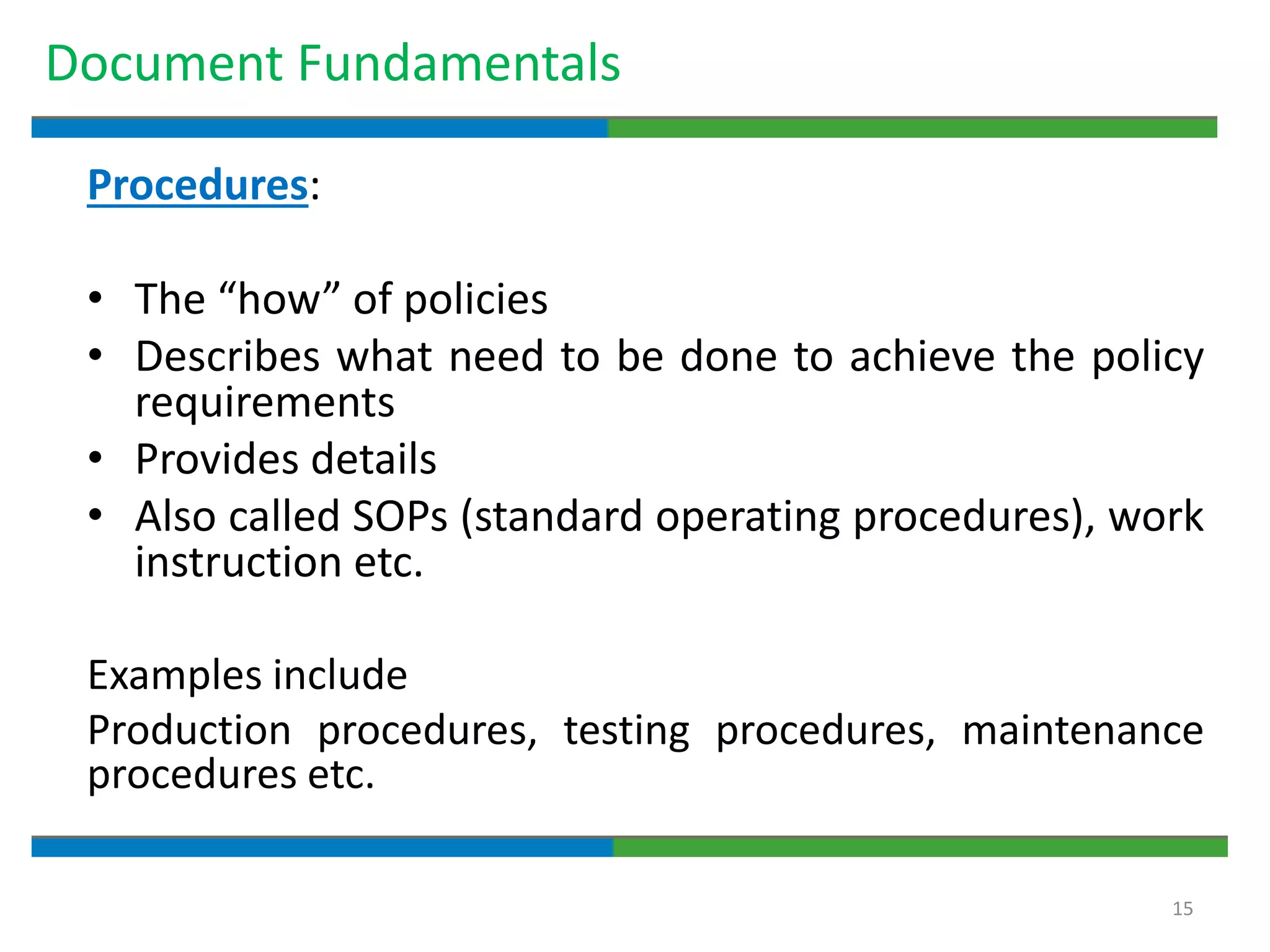
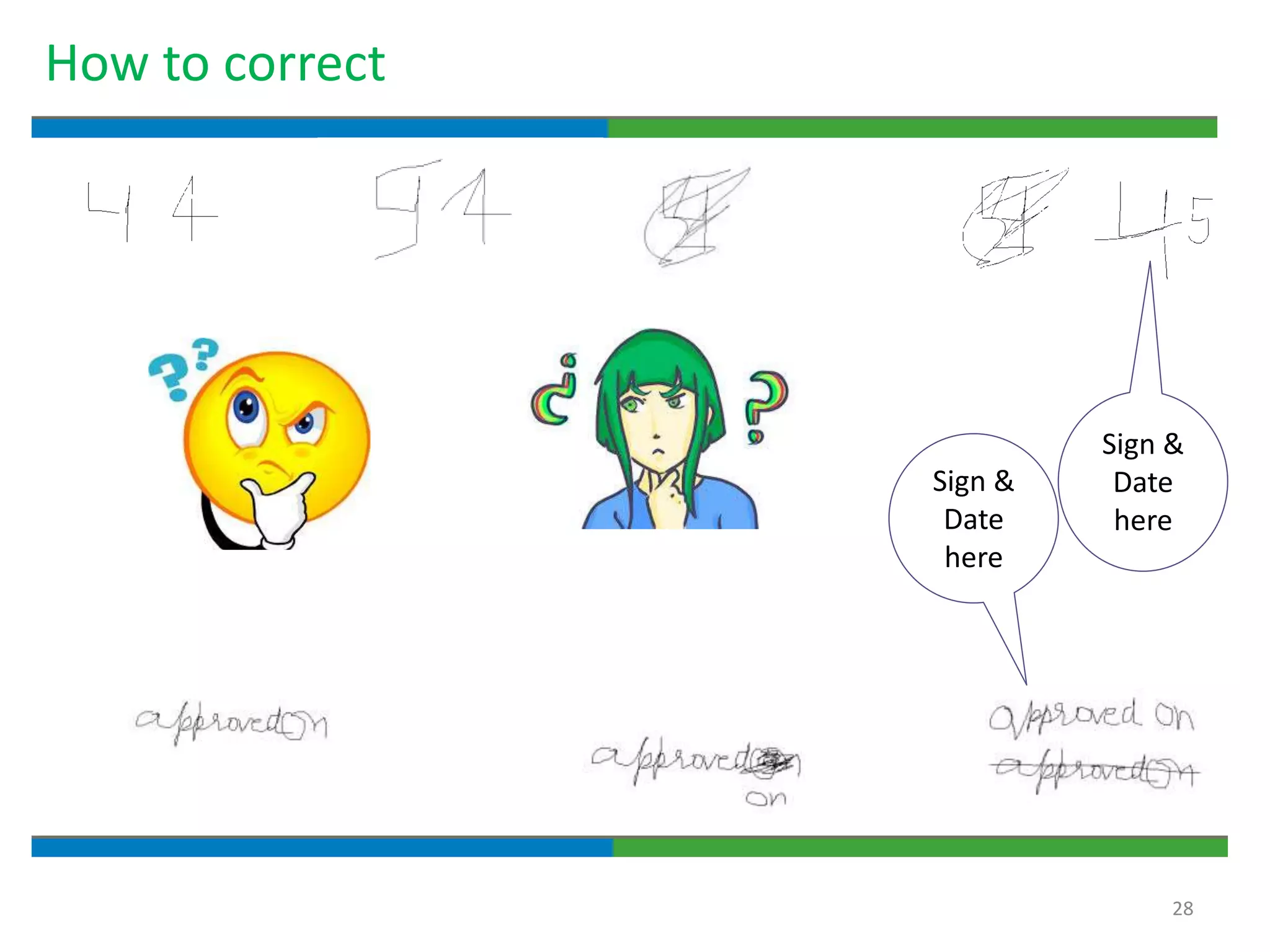
3. The document emphasizes that documentation is important for demonstrating regulatory compliance, avoiding observations, and ensuring safe and effective medicines are produced. It provides guidance on fundamental document types, practices for document control, and the importance of high quality documentation.