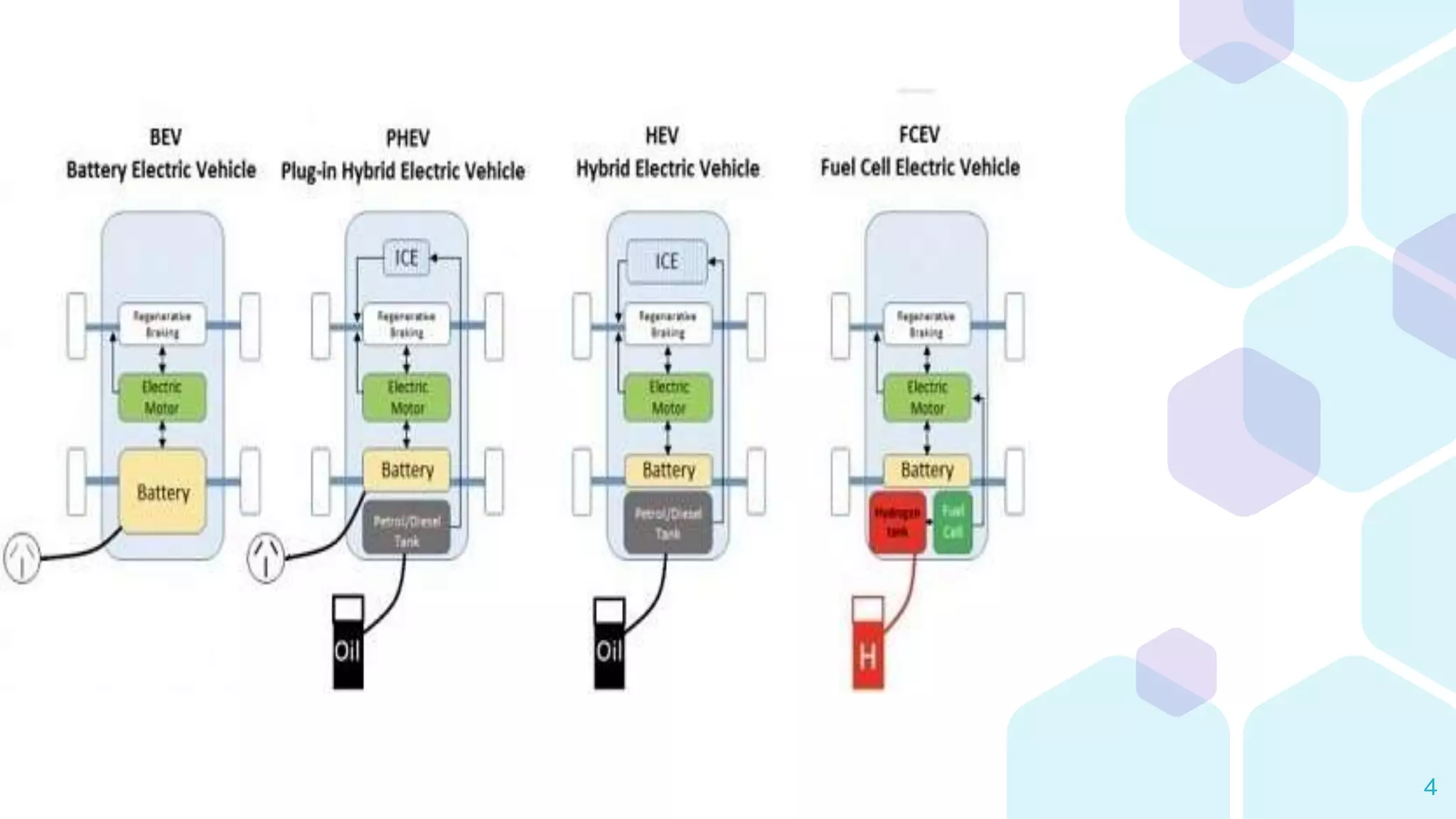
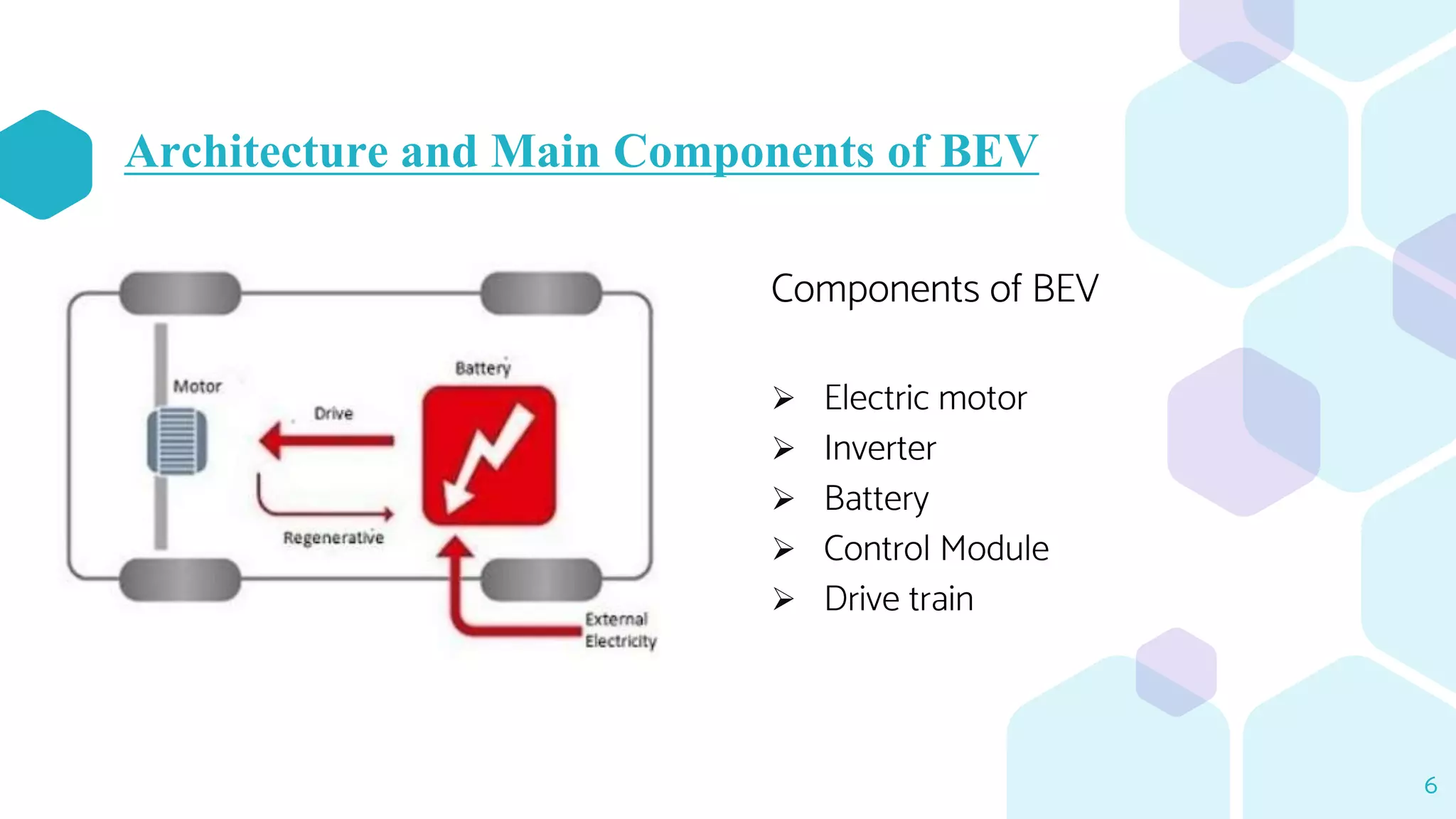
The document provides an overview of four types of electric vehicles: Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV), Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV), and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV). Each type is defined, detailing its components, working principles, and notable examples. It emphasizes the differences in energy sources and operational modes among these vehicle types.