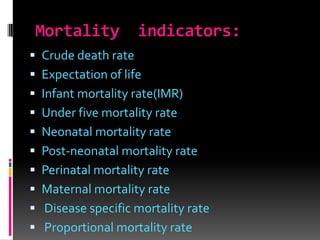
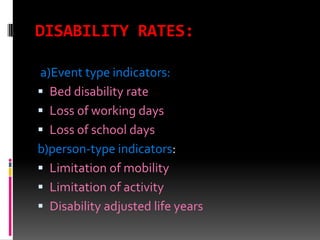
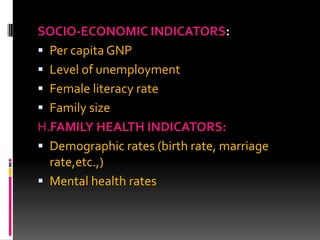
This document discusses morbidity and mortality measurements in epidemiology. It defines epidemiology and lists common measurements used, including mortality indicators like crude death rate and life expectancy. Morbidity indicators mentioned are incidence rate, prevalence rate, and attack rate. Other indicators covered include disability rates, nutritional indicators, health care delivery metrics, environmental factors, socioeconomic data, and family health measures. The document also outlines tools for measurement, including rates, ratios, and proportions. Finally, it discusses the role of nurses in collecting and analyzing health measurement data.