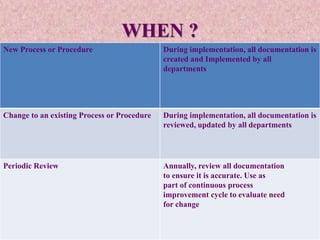
This document discusses good documentation practices for quality systems. It emphasizes recording all necessary information immediately and completely, reviewing documentation annually, and maintaining documentation throughout its life cycle. Regulatory bodies like ISO and NABL require documentation for quality assurance. Documentation provides a record, ensures traceability and accountability, and aids in communication. All personnel are responsible for properly preparing, completing, and reviewing documentation according to basic principles like using permanent ink and not erasing mistakes.