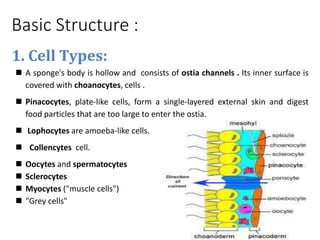
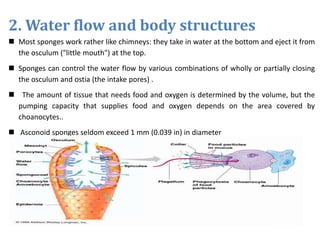
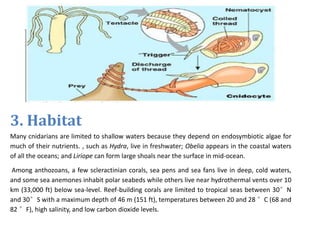
This document provides information on sponges and cnidarians. It discusses the distinguishing features, basic body structures, life functions, habitats, and evolutionary histories of these early animal phyla. Sponges are multicellular organisms that live in water and have pores but lack nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. They reproduce sexually or through budding. Cnidarians are more complex than sponges and have stinging cells called cnidocytes. They have two main cell layers and feed through predation or symbiosis. Their fossil record extends back over 500 million years.
![Topic :
Evolution of Animal Diversity
[Sponges and Cnidarians]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupno4-wpsoffice-240125101537-083e8127/85/Group-No-4-WPS-Office-pptx-1-320.jpg)