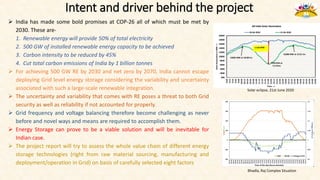
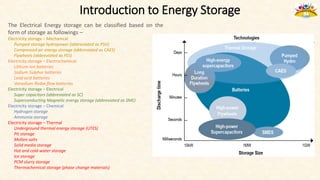
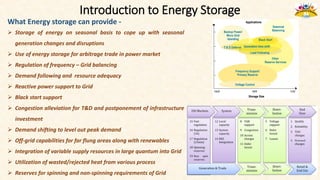
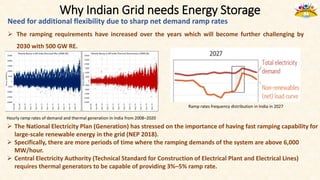
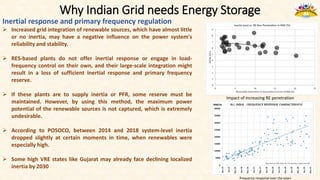
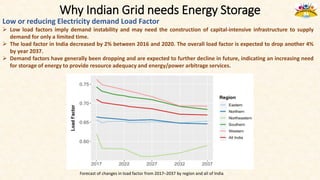
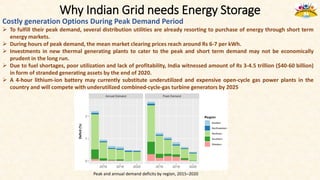
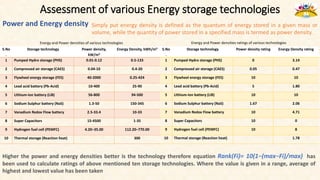
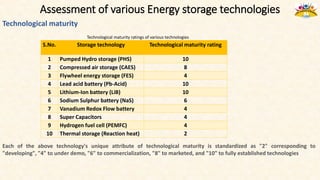
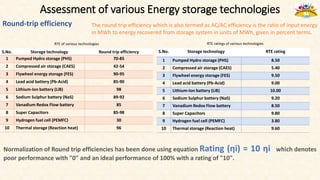
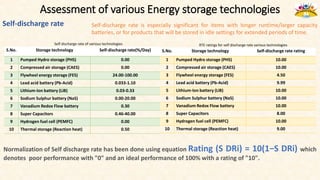
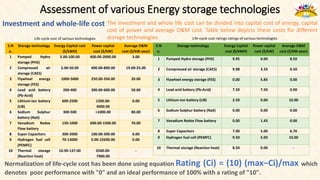
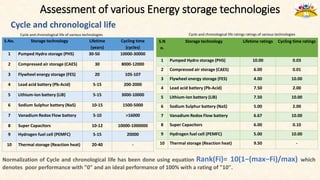
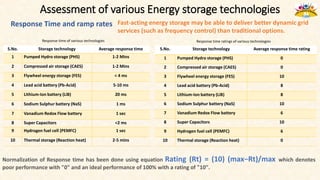
The document discusses the need for grid-scale energy storage in India to support its renewable energy goals. As India aims to source 50% of its electricity from renewables by 2030, large amounts of variable renewable generation like solar and wind will pose challenges for grid stability and reliability. Energy storage can help balance the grid by storing excess renewable energy and dispatching it when renewable output is low. The document assesses various energy storage technologies based on their power and energy density, technological maturity, efficiency, lifetime costs, response time, and environmental impacts to determine their suitability for the Indian grid. It finds that pumped hydro, lithium-ion batteries, and thermal storage show potential to facilitate India's renewable energy integration if deployed appropriately.