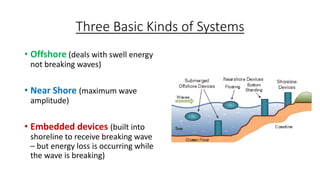
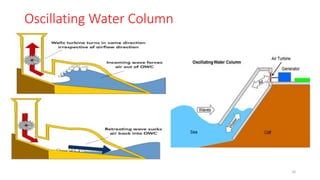
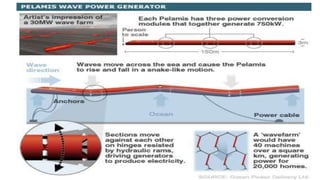
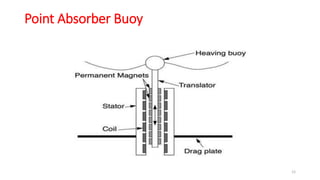
Wave energy originates from the sun heating the earth's surface and creating winds that transfer energy to ocean waters, generating waves. As waves travel vast distances across oceans, the longer and stronger the wind blows, the higher, longer, faster, and more powerful the waves become. Three main types of wave energy conversion devices interact with ocean waves to harness the kinetic energy for electricity: offshore devices dealing with swell, near shore devices capturing maximum wave amplitude, and embedded devices receiving breaking waves along shorelines. Examples of technologies include Pelamis machines that generate power from wave rolling motions and oscillating water columns that use wave pumping of air to drive turbines. Significant wave energy resources exist off coasts between 30-60 degree latitudes, and