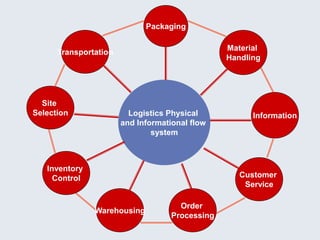
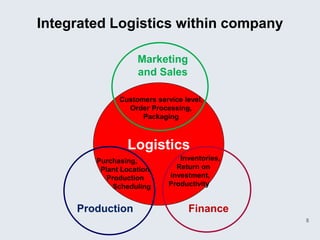
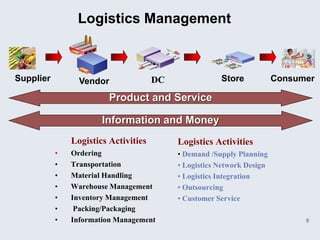
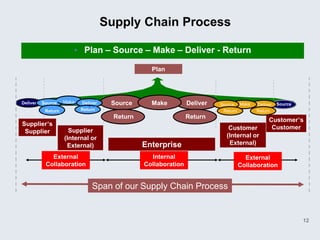
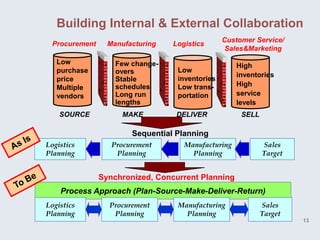
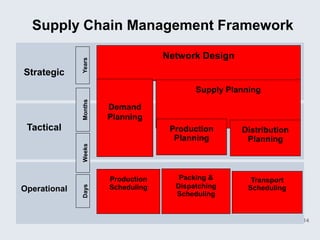
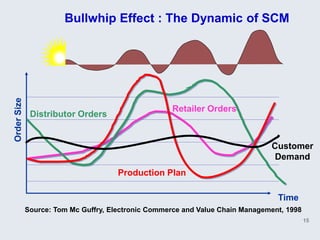
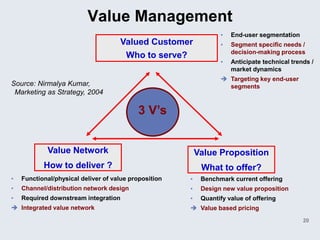
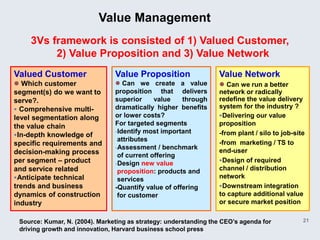
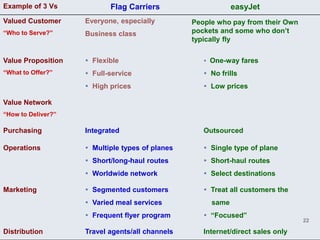
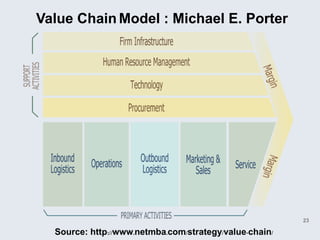
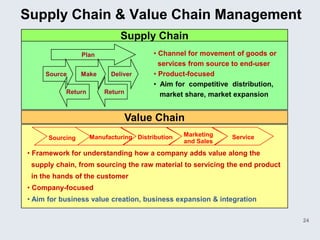
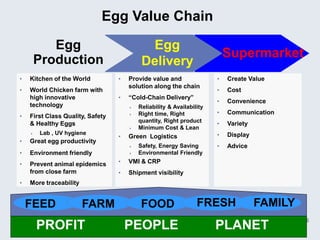
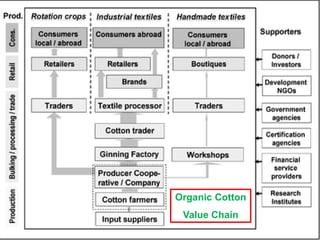
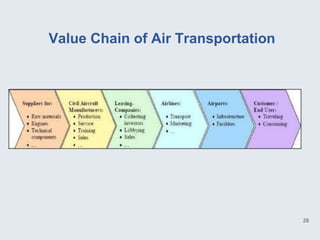
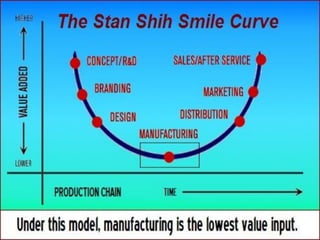
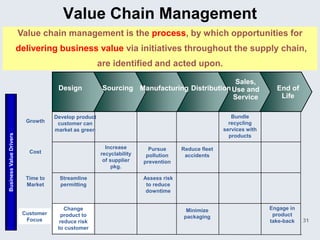
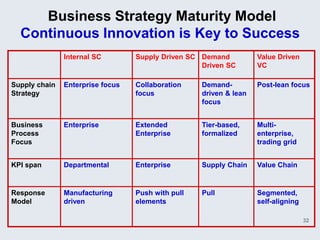
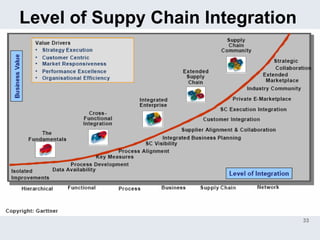
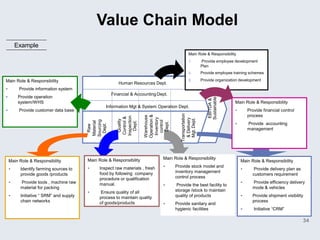
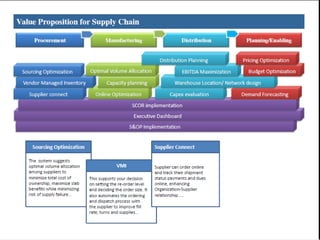
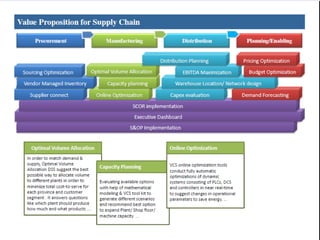
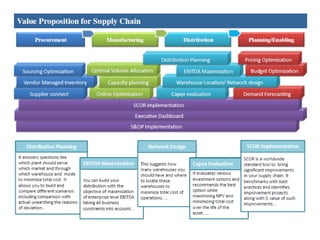
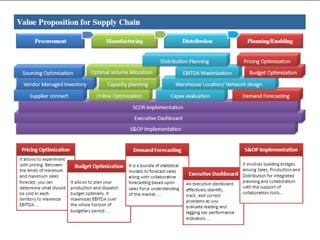
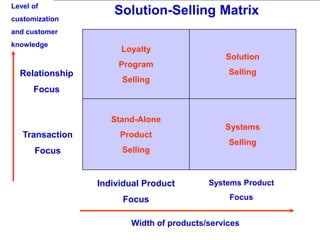
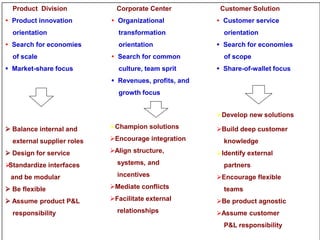
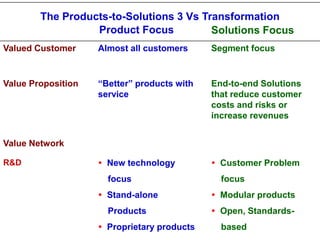
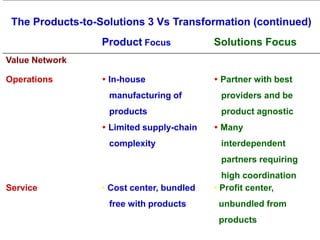
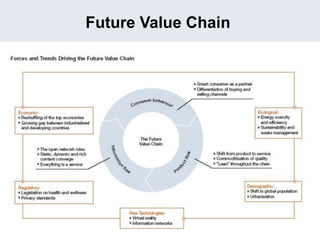
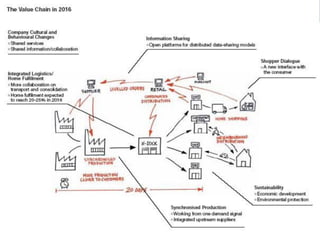
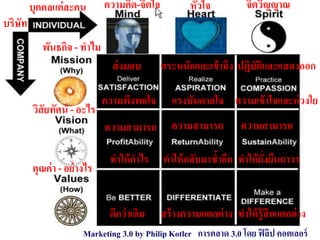
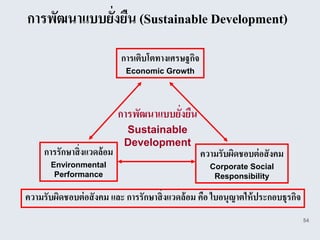
The document provides an overview of logistics management within supply chain management, emphasizing its role in efficiently managing the flow and storage of goods and related information. It outlines key logistics activities and the importance of collaboration and integration with other business functions like marketing and finance. Additionally, it discusses value chain management and its significance in creating customer value and competitive advantage.