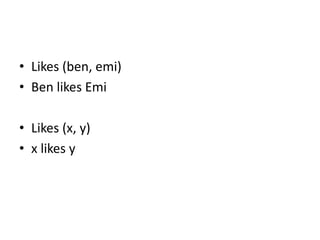This document provides an introduction to propositional and predicate logic, including examples of how they can be used to represent linguistic statements in a formal, computable way. Some key points covered include:
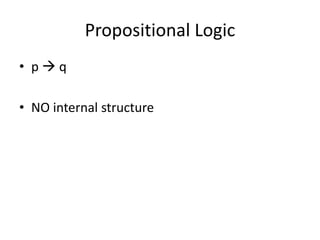
- Propositional logic uses simple statements connected with logical operators like "if-then", while predicate logic introduces predicates and variables to represent internal structures.
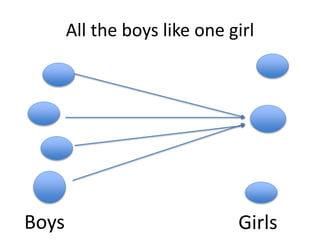
- Examples show how predicate logic can represent statements about individuals and their properties or relationships using predicates, variables, and quantifiers.
- While logic provides a useful formalism for linguistics and computer science, some argue it may not accurately capture how humans naturally understand and use language. Modern linguistics also explores how language relates to other aspects of human cognition beyond logical representations.


































































![But Logic is VERY important in
Linguistics!
• The nurse kissed every child on his birthday.
• [The nurse] kissed [every child] on his birthday.
• Kissed (nurse, every_child)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/predicatecalculus-181213051207/85/Predicate-calculus-69-320.jpg)