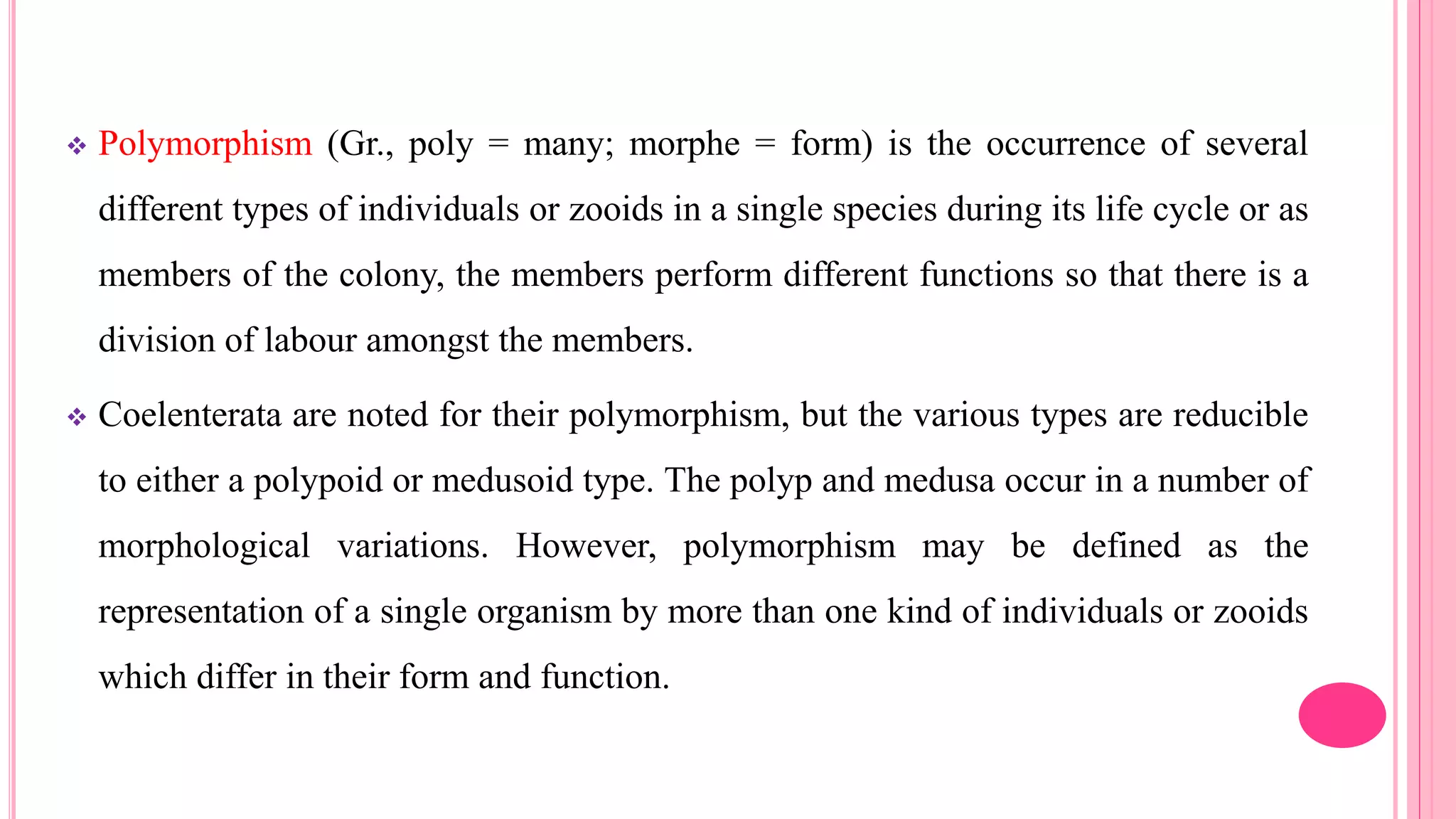
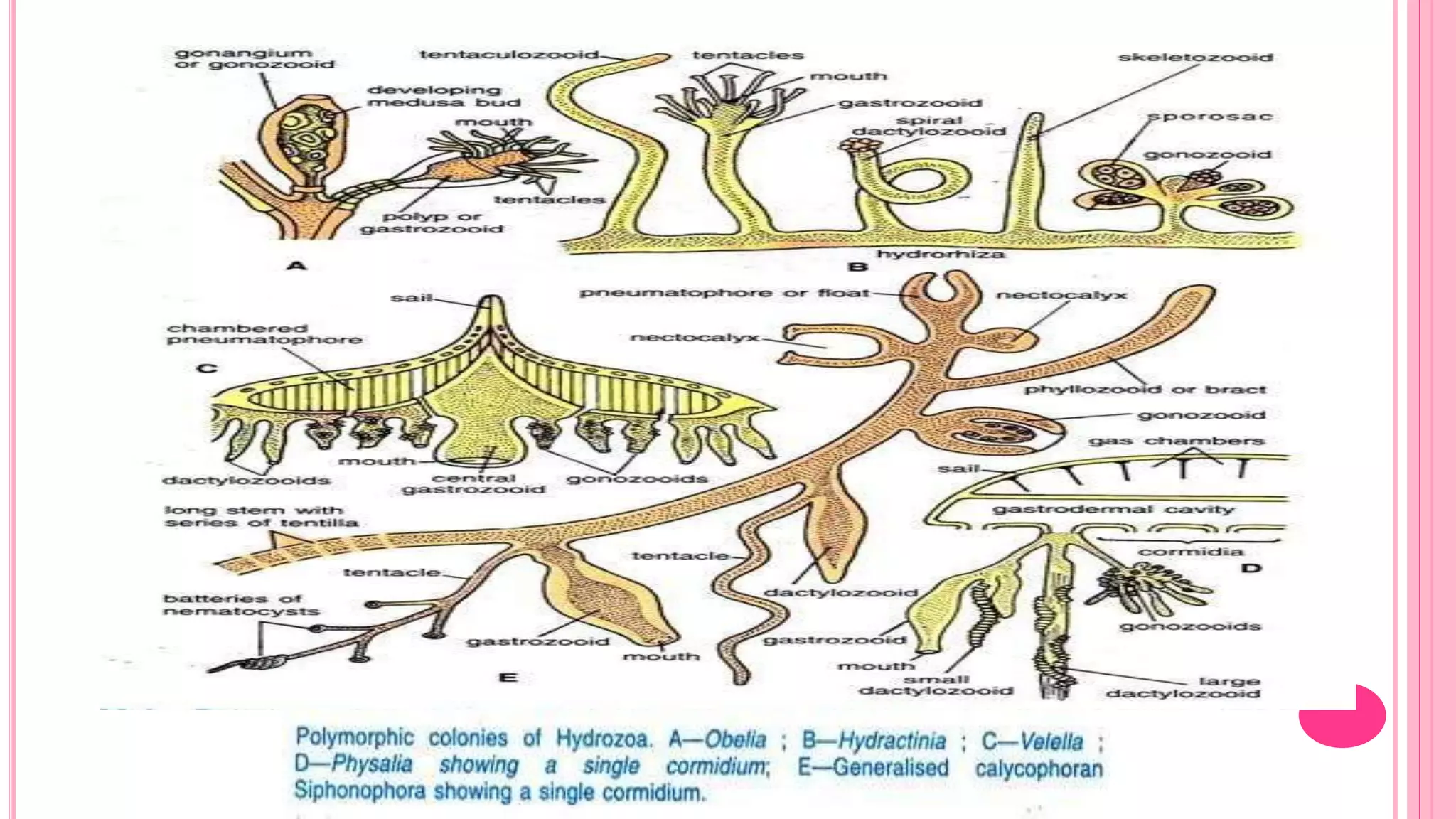
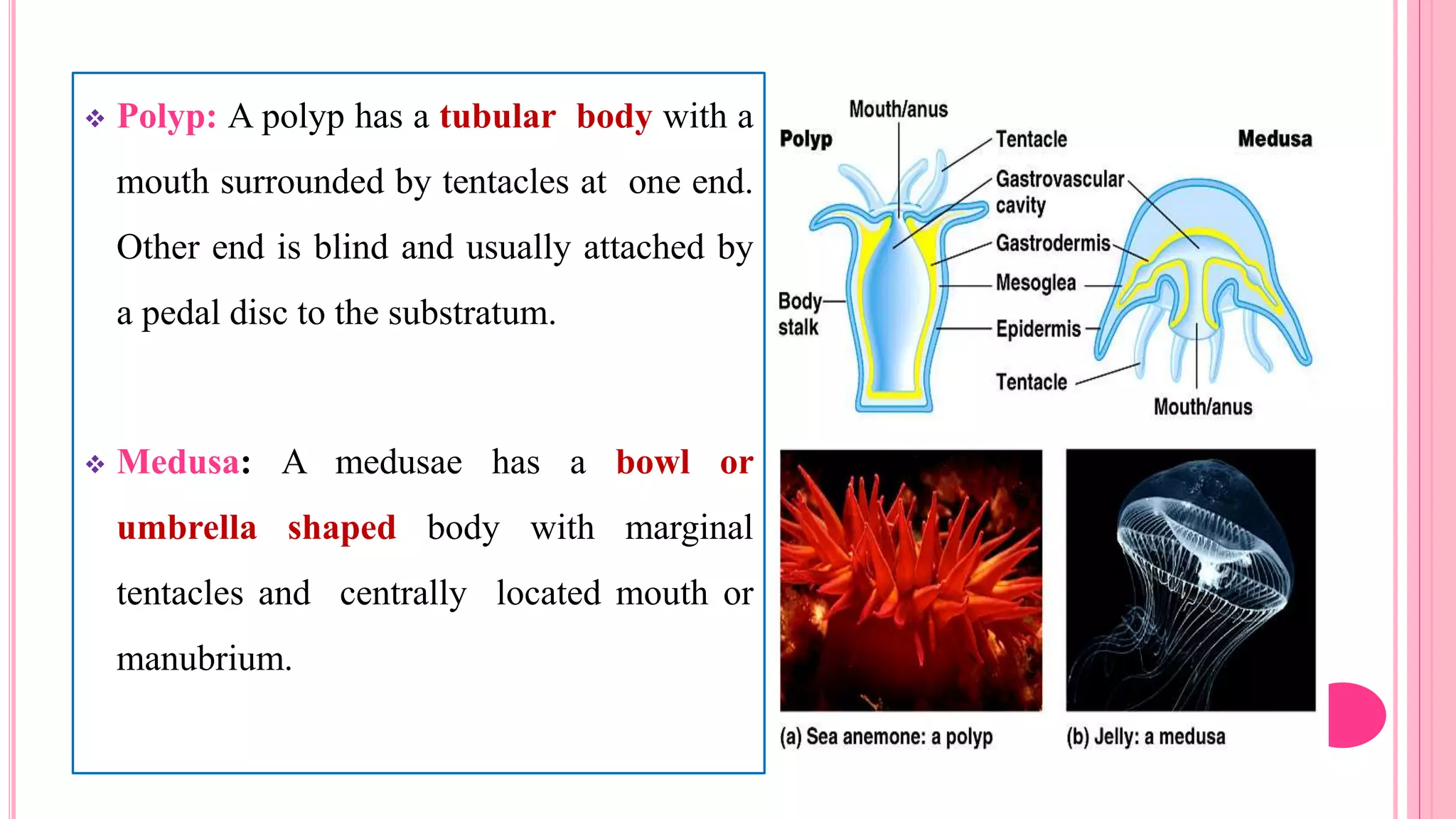
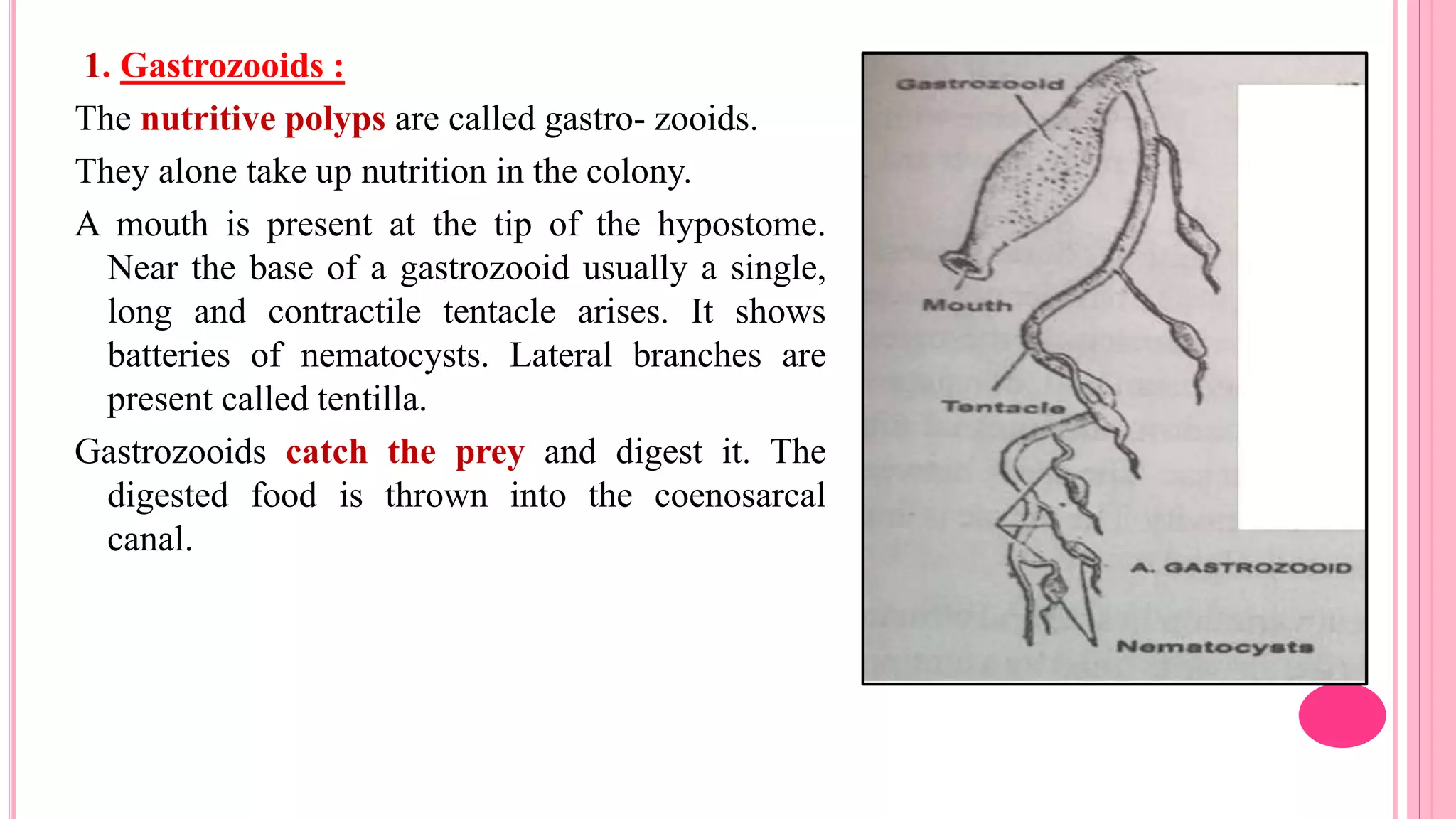
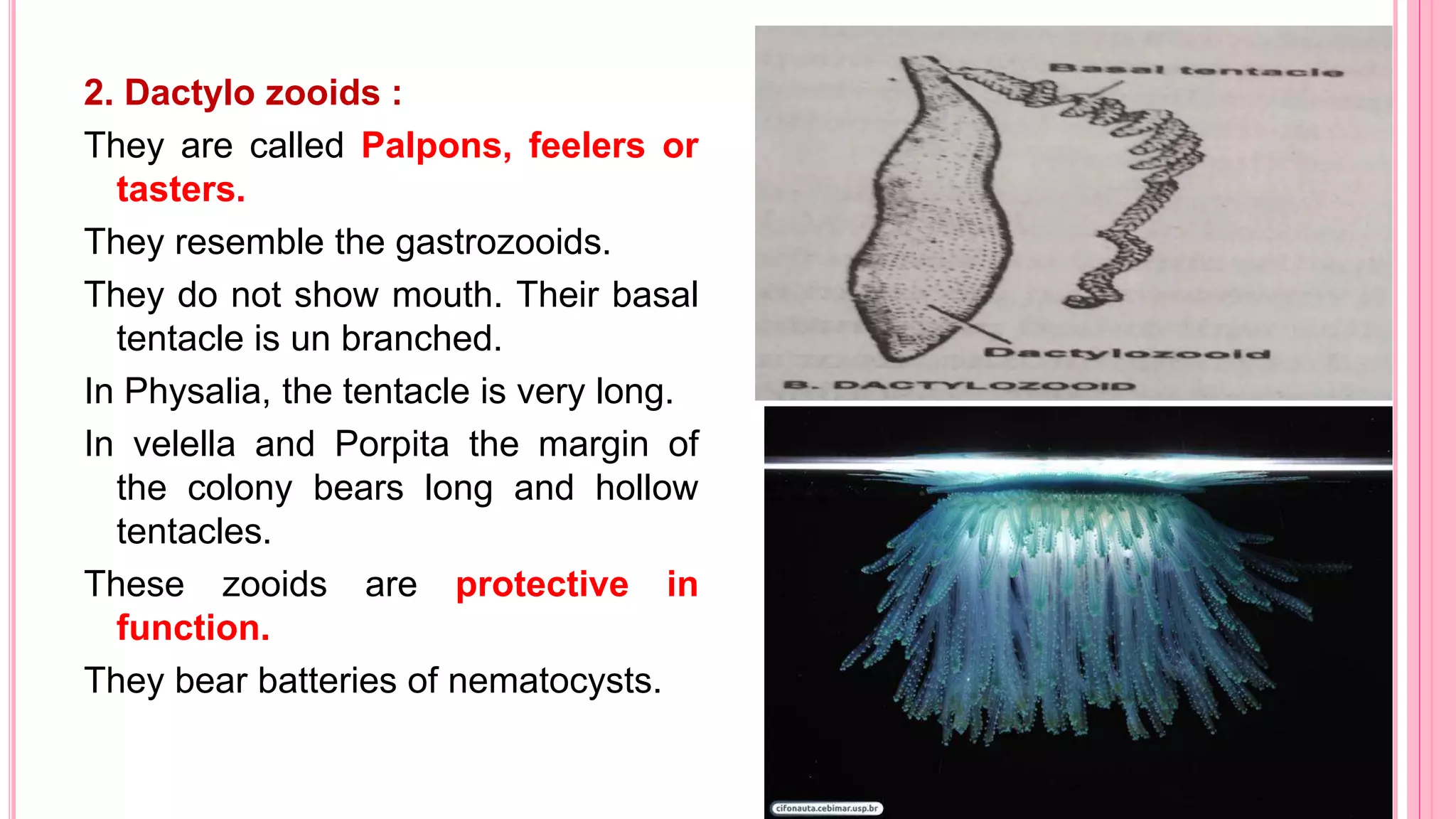
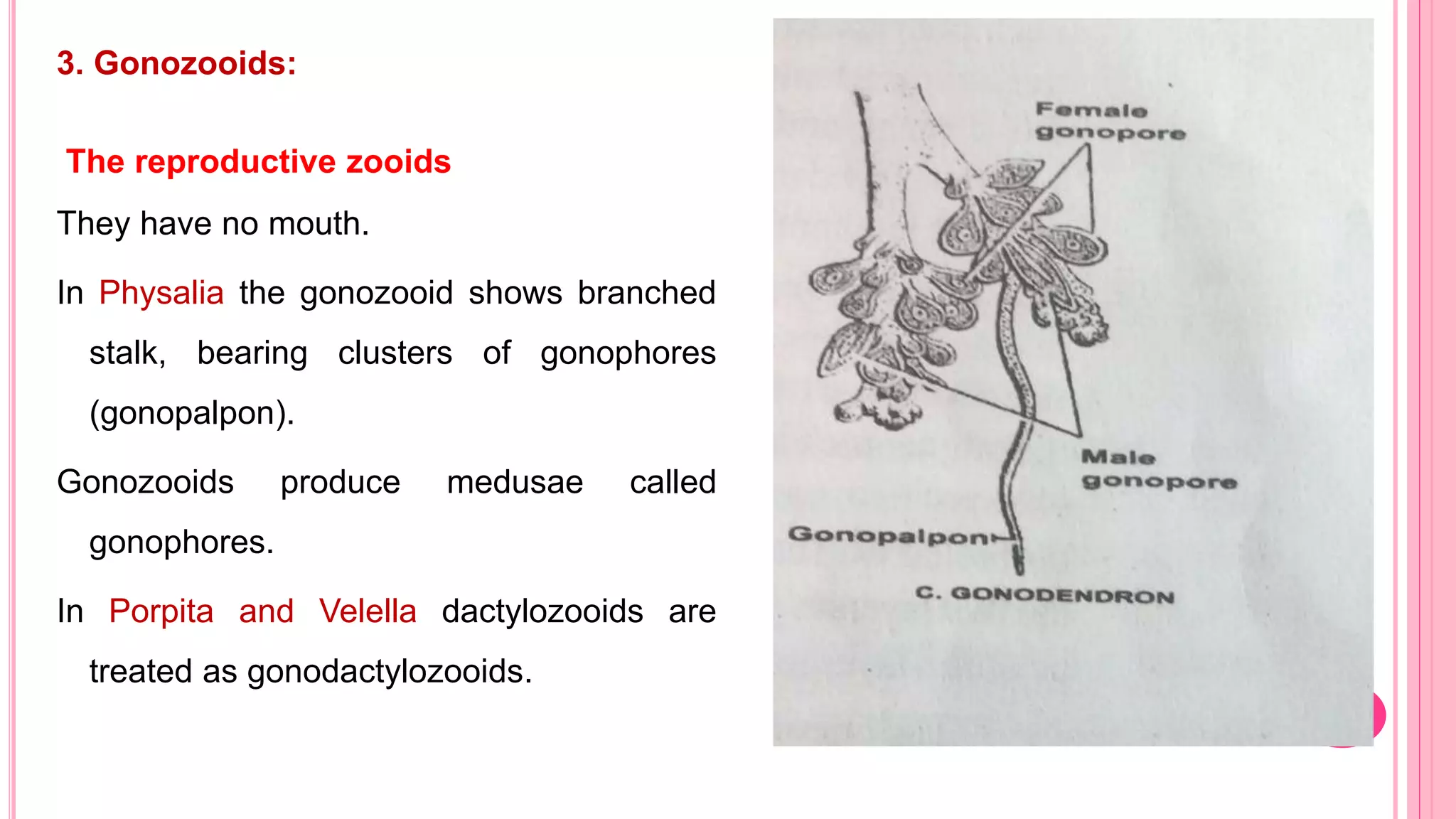
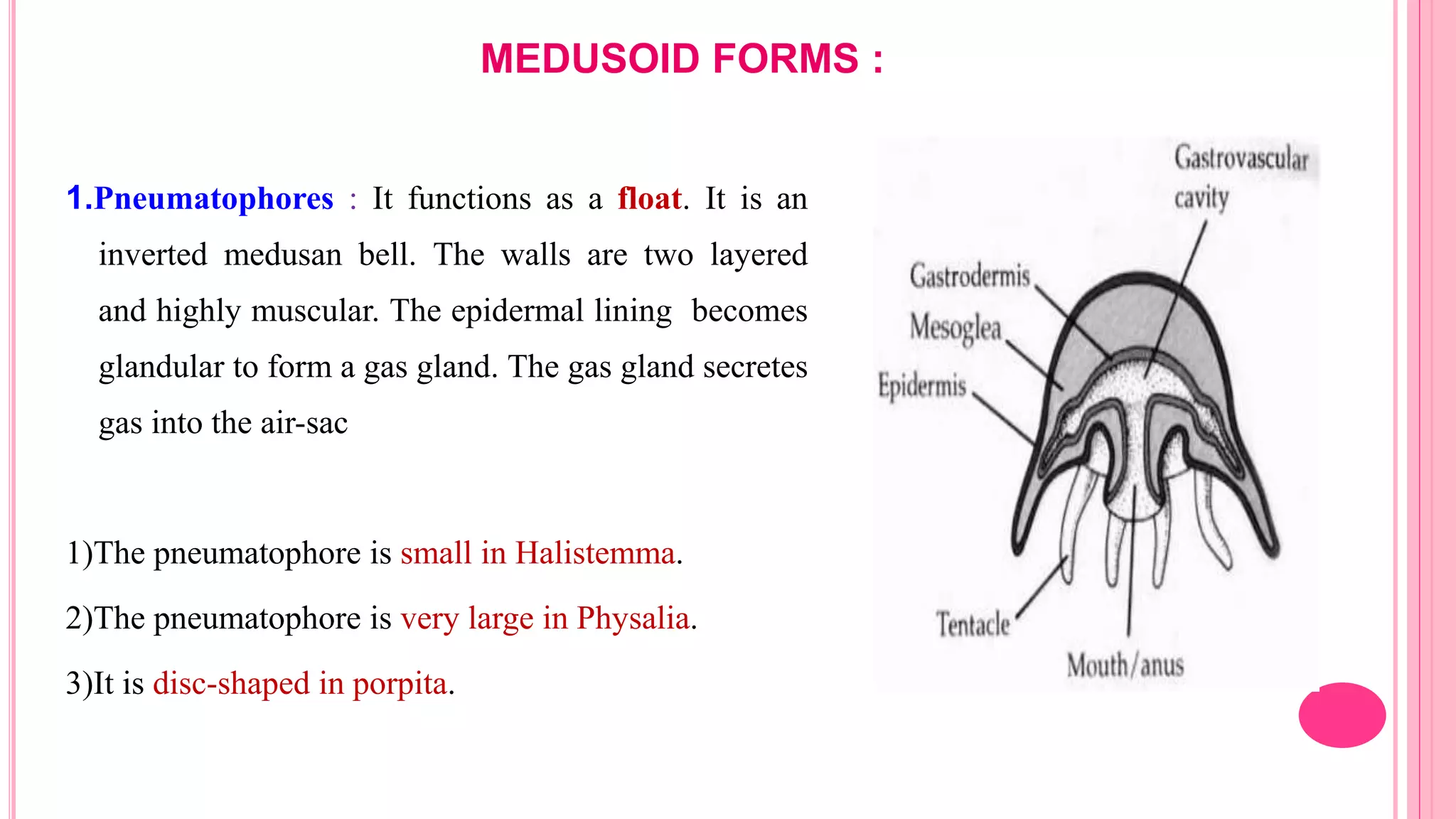
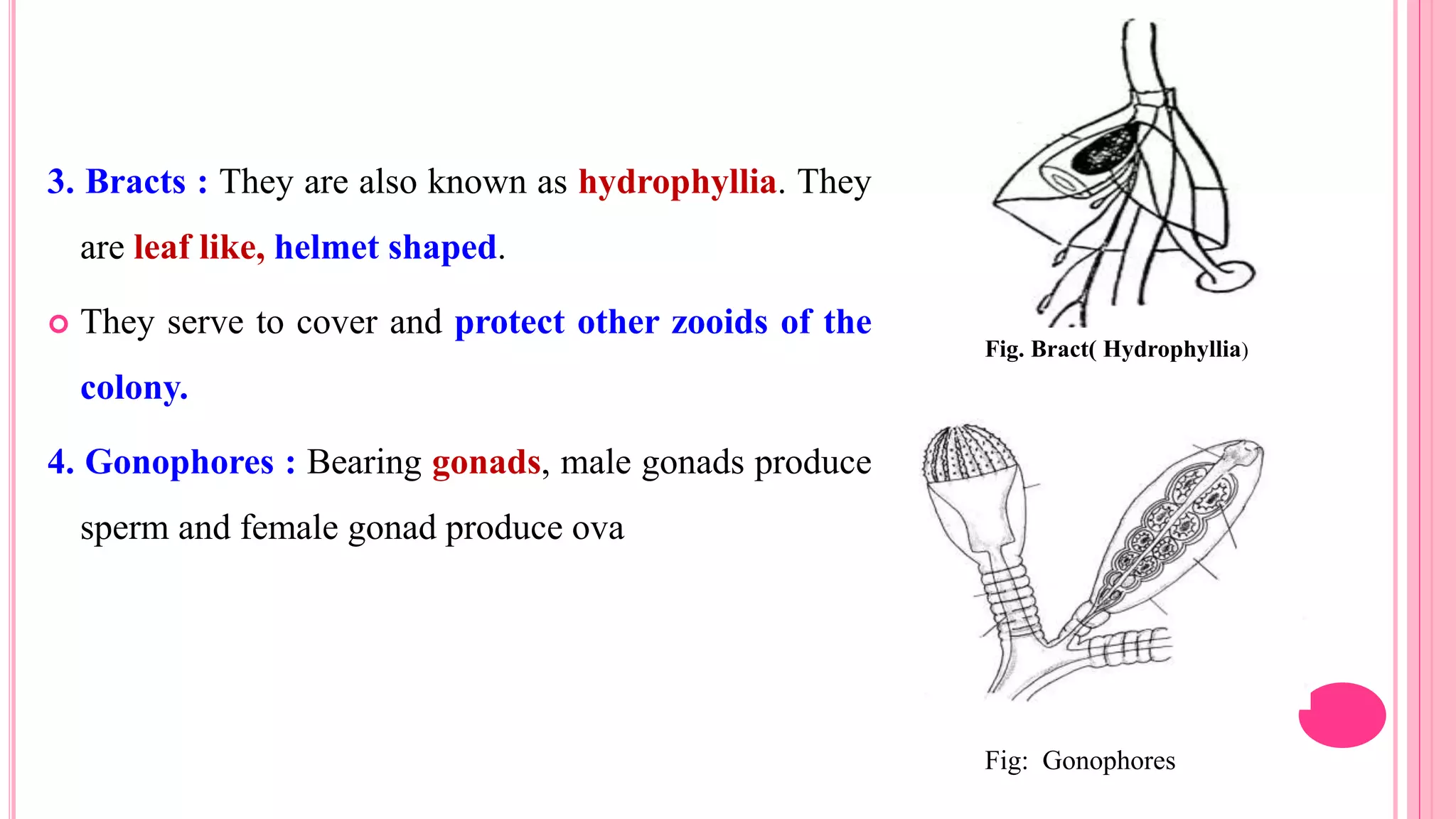
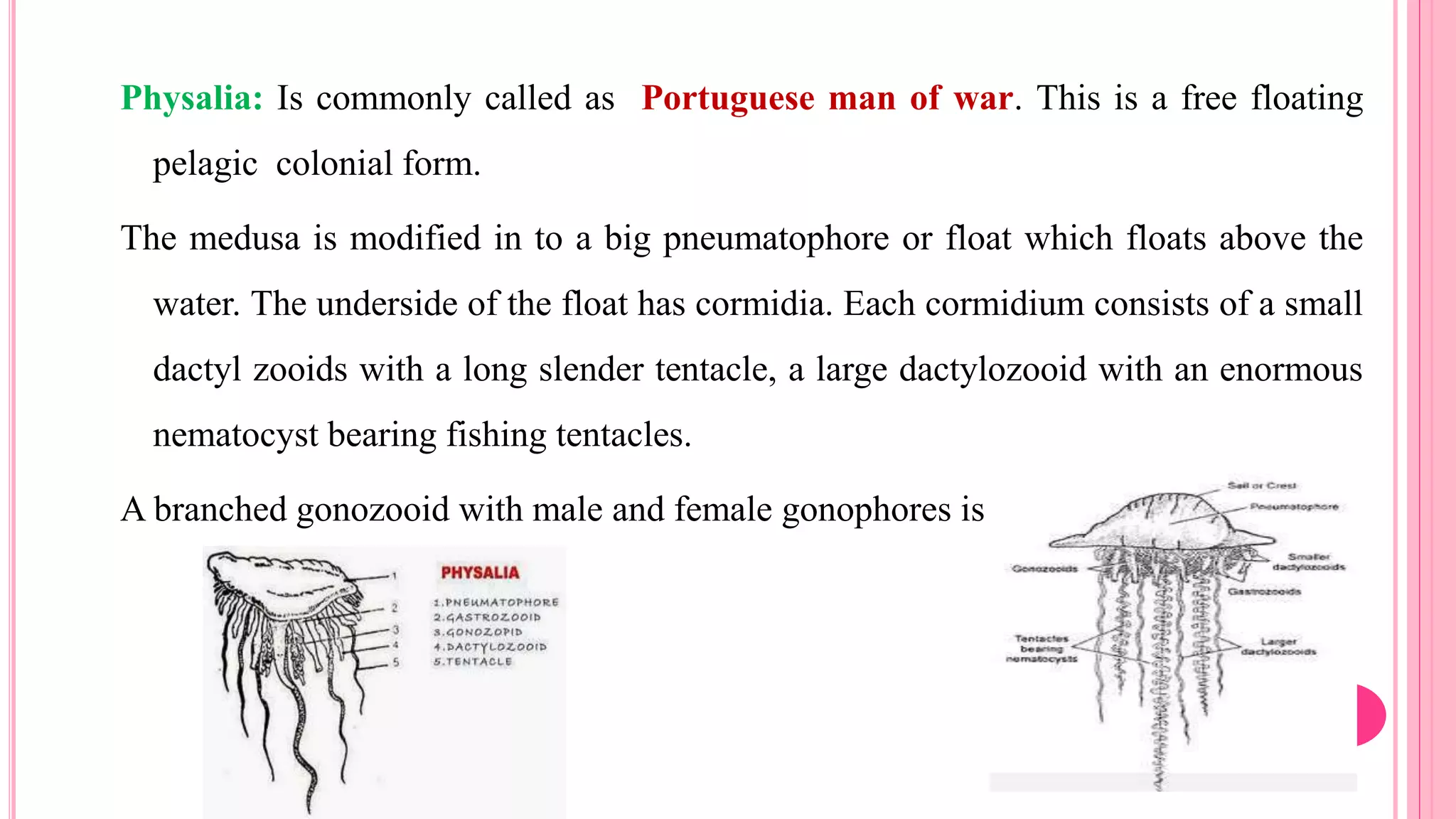
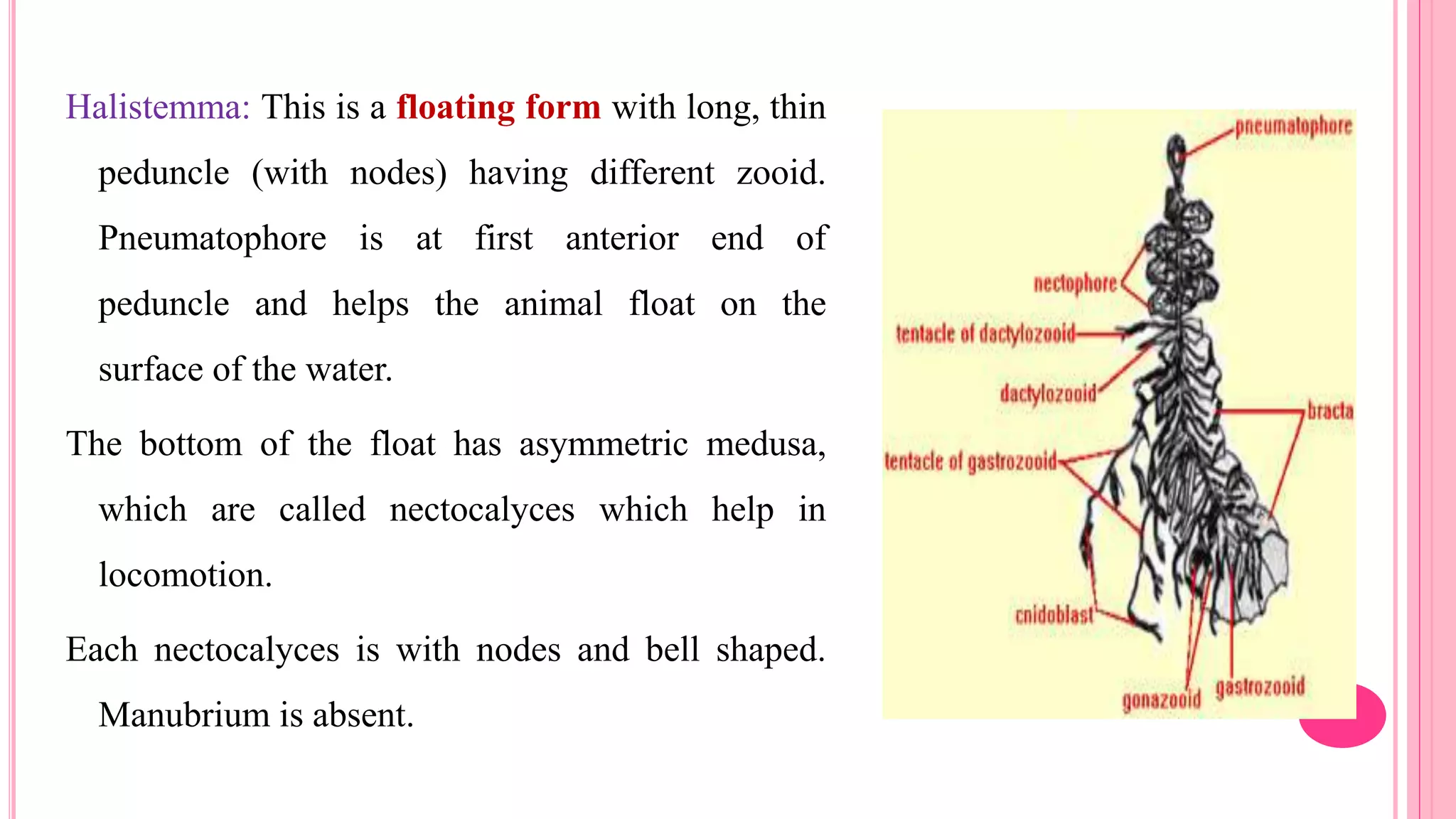
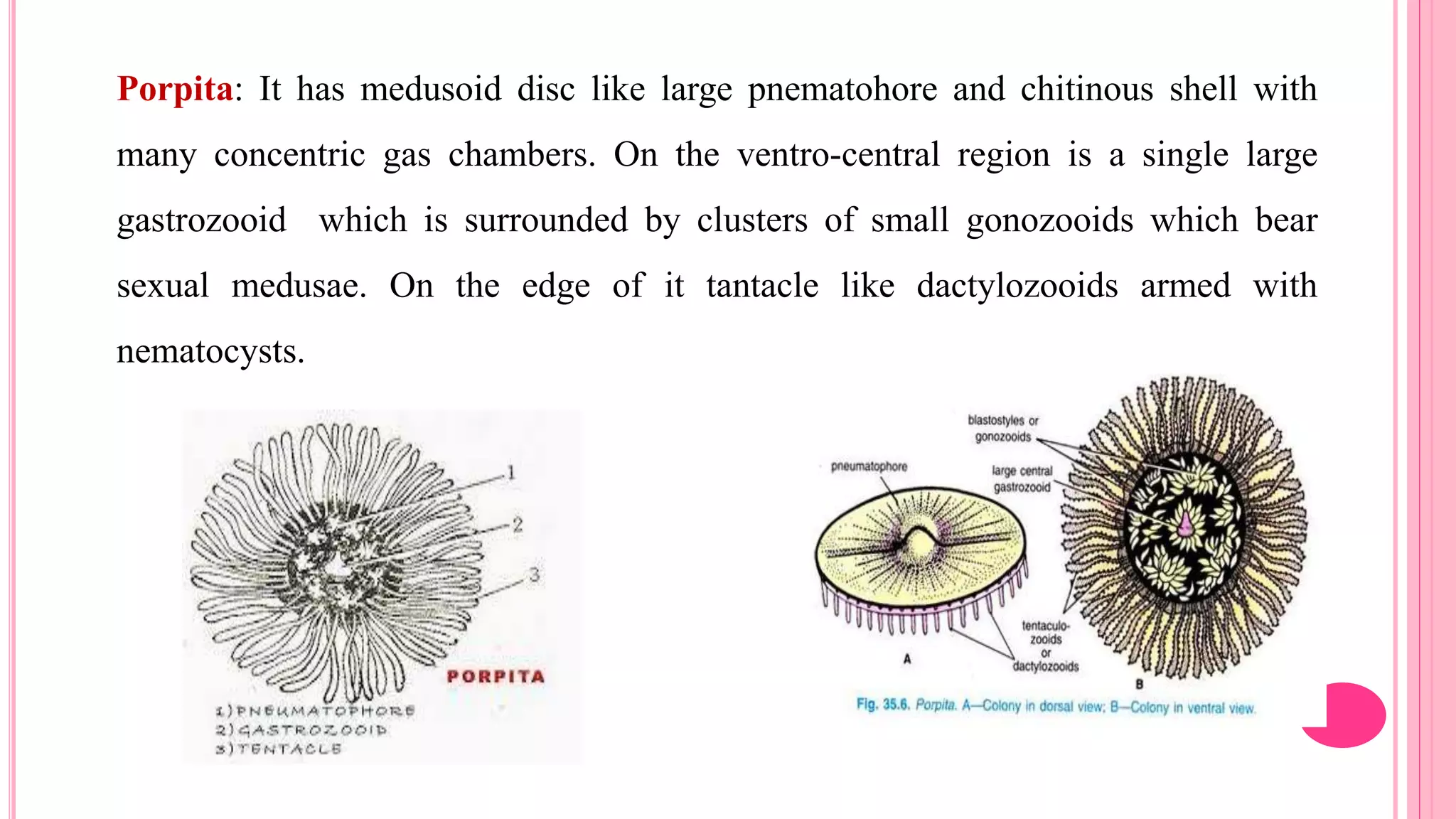
Polymorphism refers to the occurrence of different individual types, or zooids, within the same species that differ in form and function. In hydrozoans, there are commonly polyp and medusa zooids. Notable examples like Physalia, Halistemma, and Porpita exhibit complex polymorphism with specialized zooids for functions like feeding, reproduction, protection, and floating. Polymorphism allows for division of labor and specialization within colonies, conferring evolutionary advantages.