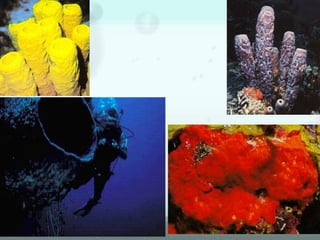
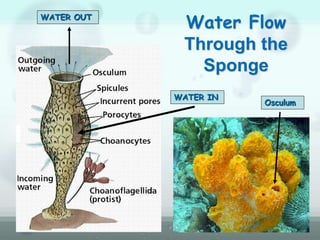
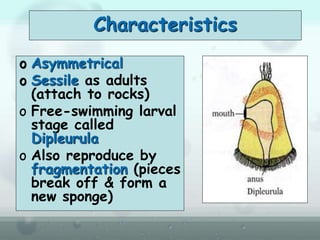
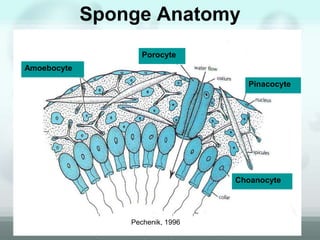
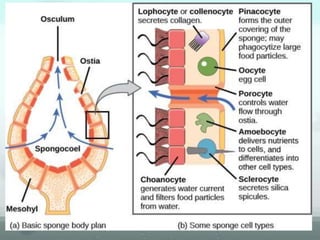
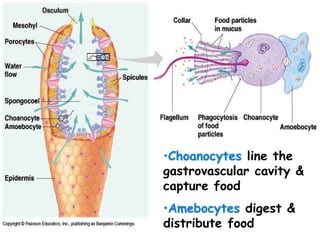
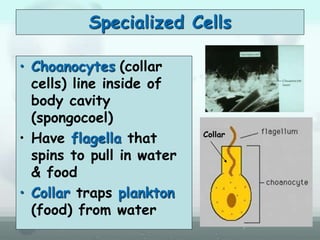
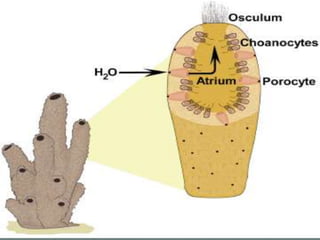
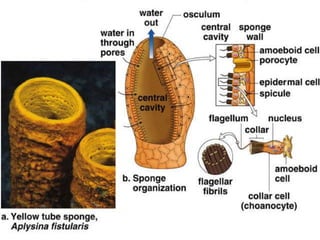
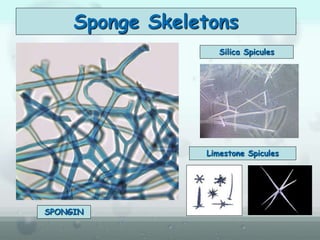
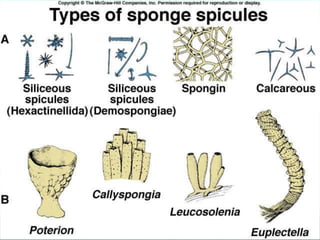
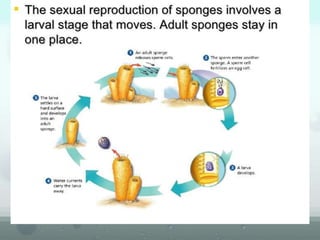
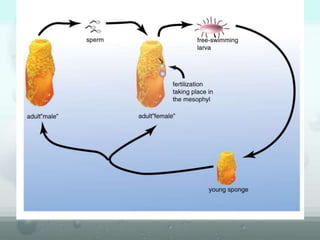
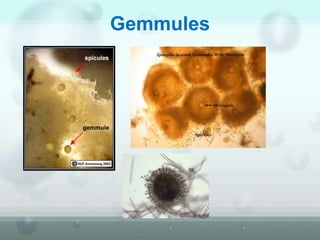
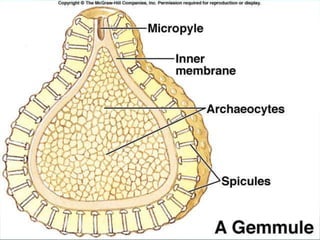
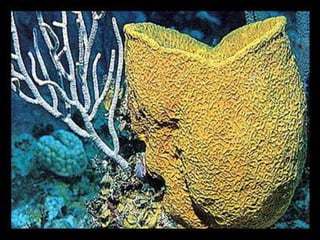
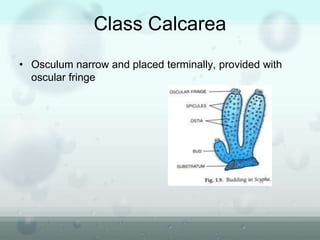
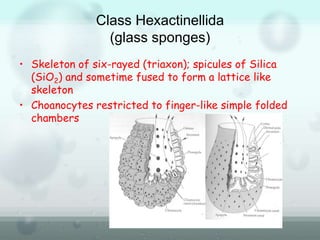
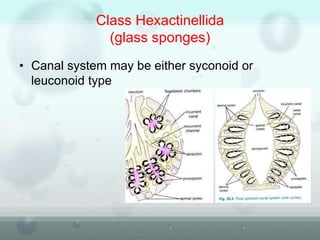
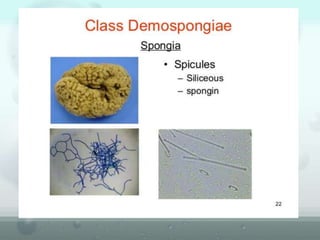
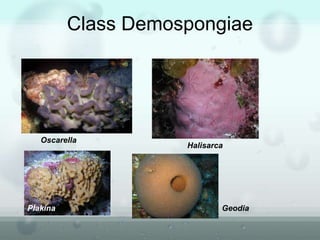
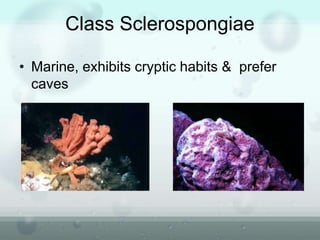
The document discusses the phylum Porifera, commonly known as sponges. It describes their key characteristics, including being the simplest multicellular organisms lacking tissues and organs. They have specialized cells but no other organization. Sponges are primarily marine filter feeders that live attached to substrates and filter water through pores to feed. They reproduce both sexually and asexually. The document outlines the four classes of sponges and their distinguishing features.