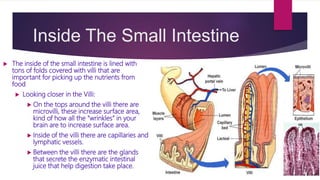
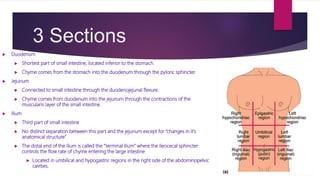
The small intestine is part of the digestive system located in the abdominal and pelvic cavities. It digests and absorbs nutrients from food. The small intestine has three sections - the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. It contains villi and microvilli that increase surface area for nutrient absorption. The small intestine is around 20 feet long and completes most digestion before nutrients pass to the large intestine.