1) The document discusses several criteria for decision making under uncertainty including maximax, maximin, minimax, minimin, and Laplace.
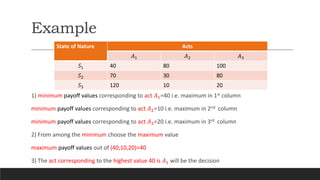
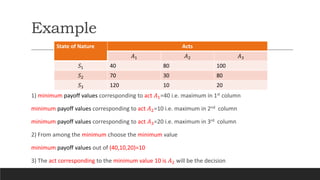
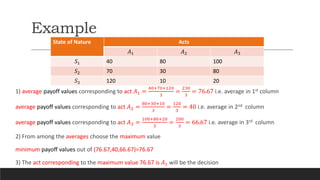
2) The maximax criterion is optimistic and chooses the alternative with the highest possible payoff. Maximin is pessimistic and chooses the alternative with the highest minimum payoff.
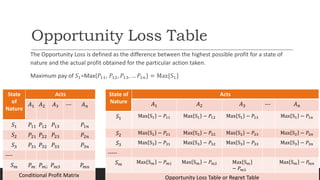
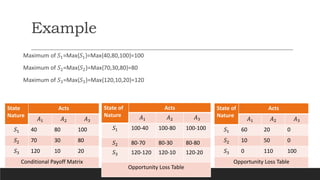
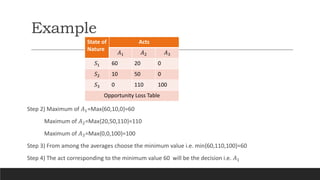
3) Minimax regret considers the maximum regret for each alternative and chooses the one with the minimum maximum regret. This accounts for opportunity loss across states of nature.