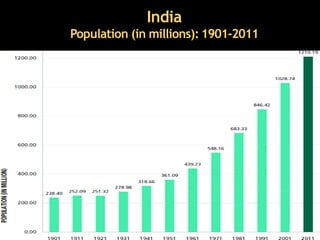
The document discusses the concept of population in sociology, highlighting statistics about the world's most populous countries, with China and India at the forefront. It covers India's population demographics, processes of population change, and presents arguments for and against overpopulation. It concludes with projections and notable facts regarding India's growing population and its implications.