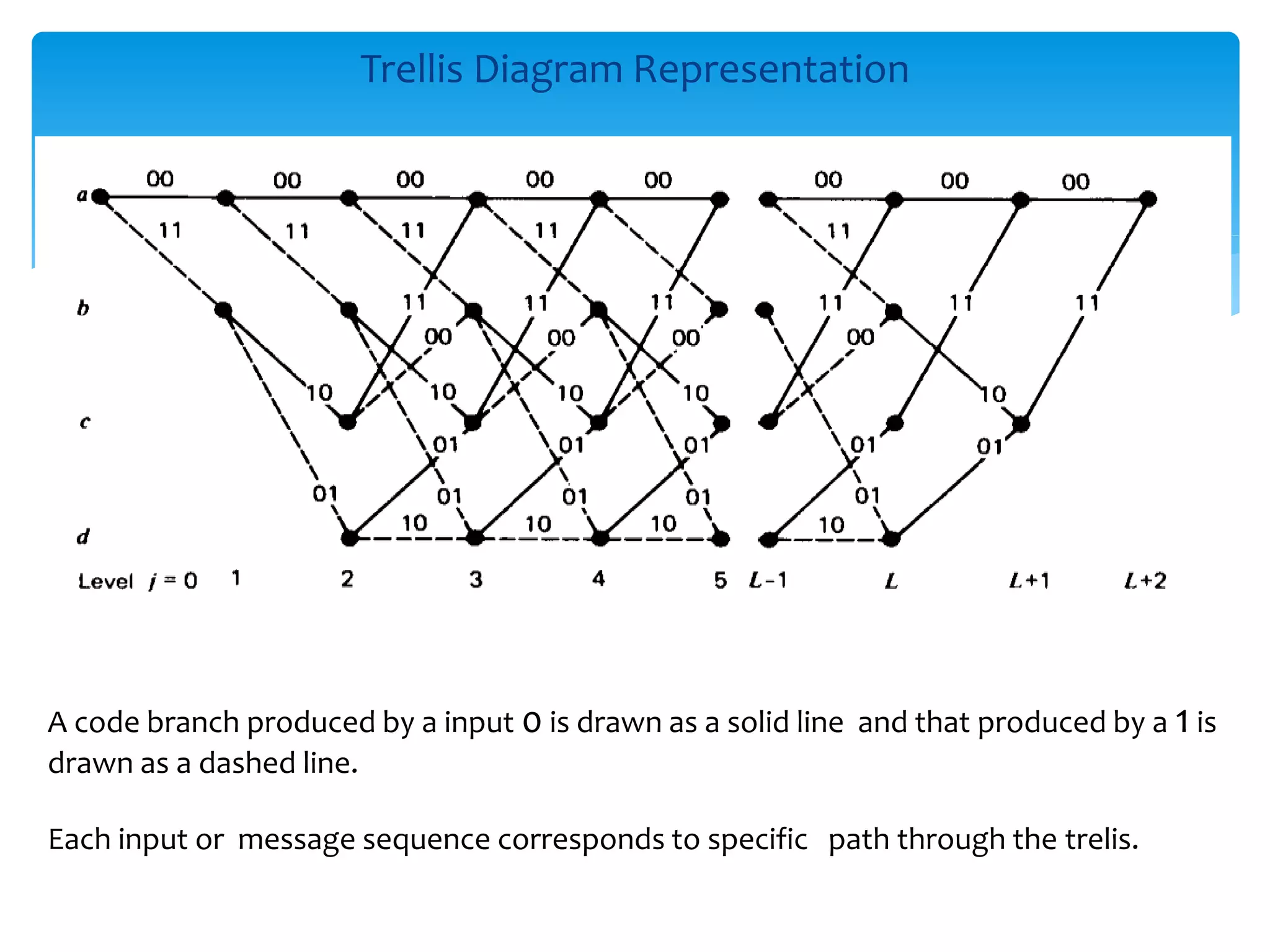
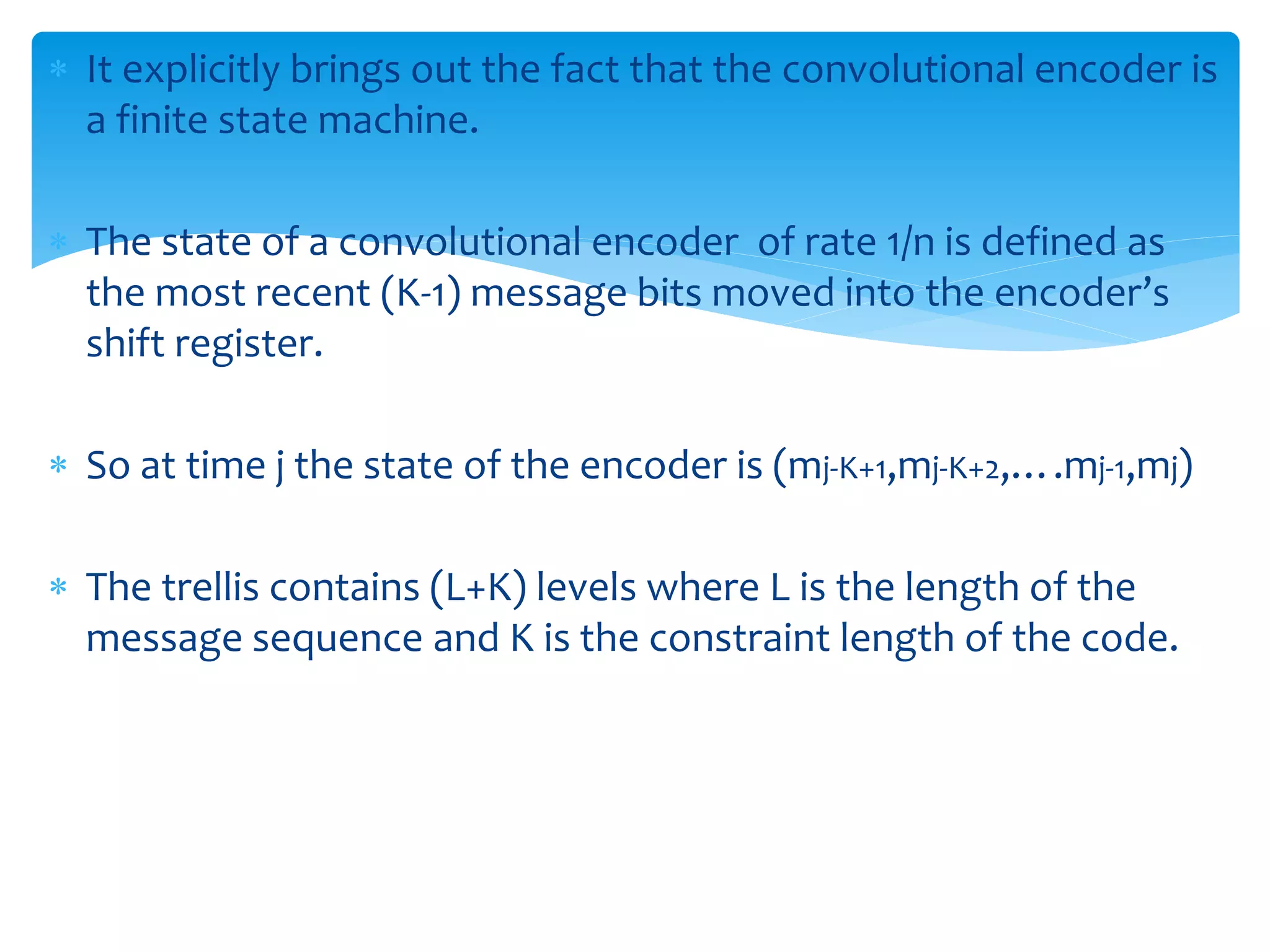
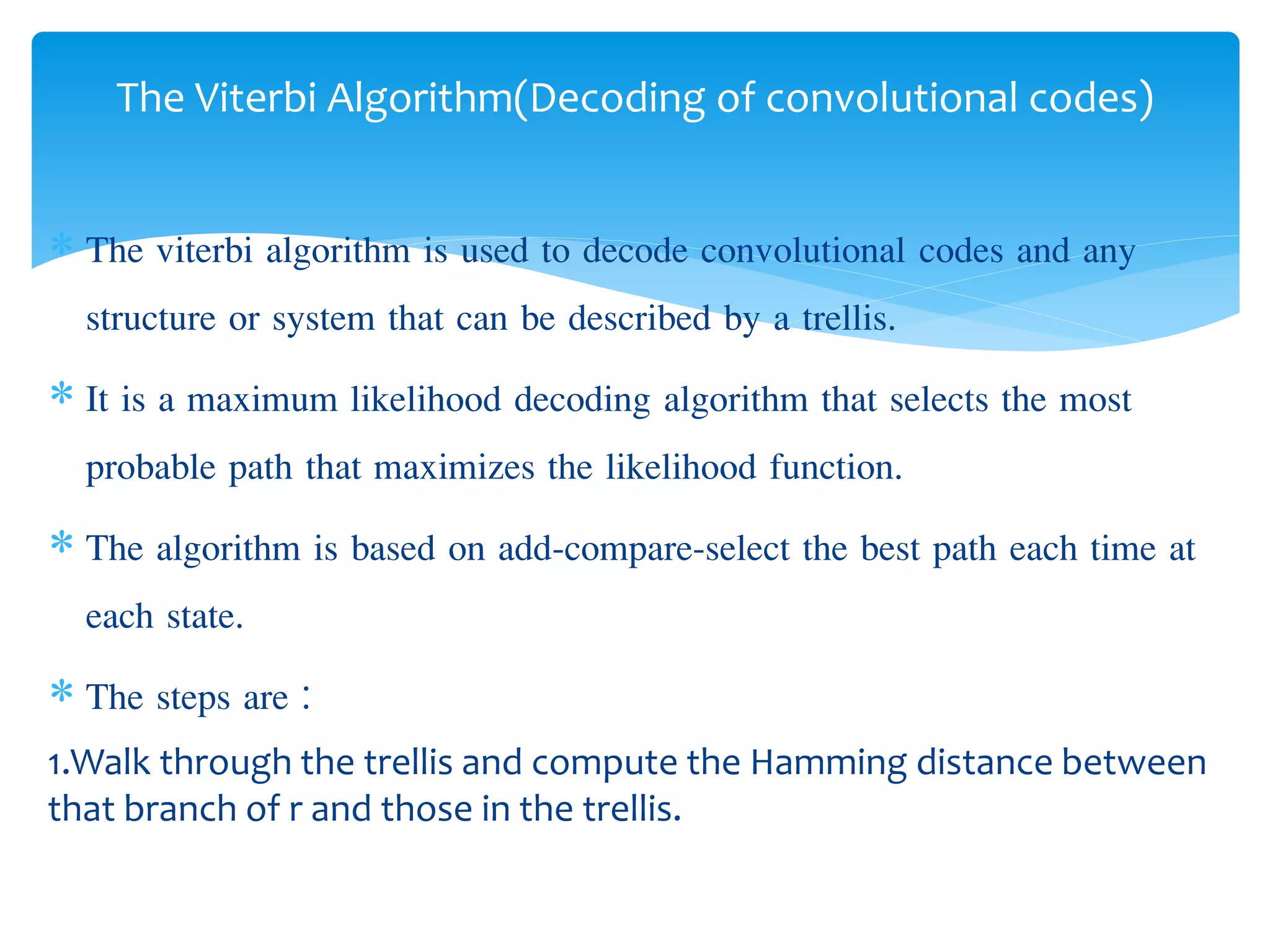
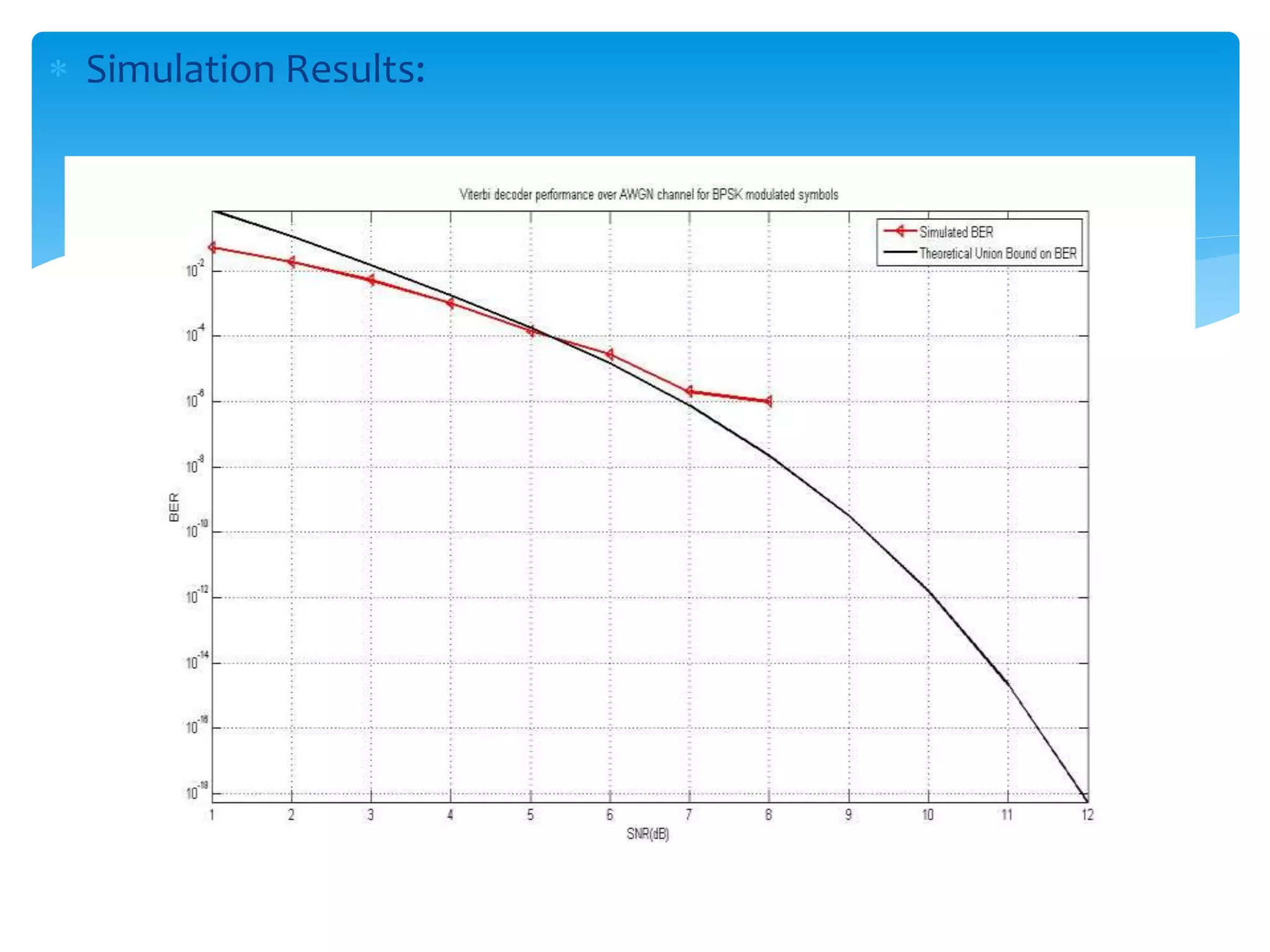
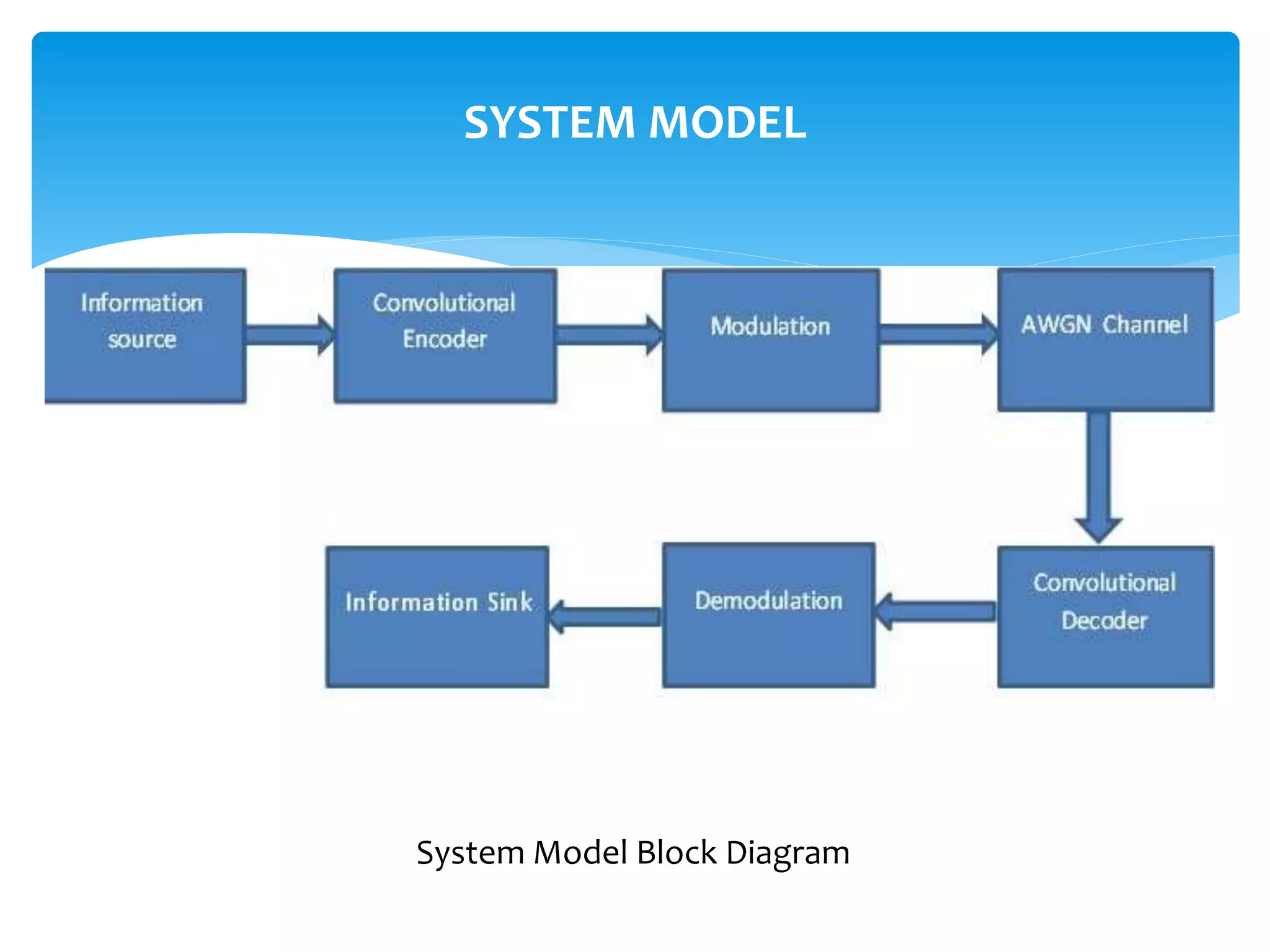
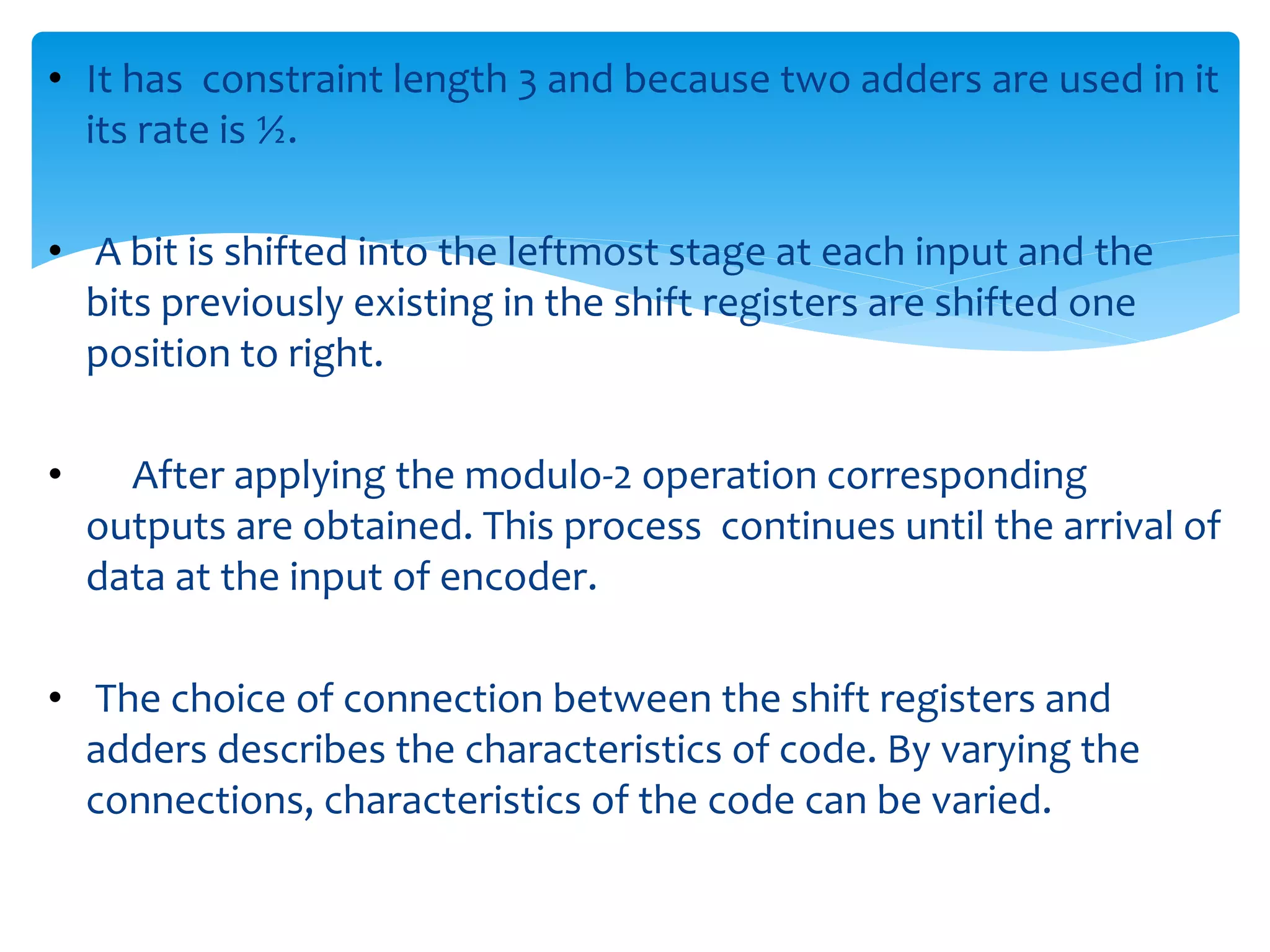
This document describes convolutional codes for channel coding in communication systems. Convolutional codes are represented by parameters like constraint length K, where K is the number of shift registers used. The convolutional encoder operates like a finite state machine, with the state defined by the most recent K-1 message bits. The trellis diagram provides an explicit representation of the convolutional encoder as a finite state machine. Convolutional codes are decoded using the Viterbi algorithm, which performs maximum likelihood decoding by selecting the most probable path through the trellis. Simulation results show the performance of the convolutional encoding and decoding system.

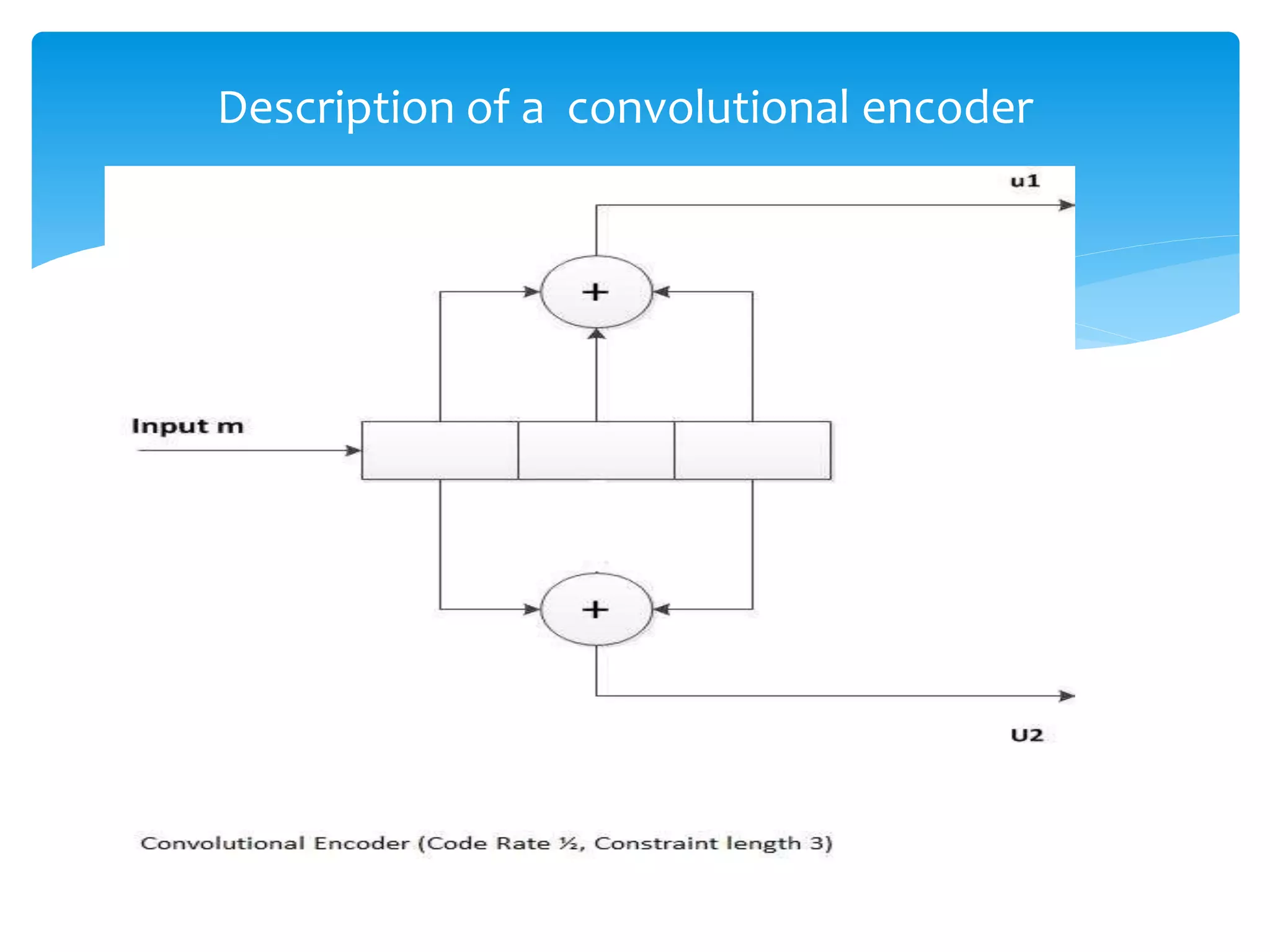
![• To describe an encoder, set of “m” connection vectors are required.
These vectors have the same dimension as that of K (shift registers).
These connections describe which shift register is connected with m
adders.
• A value of “1” in the position demonstrates that, that shift register is
connected to the adder and a “0” in given position will indicate that
not a single connection exits between the stage and adder.
• For encoder shown in Fig. we can write the connection vector for
upper connection and for lower connection as follows:
h1=[1 1 1]…………..(1)
h2=[1 0 1]…………..(2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-141204004443-conversion-gate02/75/Presentation-1-9-2048.jpg)