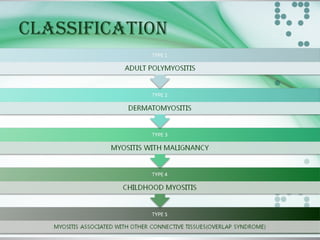
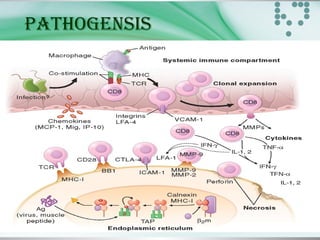
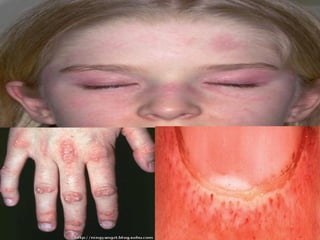
This document provides an overview of polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Polymyositis is an idiopathic inflammatory myopathy that causes symmetrical proximal muscle weakness. It is caused by defective cellular immunity and can be associated with viral infections, malignancies or drugs. Symptoms include proximal muscle weakness in the upper and lower limbs and may include extra skeletal symptoms. Investigations include blood tests, EMG and muscle biopsy. Treatment involves corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents. Dermatomyositis is a similar condition with additional characteristic skin manifestations. Both conditions are treated with corticosteroids, immunosuppressants and addressing any skin symptoms.