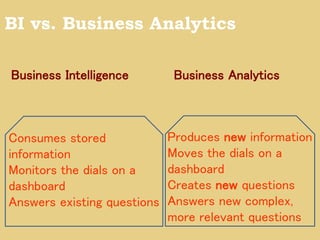
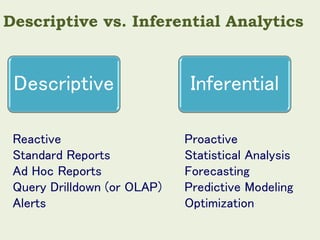
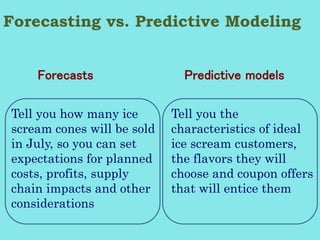
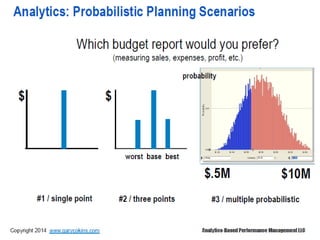
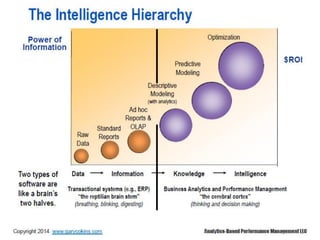
Gary Cokins, an expert in performance improvement and cost management, presented insights into business analytics at a seminar. He emphasized the importance of analytics in making informed decisions, differentiating between business intelligence and business analytics, and the benefits of predictive modeling over traditional forecasting. The presentation also discussed the necessity of overcoming barriers to effective analytics implementation and the role of customer lifetime value in strategic decision-making.