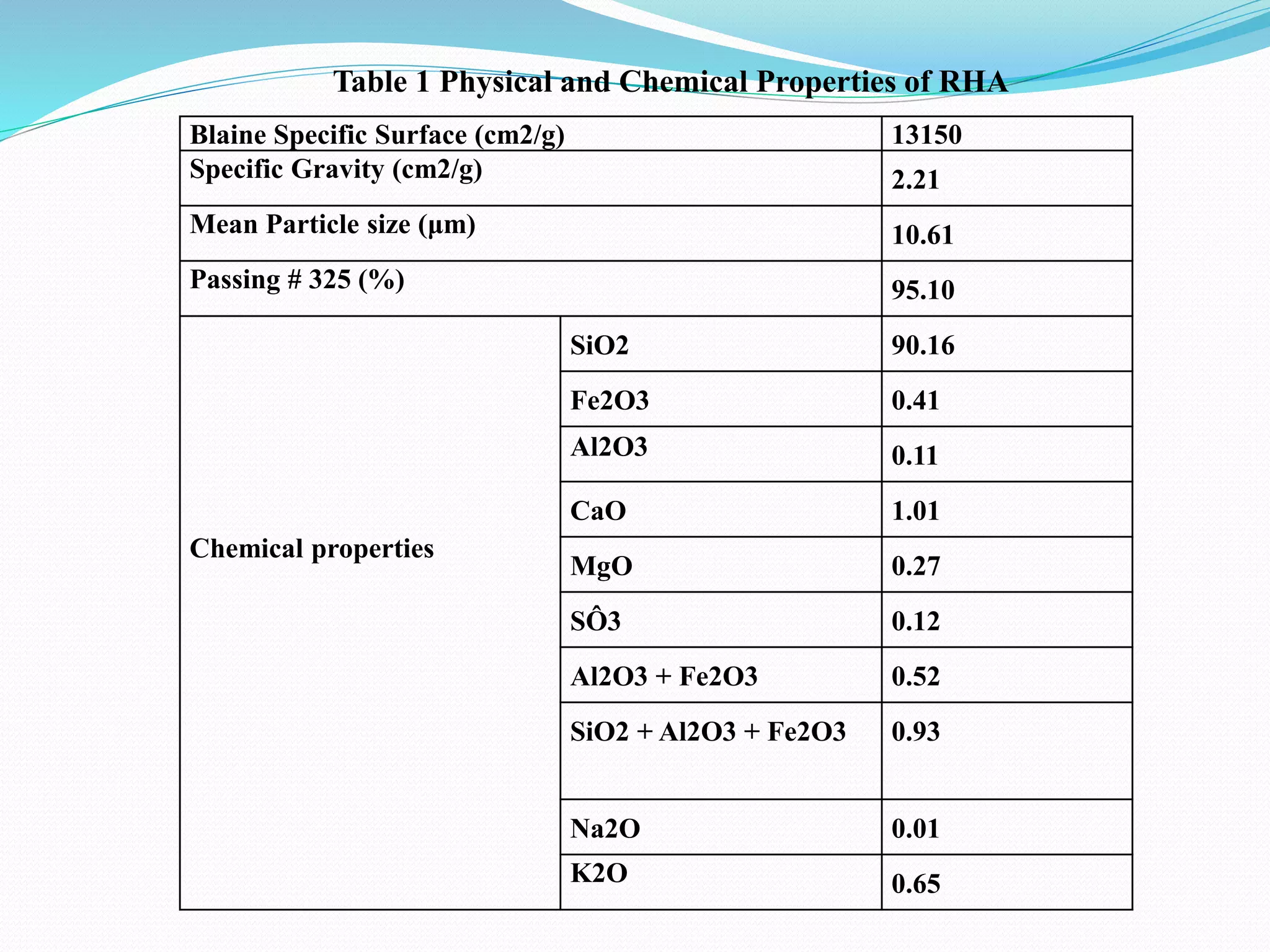
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on rice husk ash (RHA). RHA is obtained by burning rice husks between 600-700°C for 2 hours. It is composed primarily of silicon dioxide and can be used to partially replace cement in concrete production. The addition of RHA increases strength and durability by reducing calcium hydroxide levels in concrete. It also reduces efflorescence and susceptibility to chemical and sulfate attacks. Using RHA in concrete can help reduce carbon dioxide emissions from cement production and provides an economic use for the agricultural waste product of rice husks. The seminar outlines the physical and chemical properties of RHA and reviews its advantages and disadvantages when used in concrete.