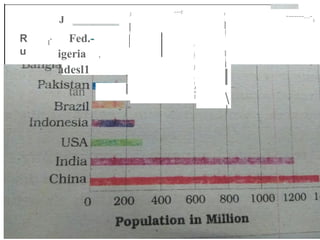
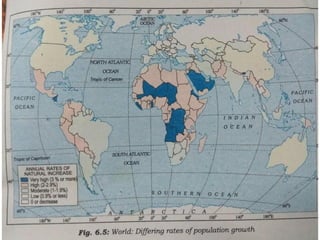
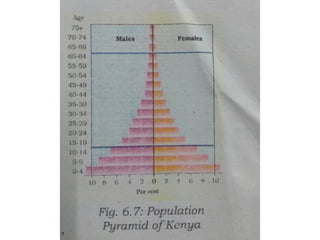
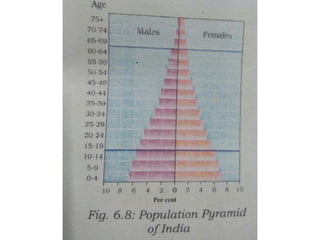
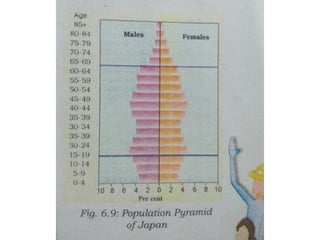
The document discusses the concept of human resources, emphasizing that people are a nation's greatest asset and how various factors affect population distribution and density. It explores the historical trends of the world's population growth, including birth and death rates, as well as the importance of understanding population composition through tools like population pyramids. The conclusion highlights the significance of educating and equipping young people with skills for the future.