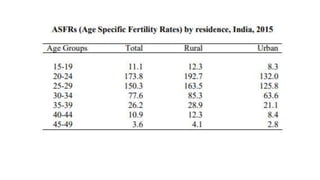
This document defines various fertility indicators and measurements used to assess fertility rates. It discusses crude birth rate, general fertility rate, age-specific fertility rate, total fertility rate, and other indicators. These indicators use live births, population sizes, and age groups in their calculations to measure fertility while accounting for factors like age, marital status, and mortality rates. The document aims to explain how demographers measure and analyze fertility levels in populations.