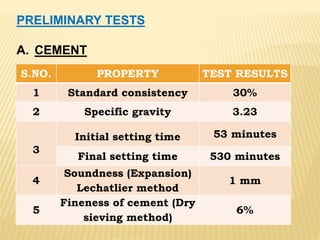
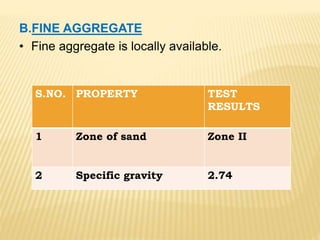
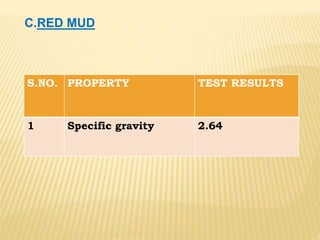
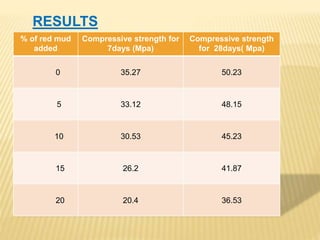
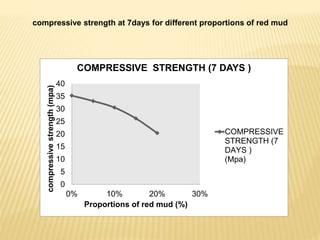
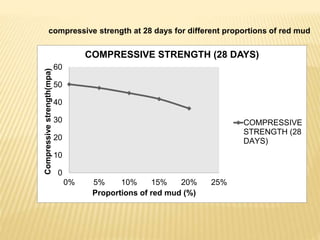
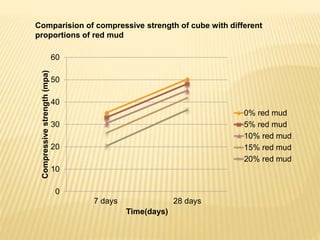
This document discusses a study on using natural red mud as a partial replacement for cement in cement mortar. Preliminary tests were conducted on cement, fine aggregate, and red mud. Cement mortar cubes were prepared with 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20% replacements of cement with red mud. The compressive strengths of the cubes were tested at 7 and 28 days. The results showed that compressive strength decreased as the proportion of red mud increased. Specifically, compressive strengths dropped by 15-25% with a 20% replacement of cement with red mud. Therefore, red mud has potential as a partial cement replacement but reduces the strength of cement mortar.