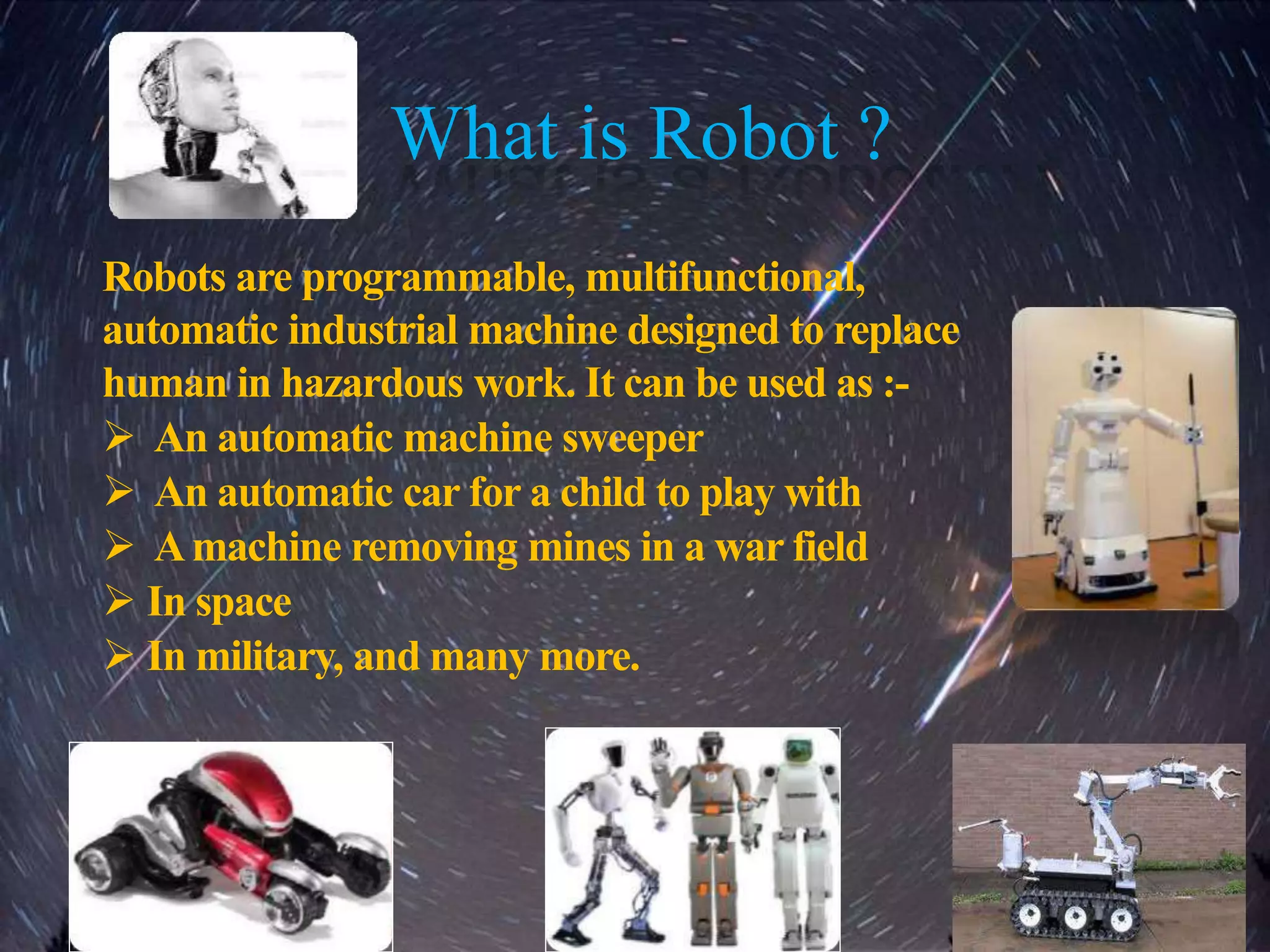
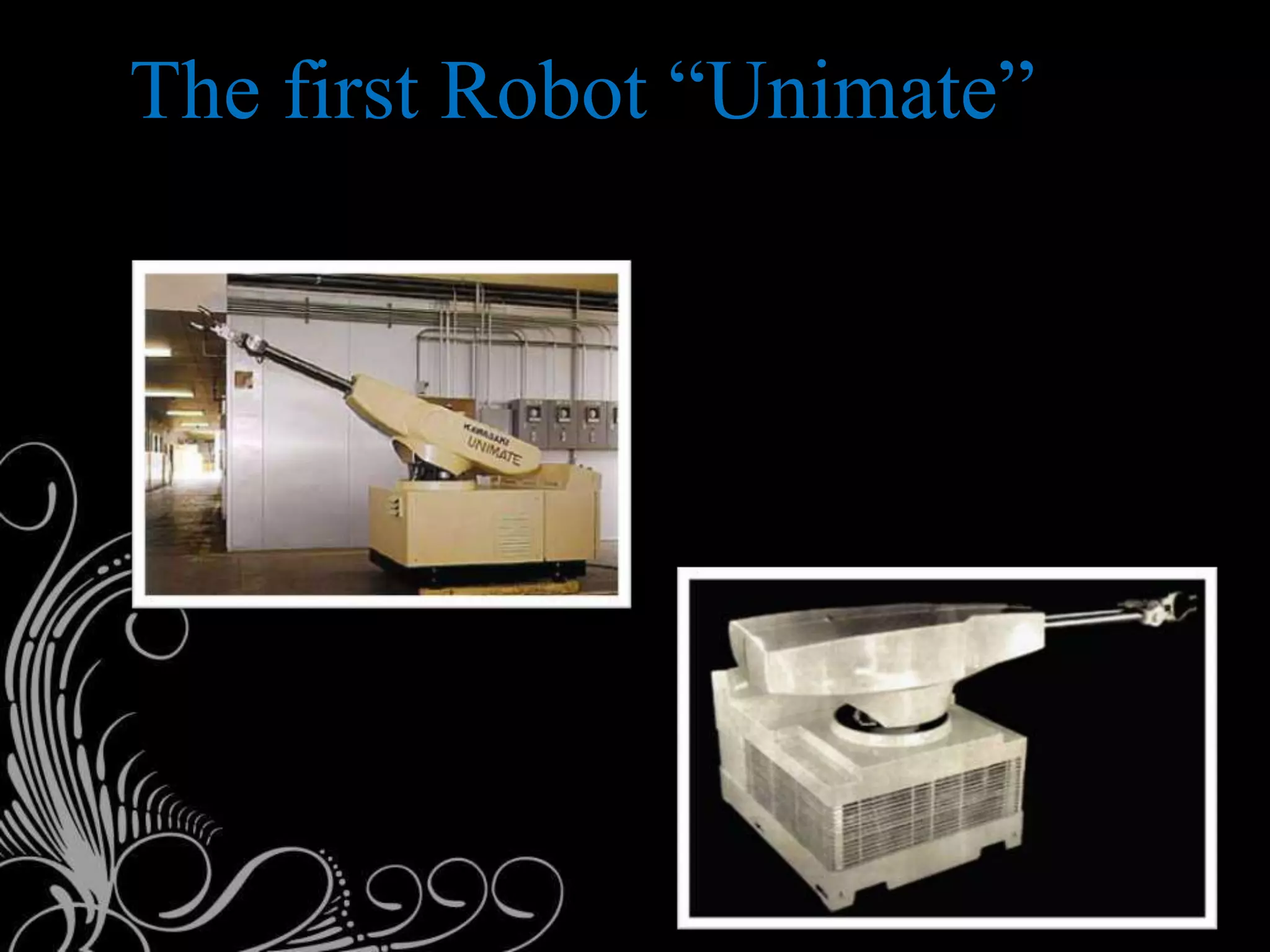
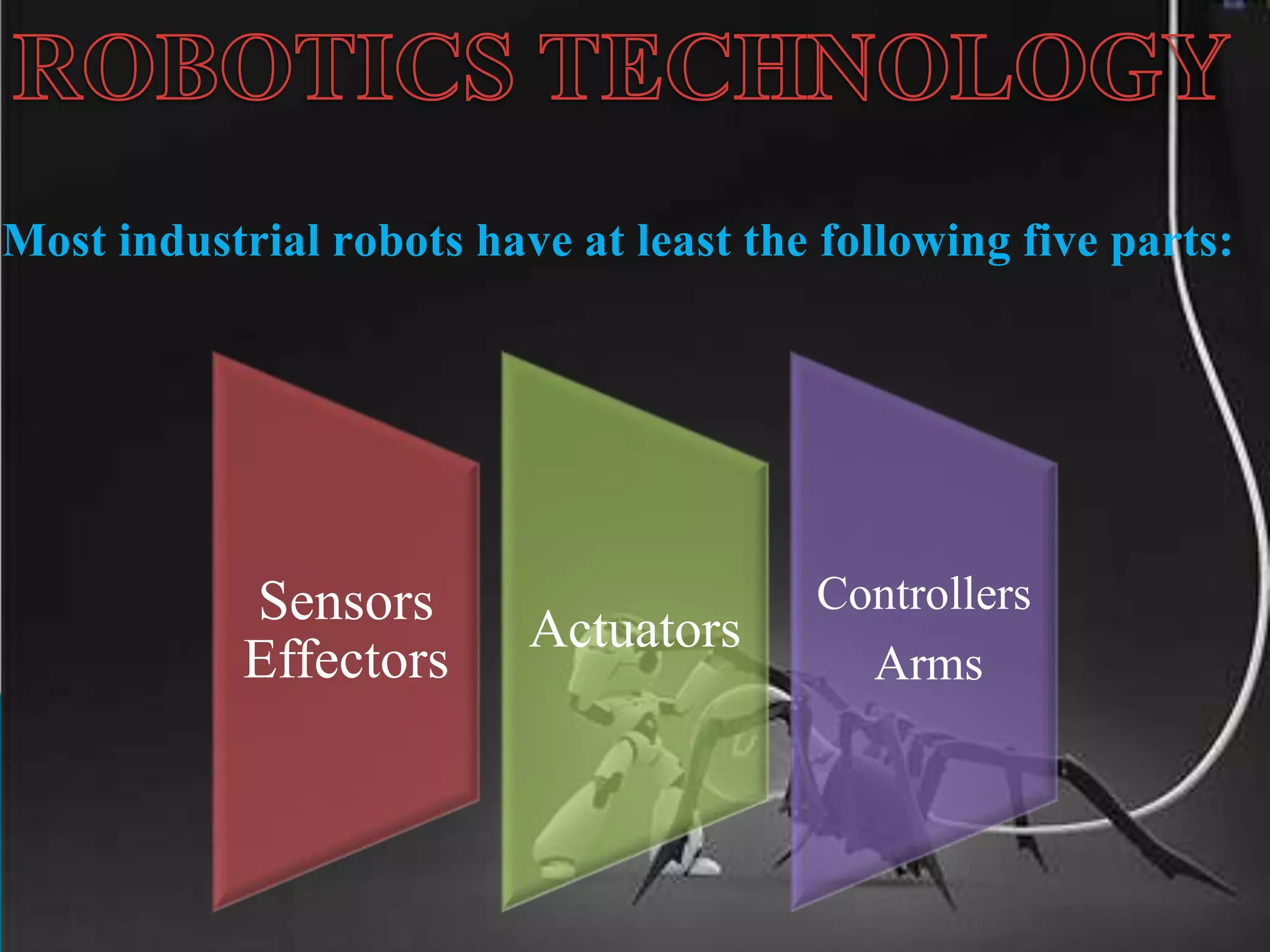
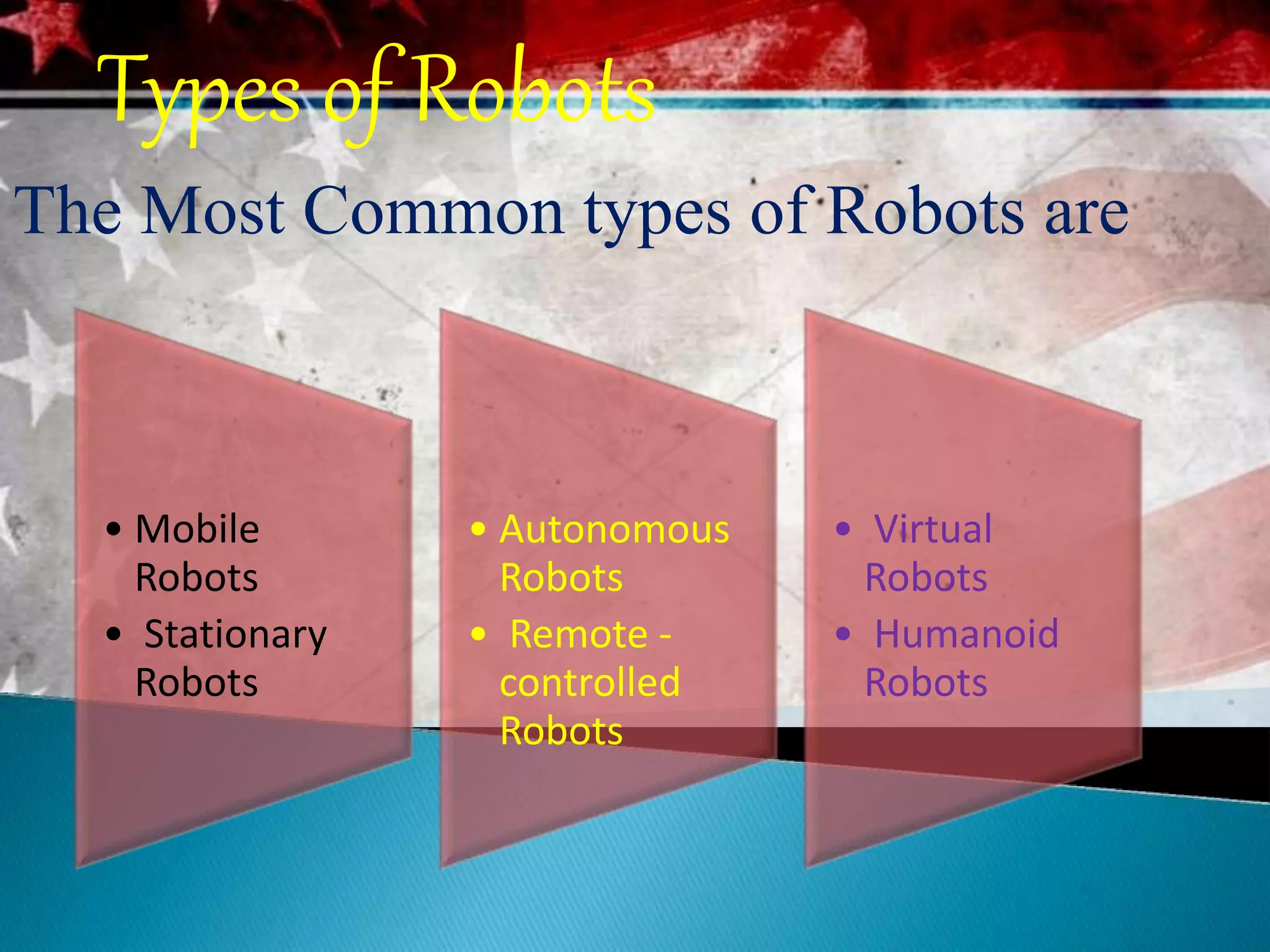
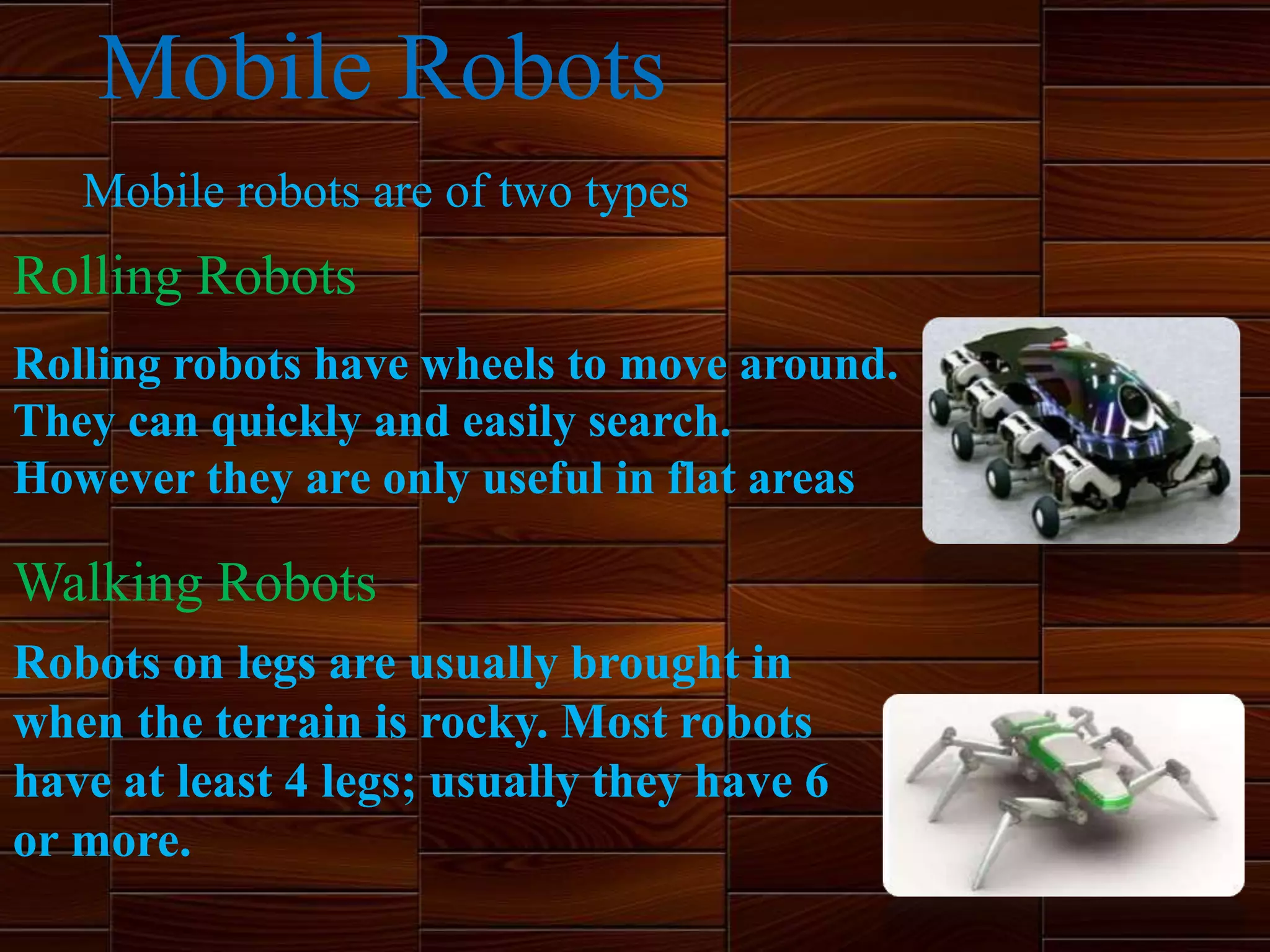
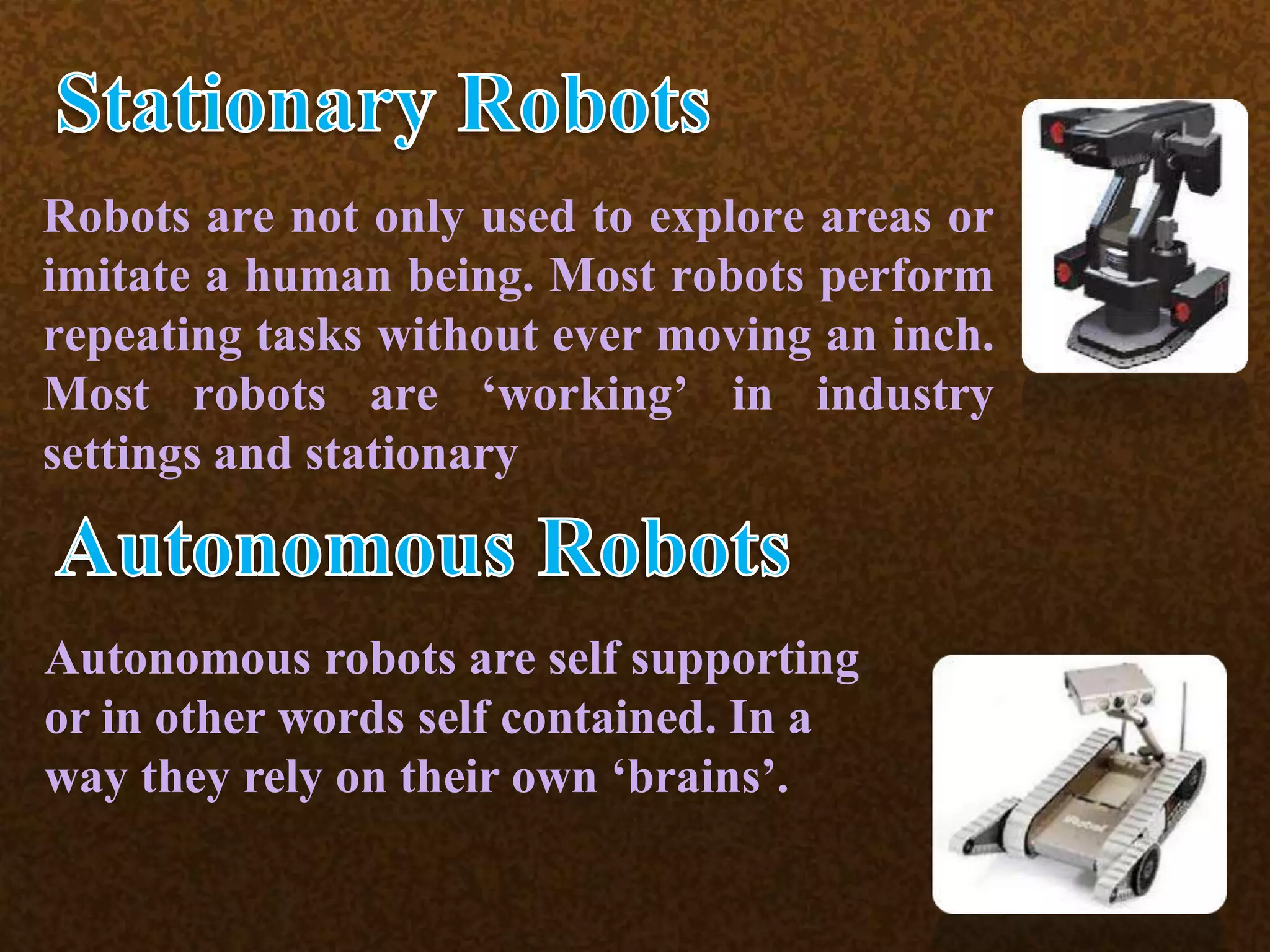
This document discusses robots and robotics. It defines a robot as a programmable, multifunctional machine designed to replace humans in hazardous work. It then discusses the history and development of robotics, including the first use of the term "robotics," Isaac Asimov's Three Laws of Robotics, and the first industrial robot called Unimate. The document also describes the main components of robots, different types of robots including mobile, stationary, autonomous, remote-controlled, virtual, and humanoid robots. Finally, it discusses some advantages and disadvantages of using robots.