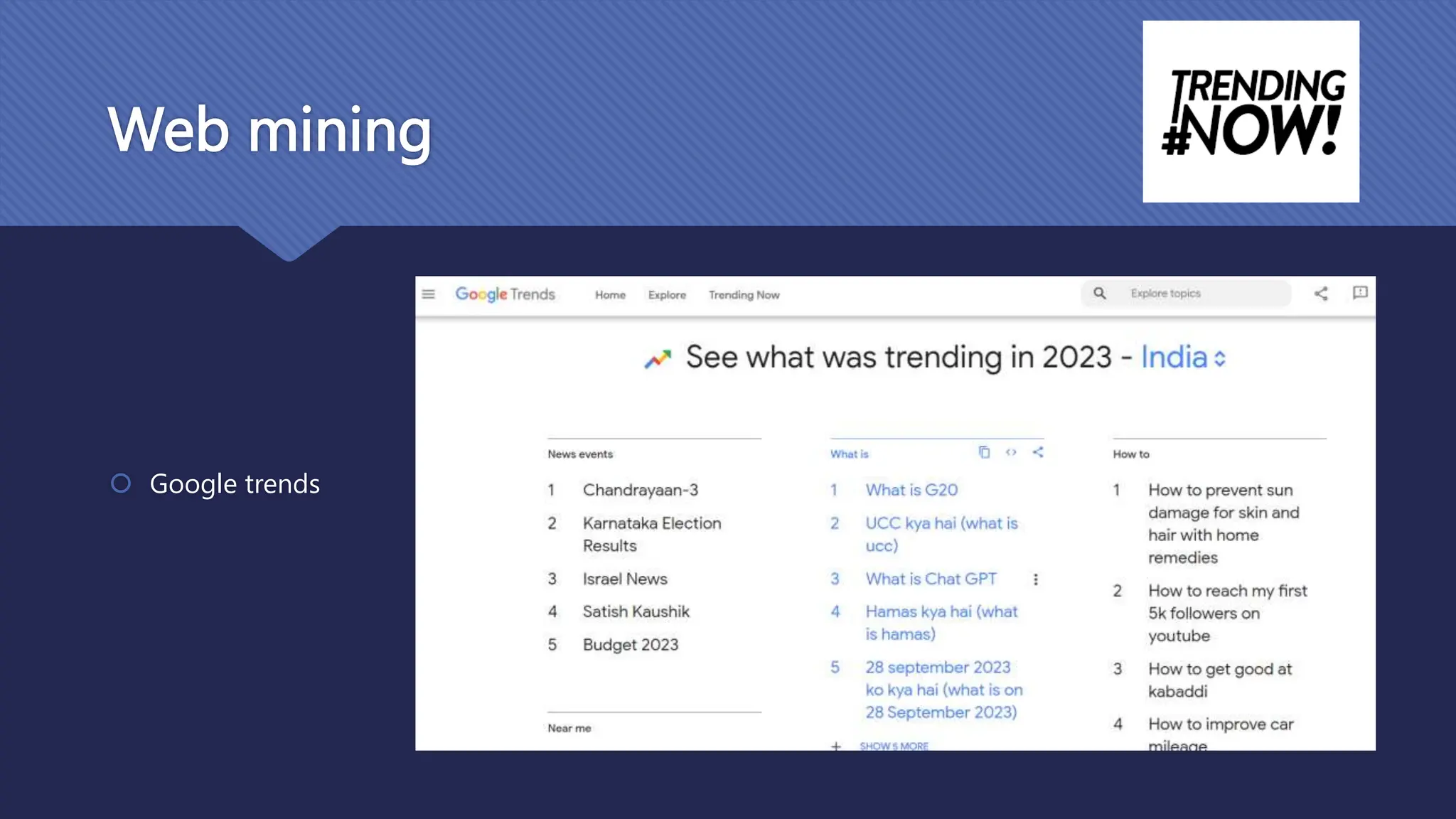
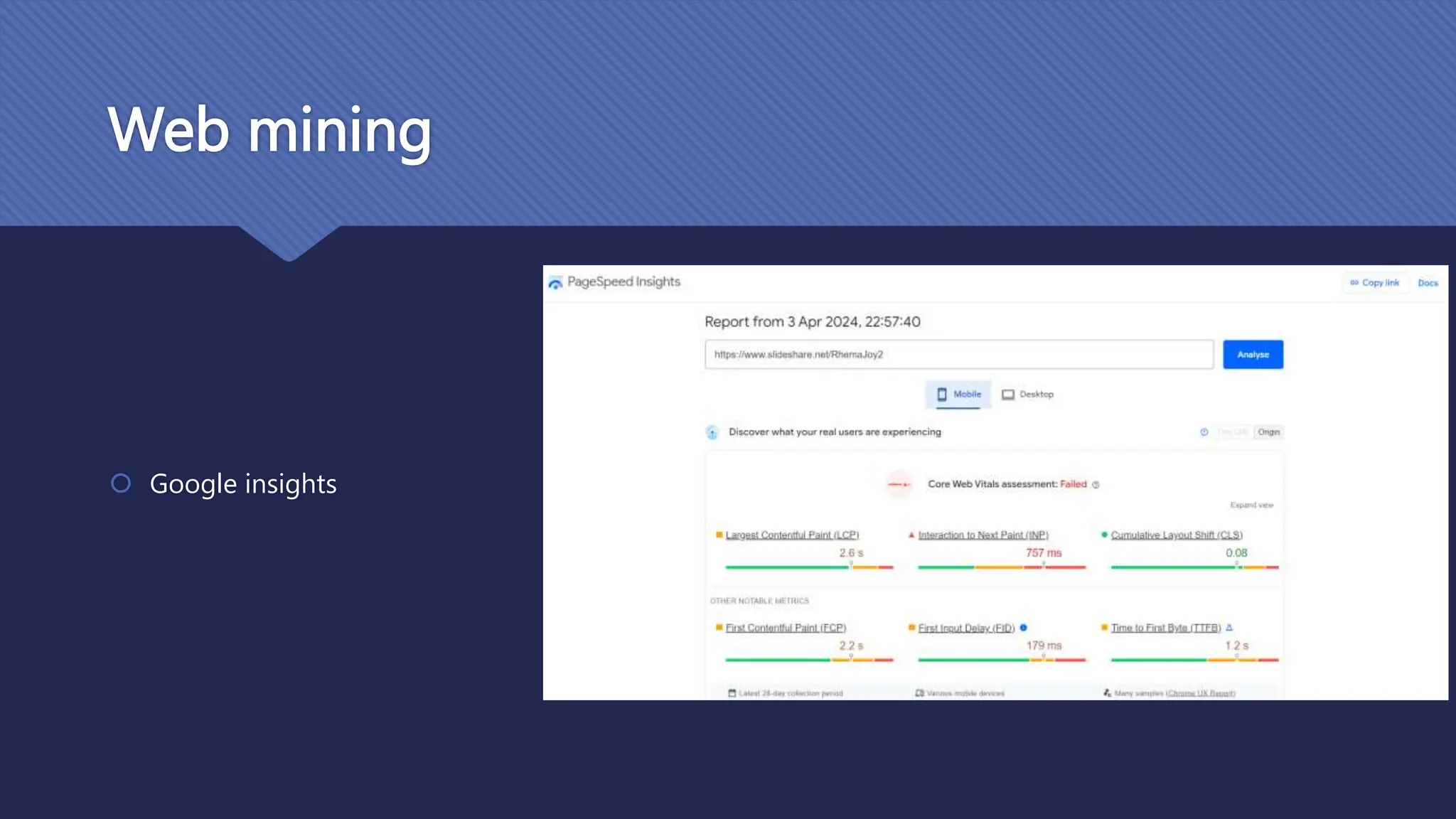
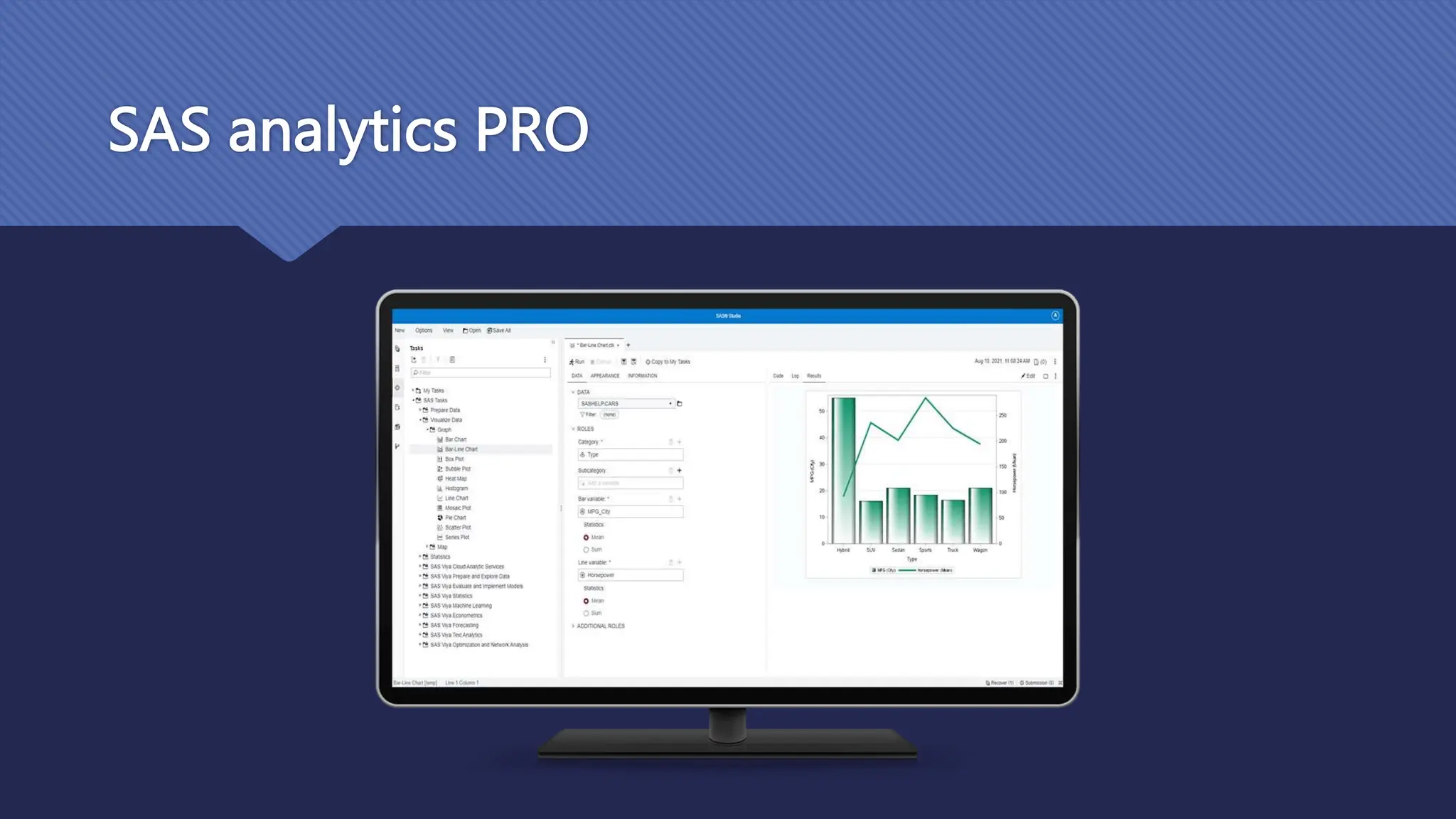
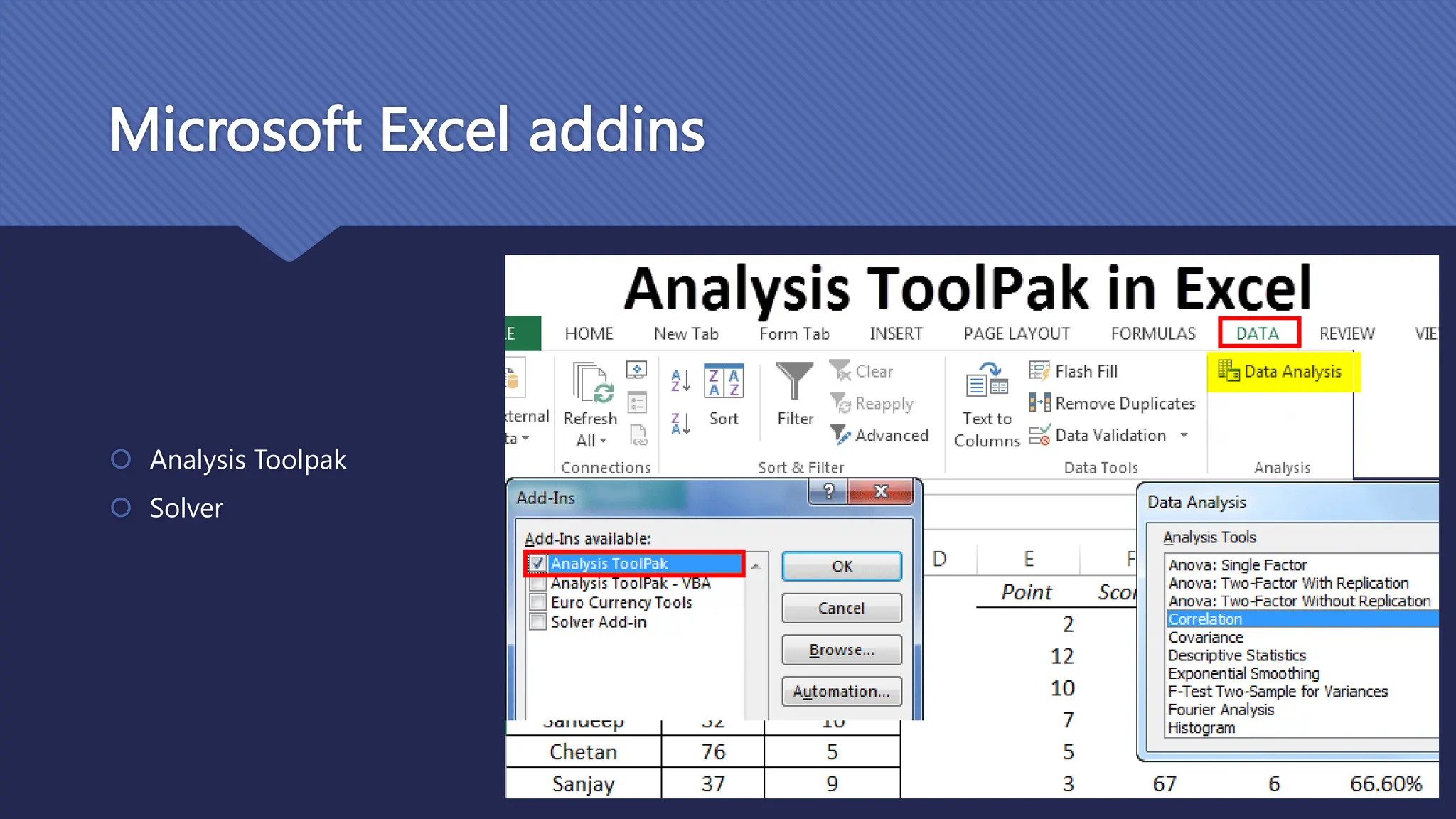
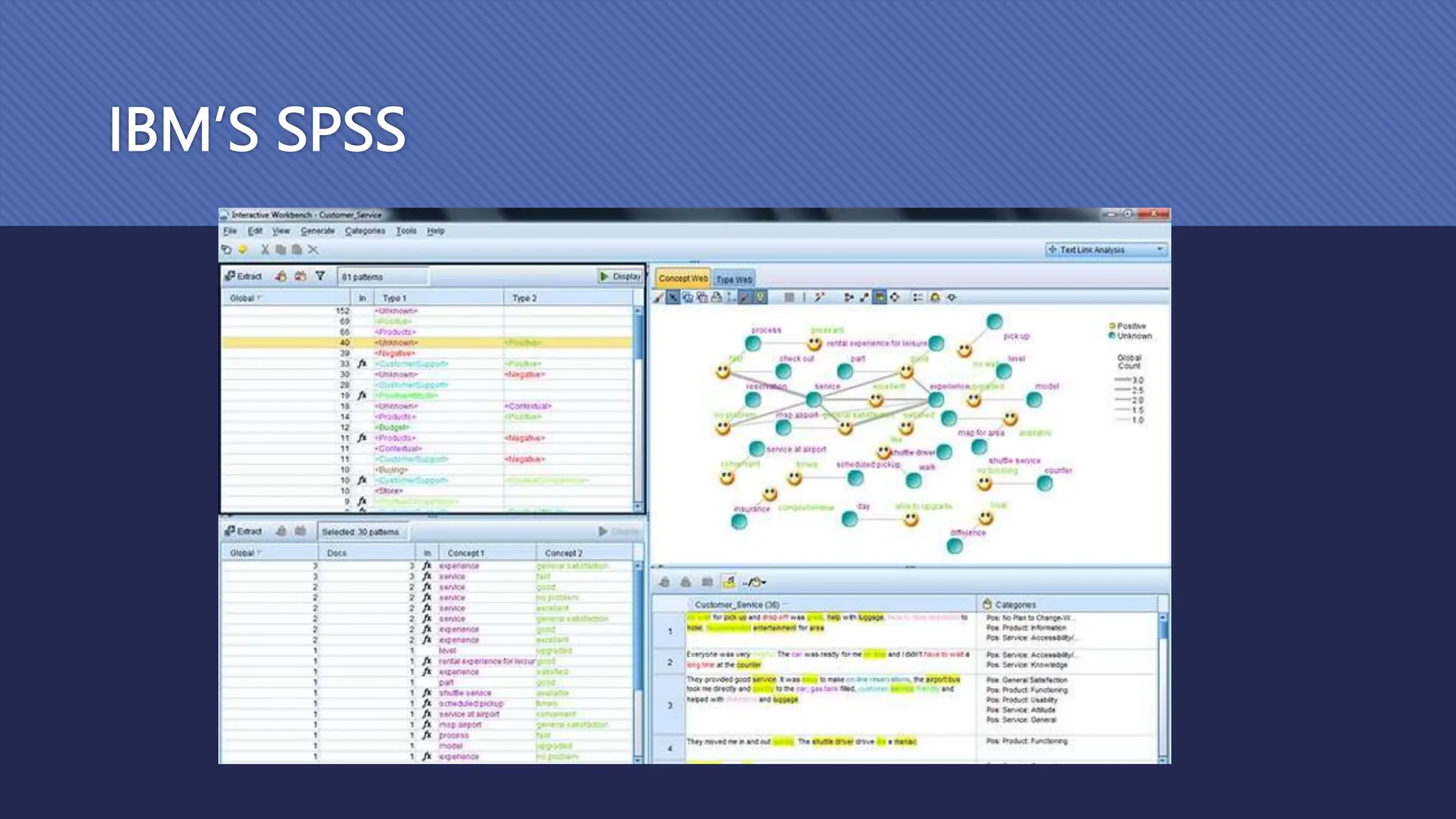
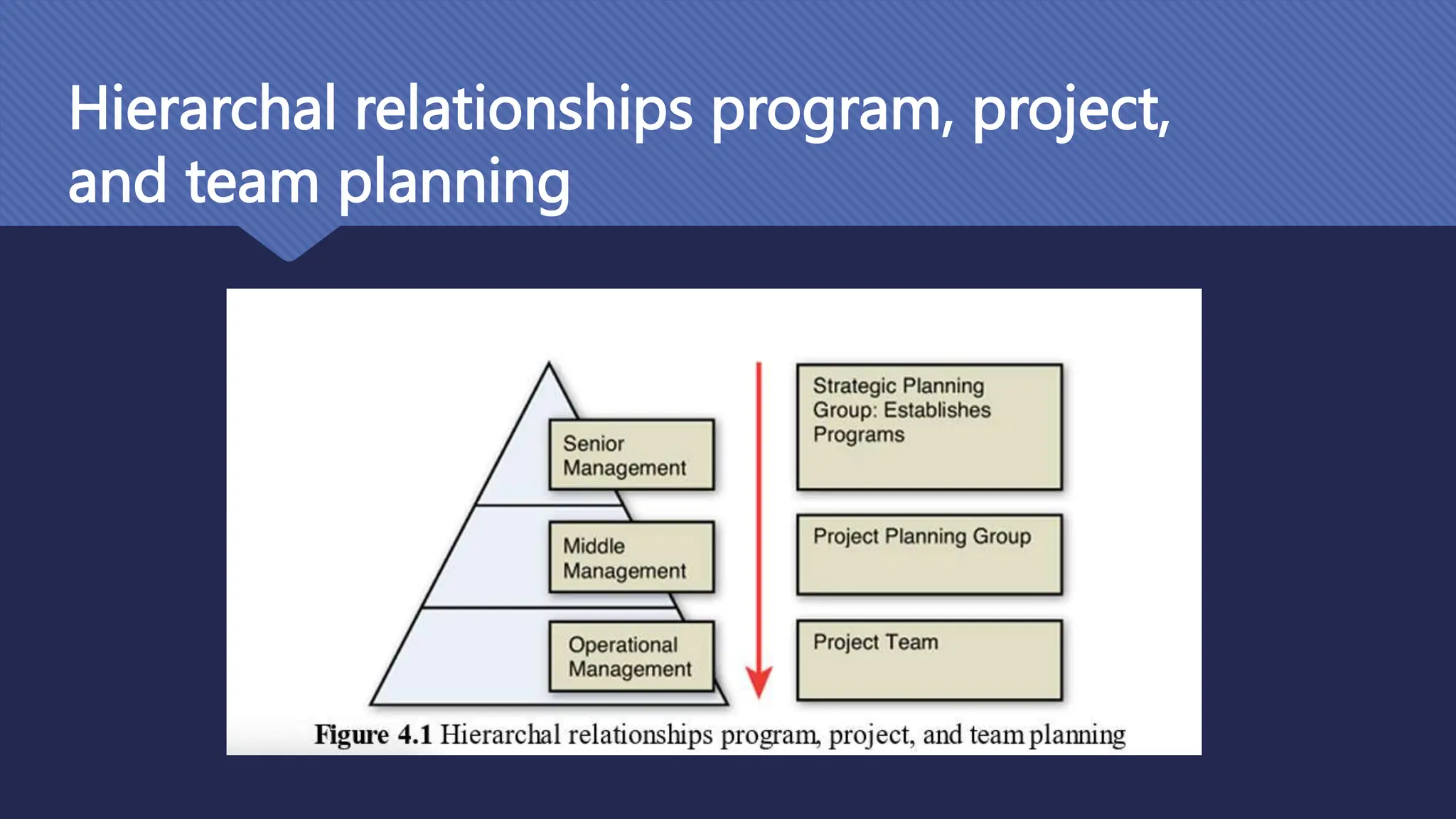
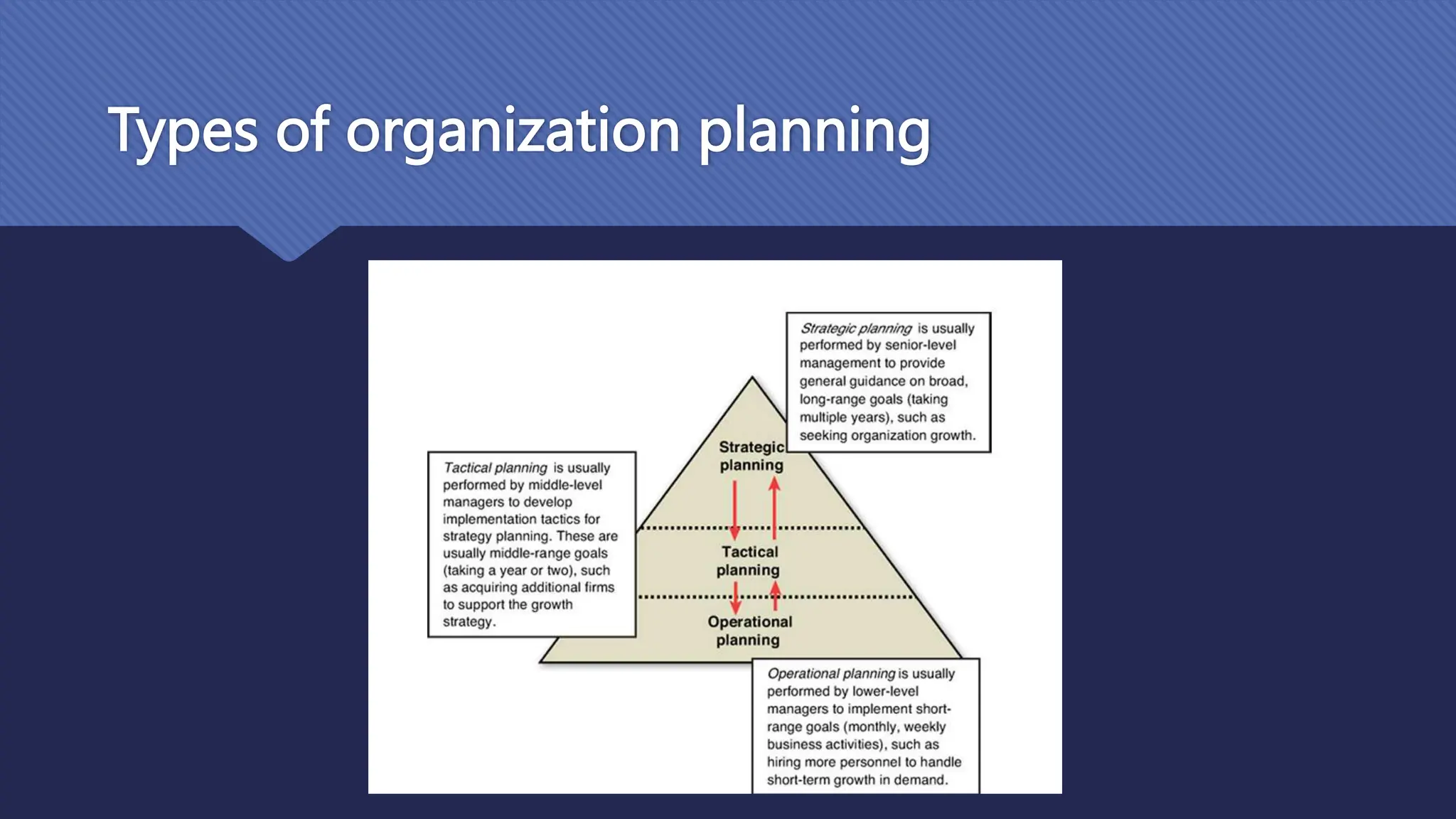
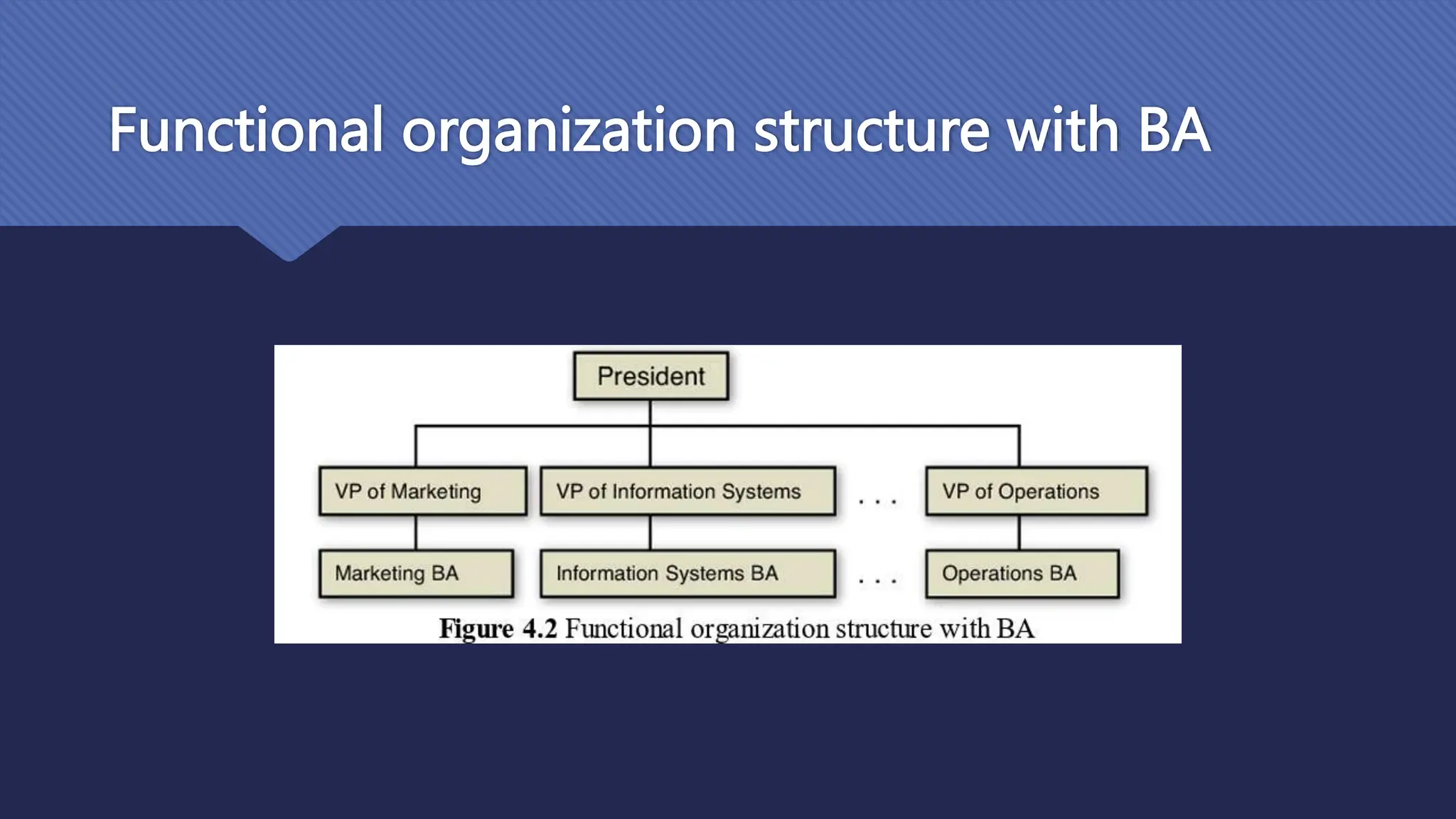
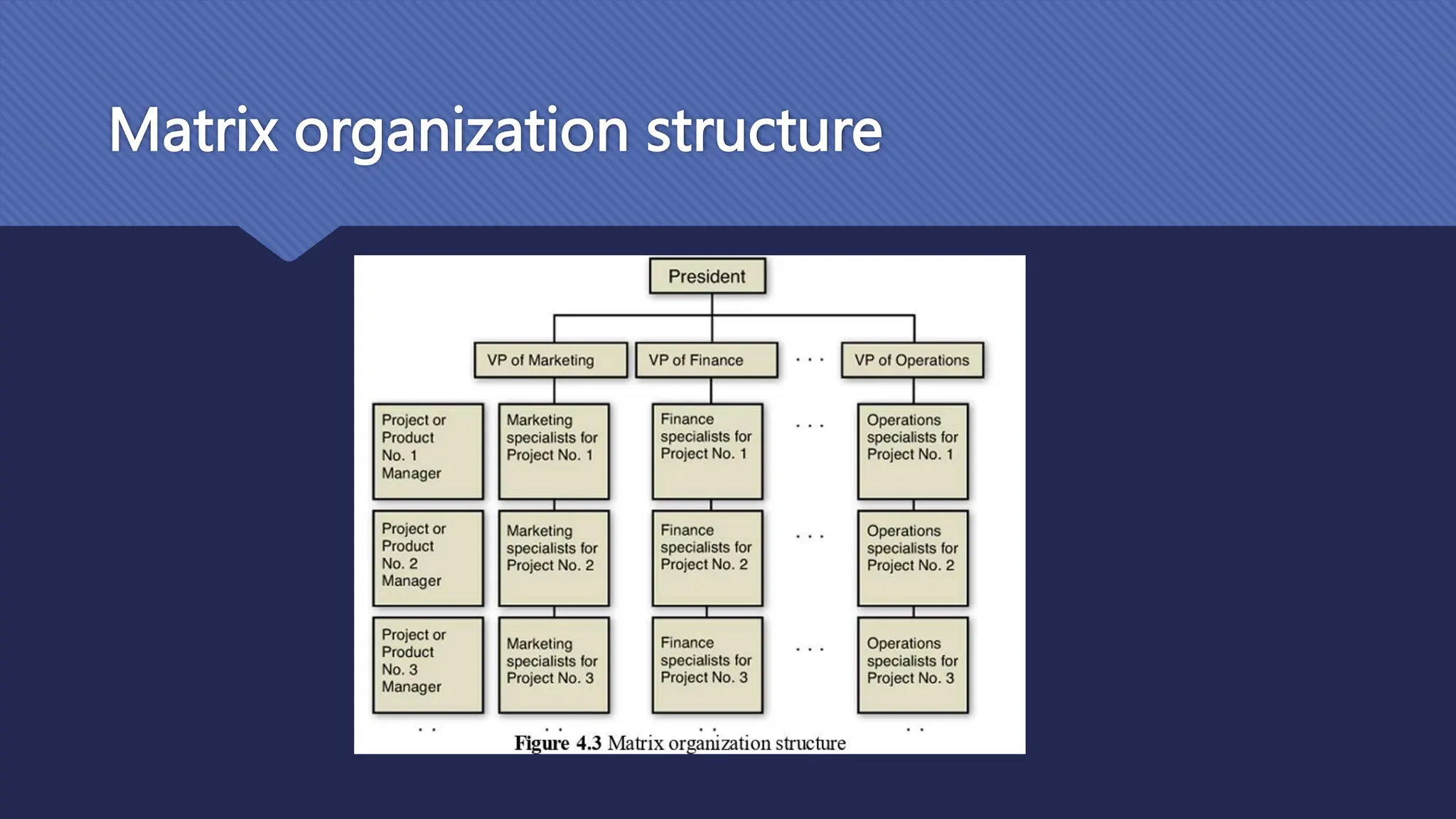
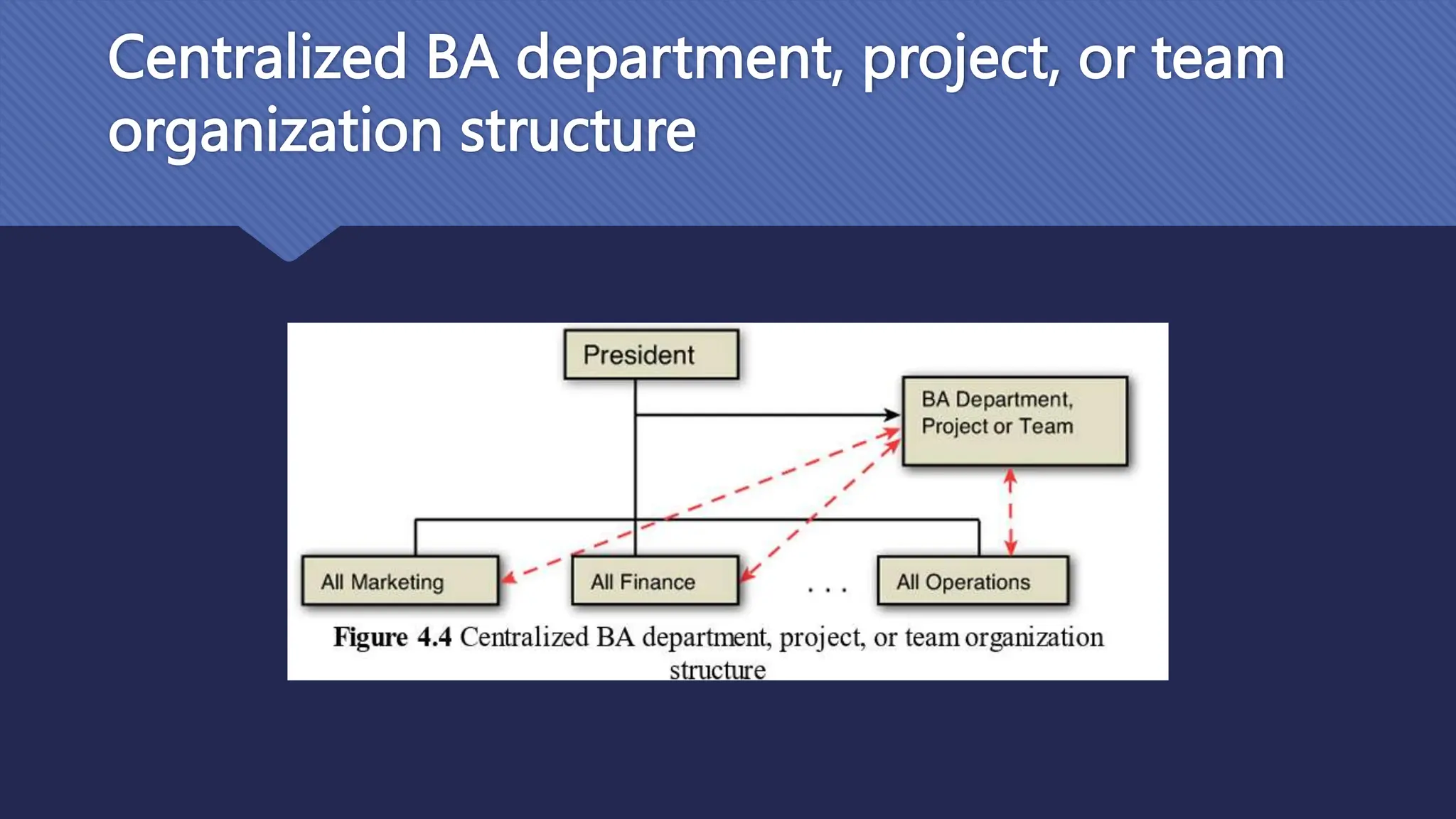
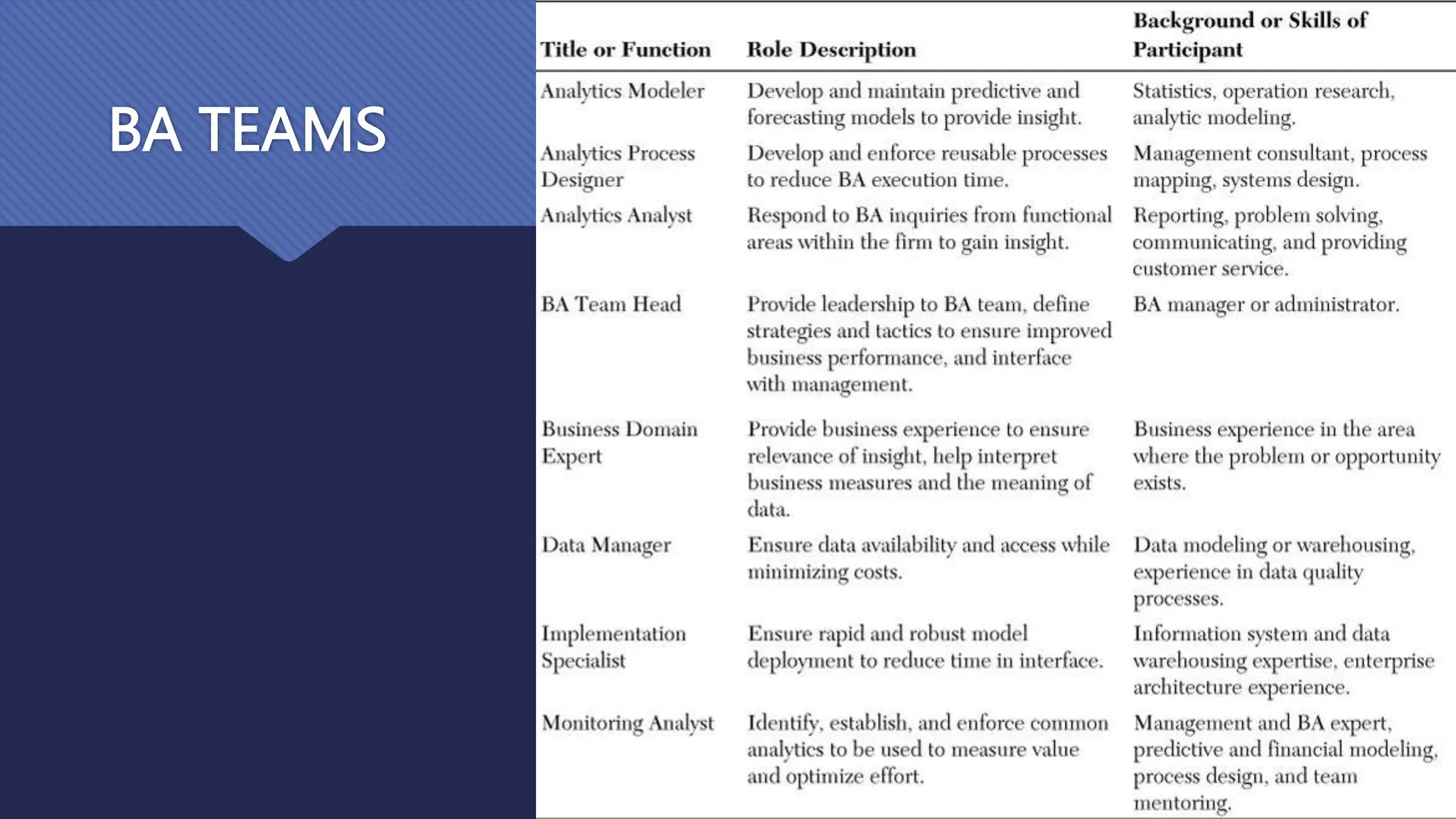
The document outlines the role and skills of business analysts (BAs), including their responsibilities in various phases of project management and the types of data they work with. It emphasizes the importance of data quality, primary and secondary data sources, and the use of various technologies, methodologies, and organizational structures in business analytics. Additionally, it addresses challenges in managing BAs, ensuring data quality, and evaluating the contribution of analytics to organizational performance.