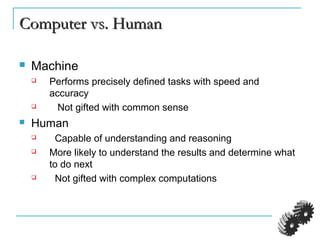
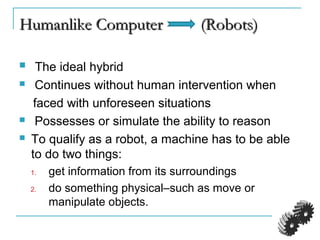
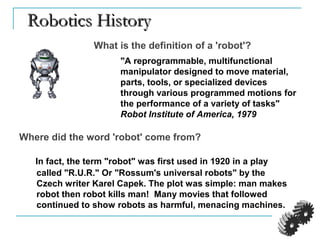
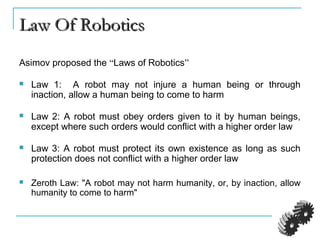
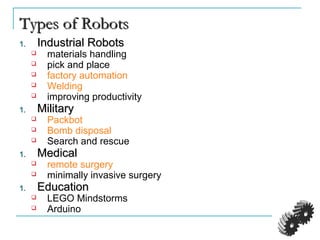
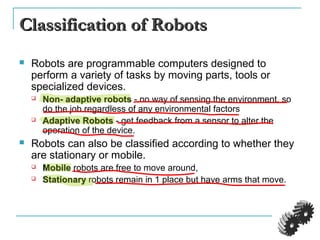
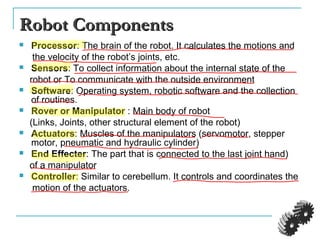
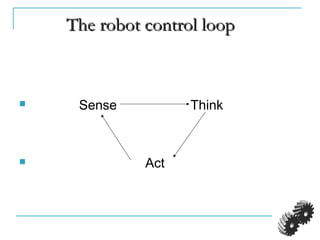
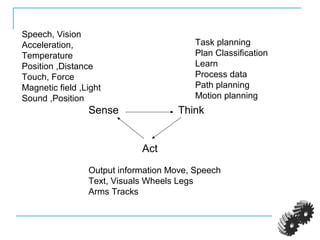
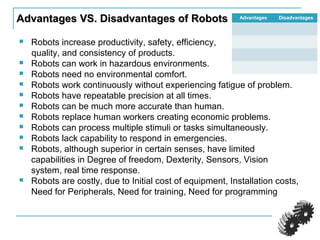
The document provides an introduction to robotics. It discusses the differences between computers/machines and humans, describing machines as precisely performing tasks while lacking common sense, and humans as capable of understanding and reasoning. It defines a robot as a machine that can obtain information from its surroundings and perform physical tasks. The document outlines the history of robots from ancient imaginings to modern usage of the term by Karel Capek in 1920. It discusses Isaac Asimov's three laws of robotics and provides examples of different types of robots including industrial, military, medical, and domestic robots. It describes robot components and the robot control loop of sensing, thinking, and acting. It discusses advantages and disadvantages of robots.


![Robotics TerminologyRobotics Terminology
Au-ton-o-mousAu-ton-o-mous
1. Not controlled by others or by outside forces; independent:
2. Independent in mind or judgment; self-directed.
Android An"droid ([a^]n"droid)Android An"droid ([a^]n"droid)
A machine or automaton in the form of a human being
Possessing human features. n.
An automaton that is created from biological materials and
resembles a human being. Also called humanoid.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptintroroboticsfor1-150601062152-lva1-app6891/85/Intro-to-Robotics-1-24-320.jpg)