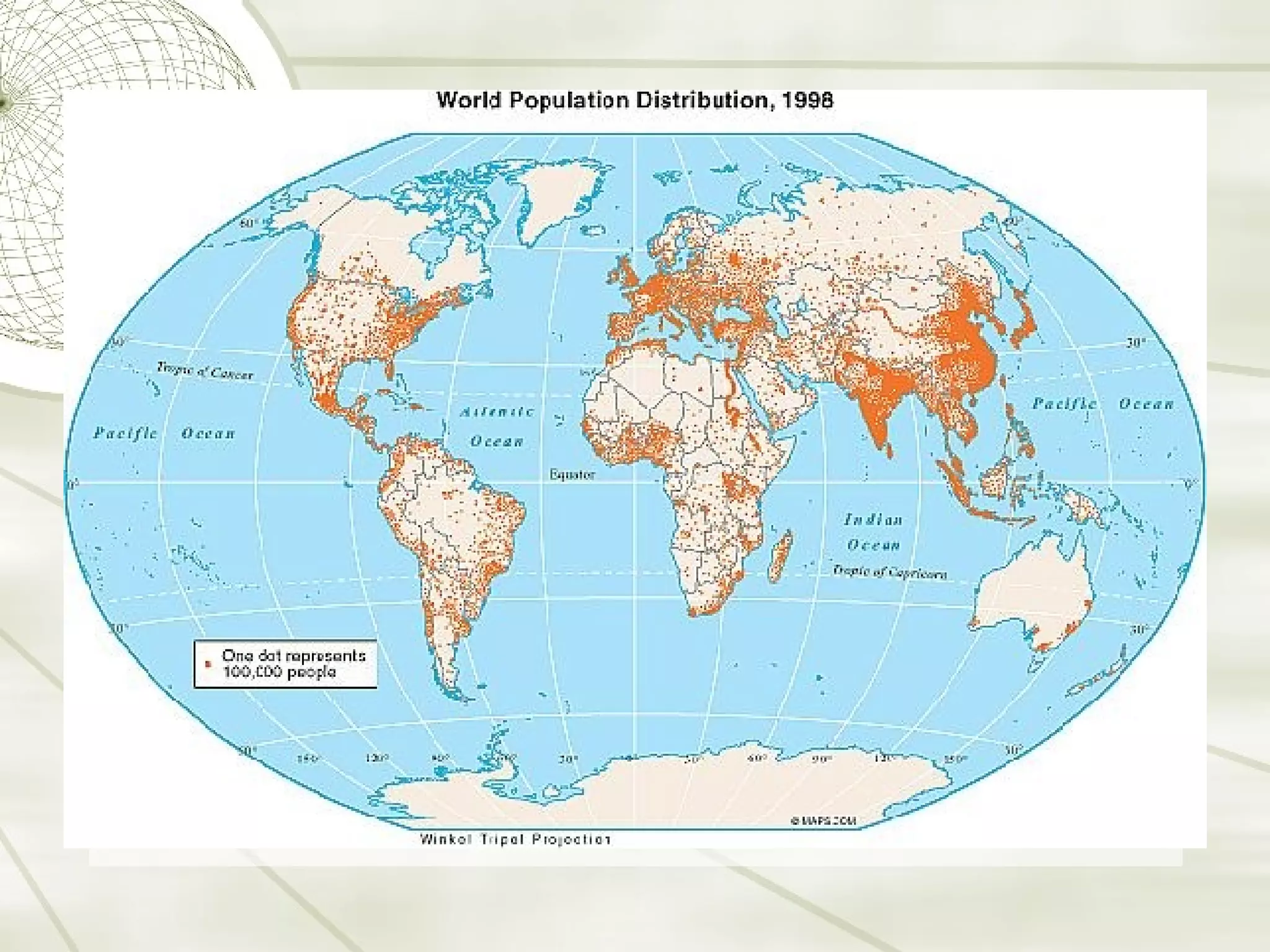
This document discusses factors that influence human population distribution and density. It explains that population is not evenly distributed globally, as people tend to settle near valuable resources like fresh water, arable land, and in areas with temperate climates and good economic opportunities. Population density is highest along coastlines, river valleys, and in cities that offer jobs, transportation, and were established historically. Government policies also impact population distribution through initiatives like China's one-child policy.