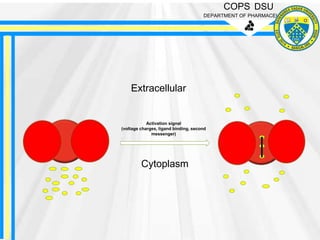
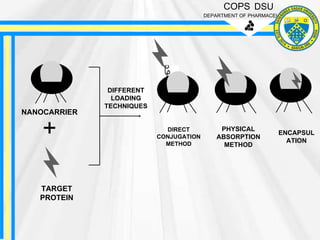
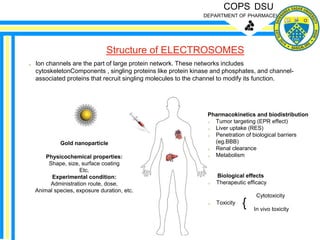
This document describes electrosomes, which are a novel surface display system composed of two compartments - a hybrid anode and cathode. The anode uses a scaffolding protein to assemble an ethanol oxidation enzyme cascade on the surface of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The cathode similarly uses a scaffolding protein to display multiple copies of a oxygen-reducing enzyme. Electrosomes were designed for use in both compartments to catalyze the conversion of chemical energy to electricity in a fuel cell. They allow high electron density and power output. The document discusses their preparation, advantages of controlled drug release and targeting applications, and disadvantages related to production costs.