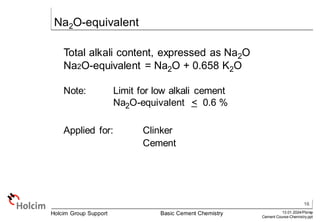
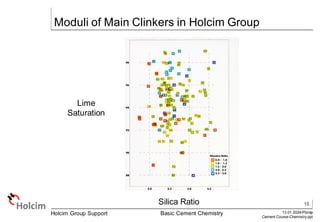
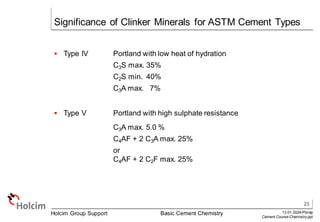
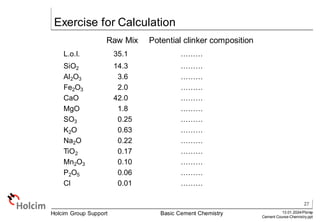
This document provides an overview of basic cement chemistry, including the chemical and mineralogical composition of cement materials, common chemical parameters used to analyze cement composition, and the Bogue calculation method for determining the mineralogical composition of clinker from its chemical analysis. Key topics covered include elemental composition, chemical formulae, titration content, lime saturation, silica and alumina ratios, and the significance of clinker minerals like C3S, C2S, C3A, and C4AF for cement properties and ASTM cement types.