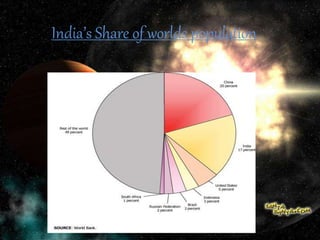
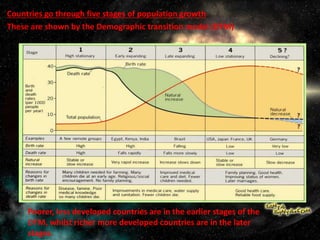
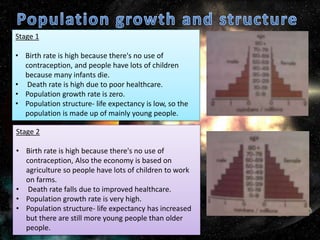
The document discusses population and migration. It defines population as a group of organisms of the same species living in the same area. It then discusses India's large population, with Uttar Pradesh being the most populated state. The document also summarizes the five stages of population growth according to the Demographic Transition Model. Rapid population growth can create social, economic and political challenges for countries. Governments implement policies like birth control programs and immigration laws to control population growth in a sustainable way. The document also discusses the impacts of aging populations and strategies countries use to address these impacts. It defines migration and discusses push and pull factors, as well as the positive and negative impacts of migration on both source and receiving countries.