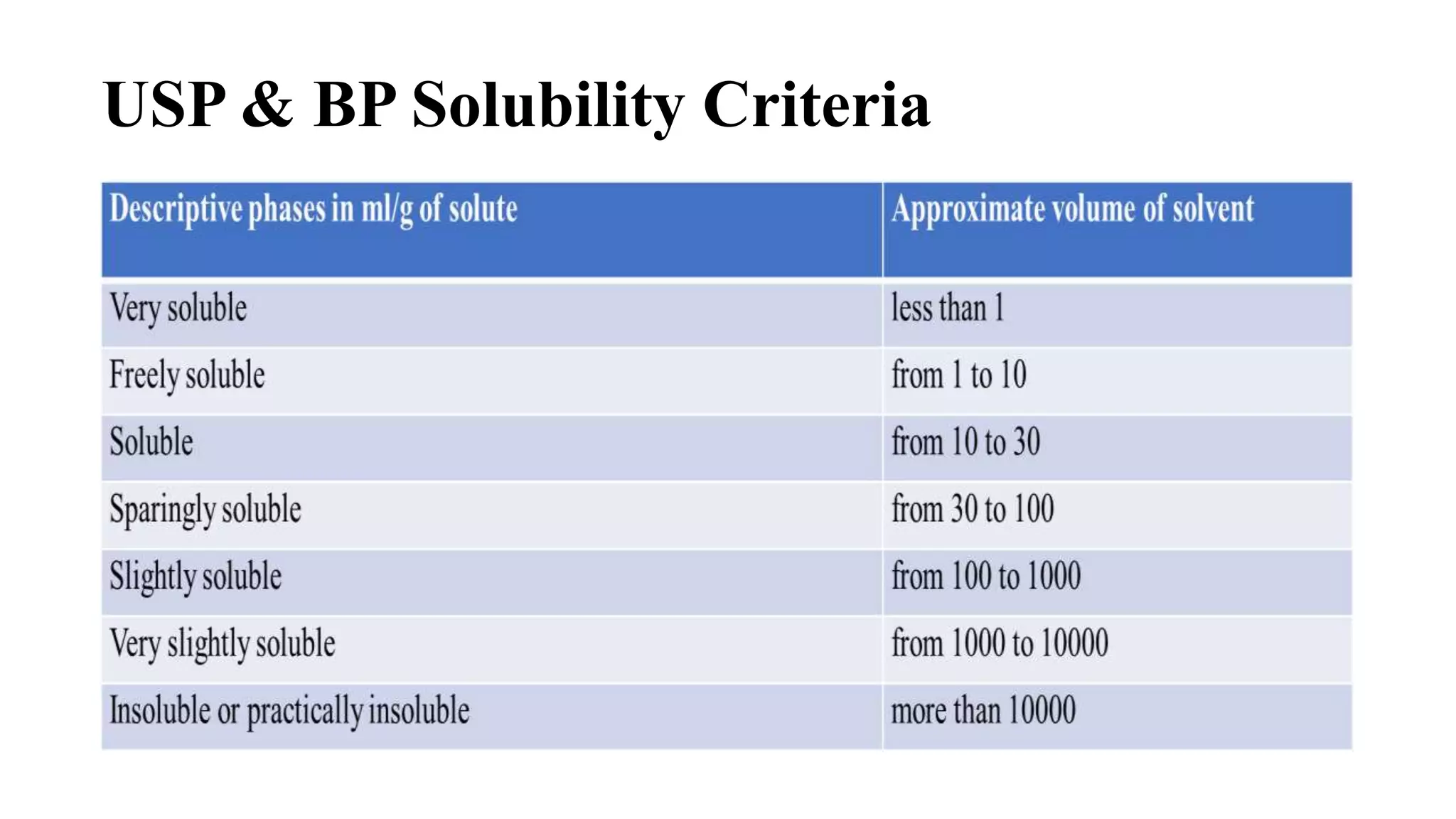
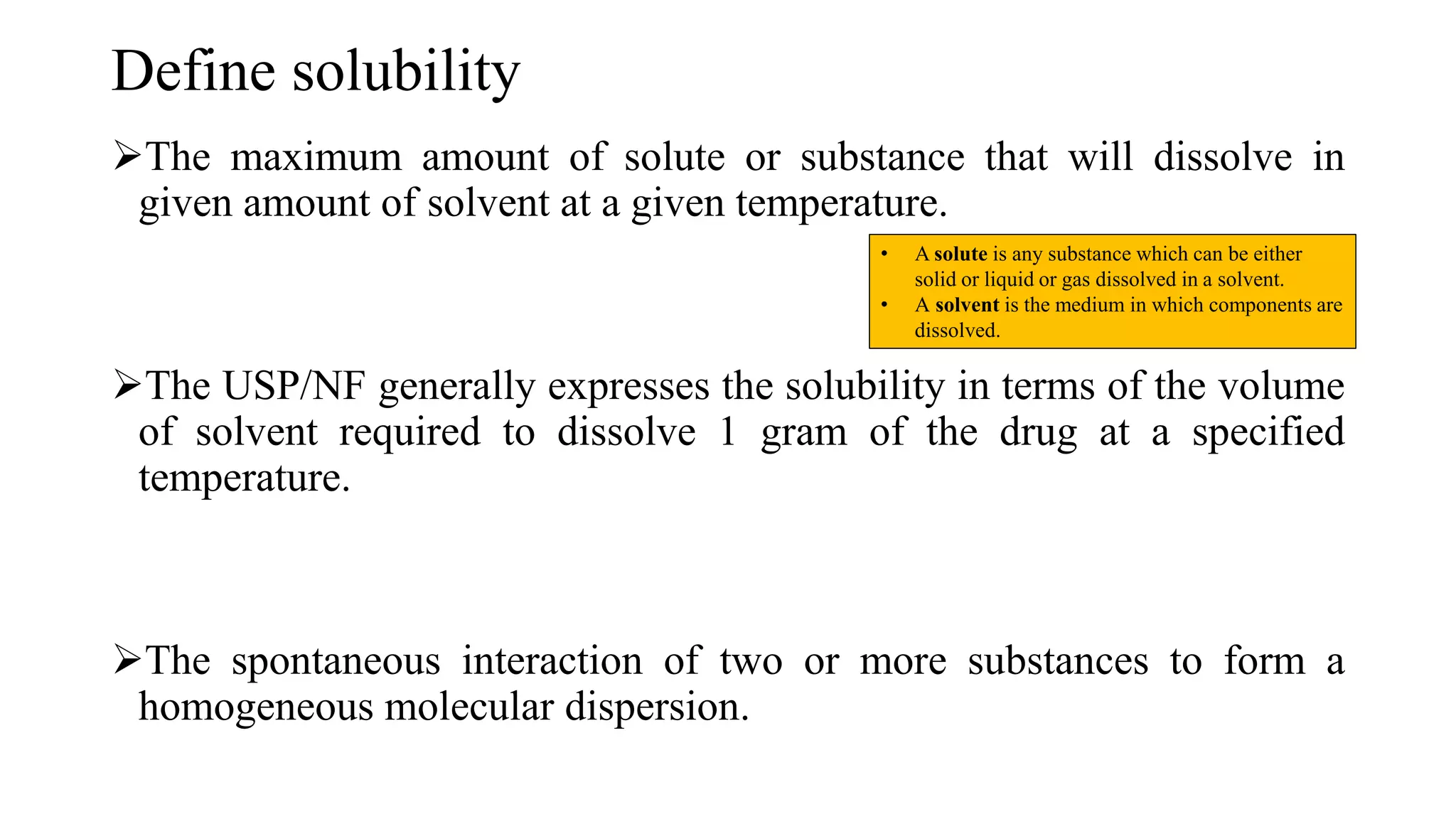
This document discusses solubility expressions and provides definitions of key terms related to solubility. It defines solubility as the maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature. The USP generally expresses drug solubility in terms of the volume of solvent required to dissolve 1 gram of drug. Several common units for expressing solubility are described, including percentage, molarity, molality, and normality. Formulas for calculating each of these units are provided. The document concludes by mentioning the USP and BP solubility criteria.






![Normality Formula
Normality = Number of gram equivalents of solute × [volume of
solution in litres]-1
Number of gram equivalents = weight of solute(gm) × [Equivalent
weight of solute]-1
N = Weight of Solute (gram) ×1000×[Equivalent weight × Volume (L)
]-1
Equivalent weight= Molar mass×n-1 *Where n is number of hydrogen atoms in an acid or hydroxide atoms in a base.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powerpointpresentationsolubilityexpressions-220824185513-3bea565f/75/PowerPoint-Presentation-solubility-expressions-pptx-8-2048.jpg)