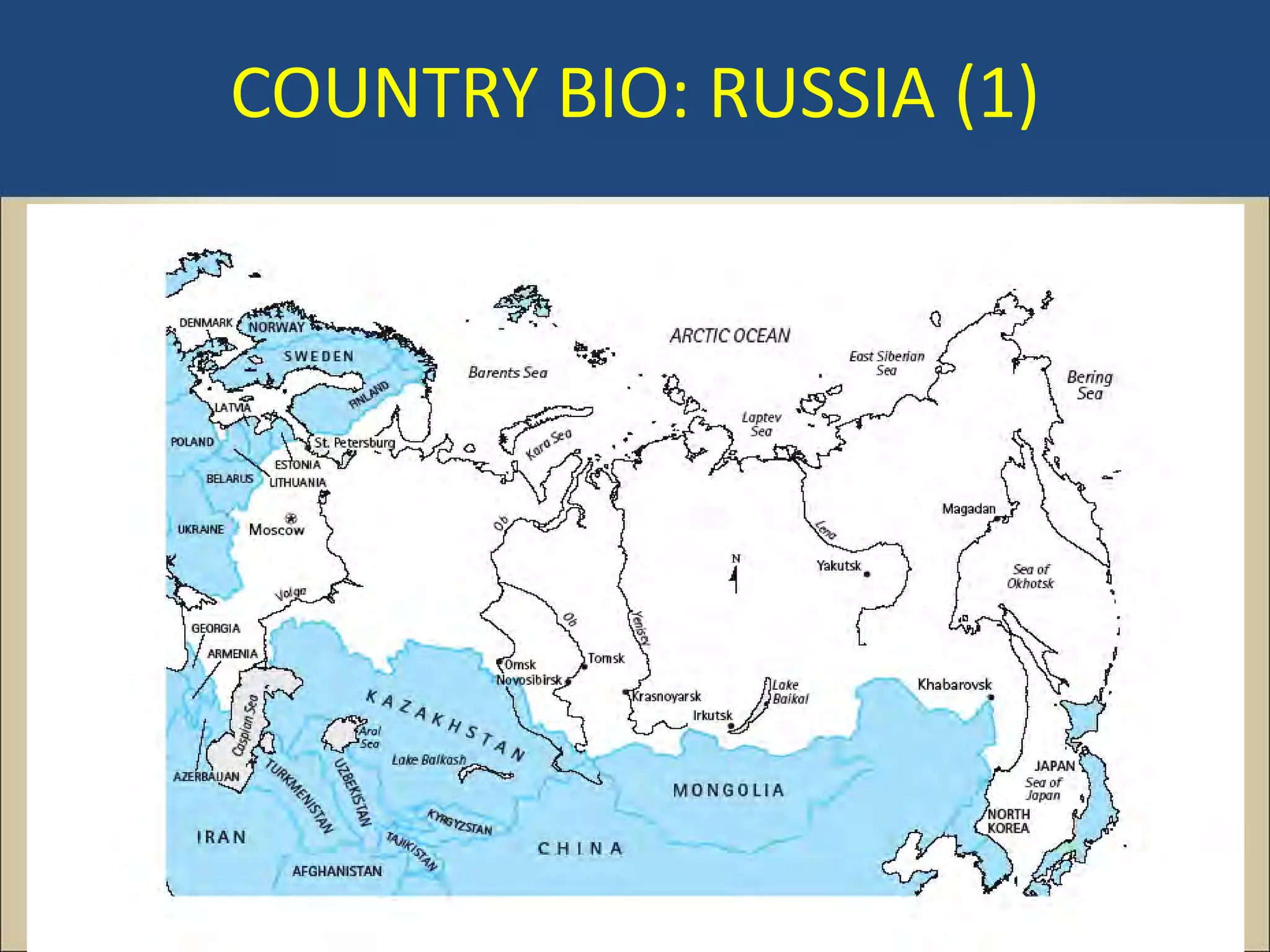
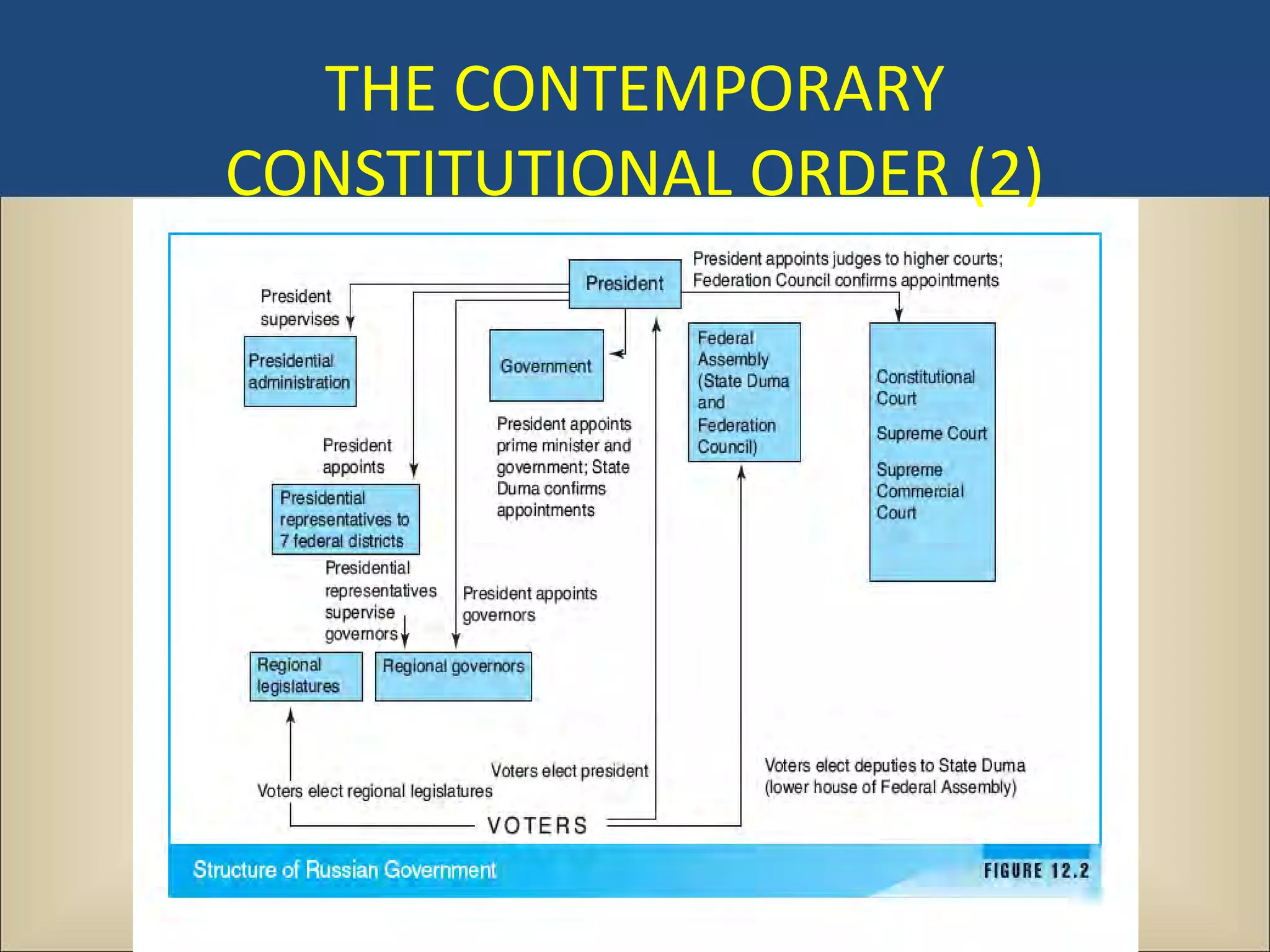
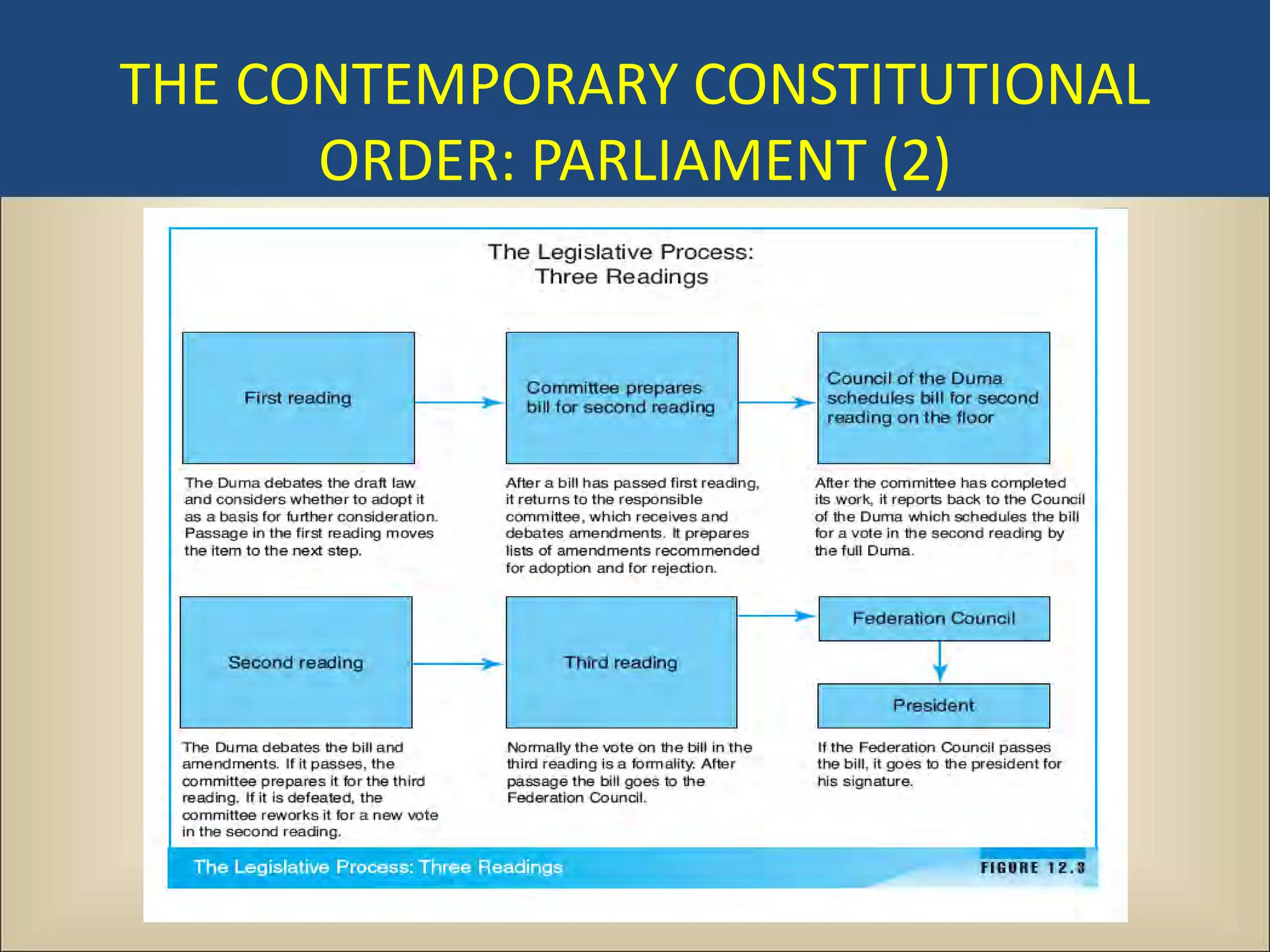
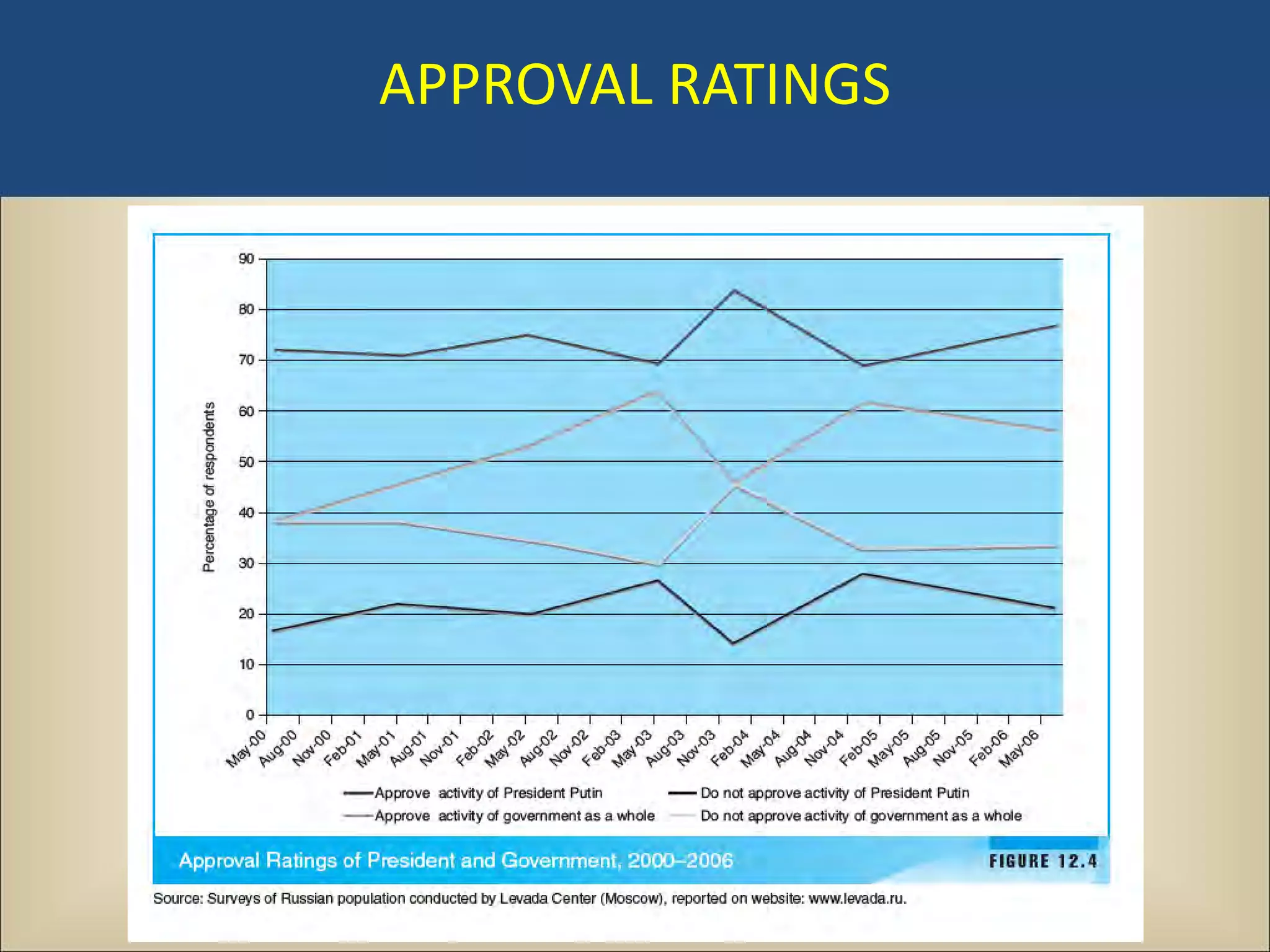
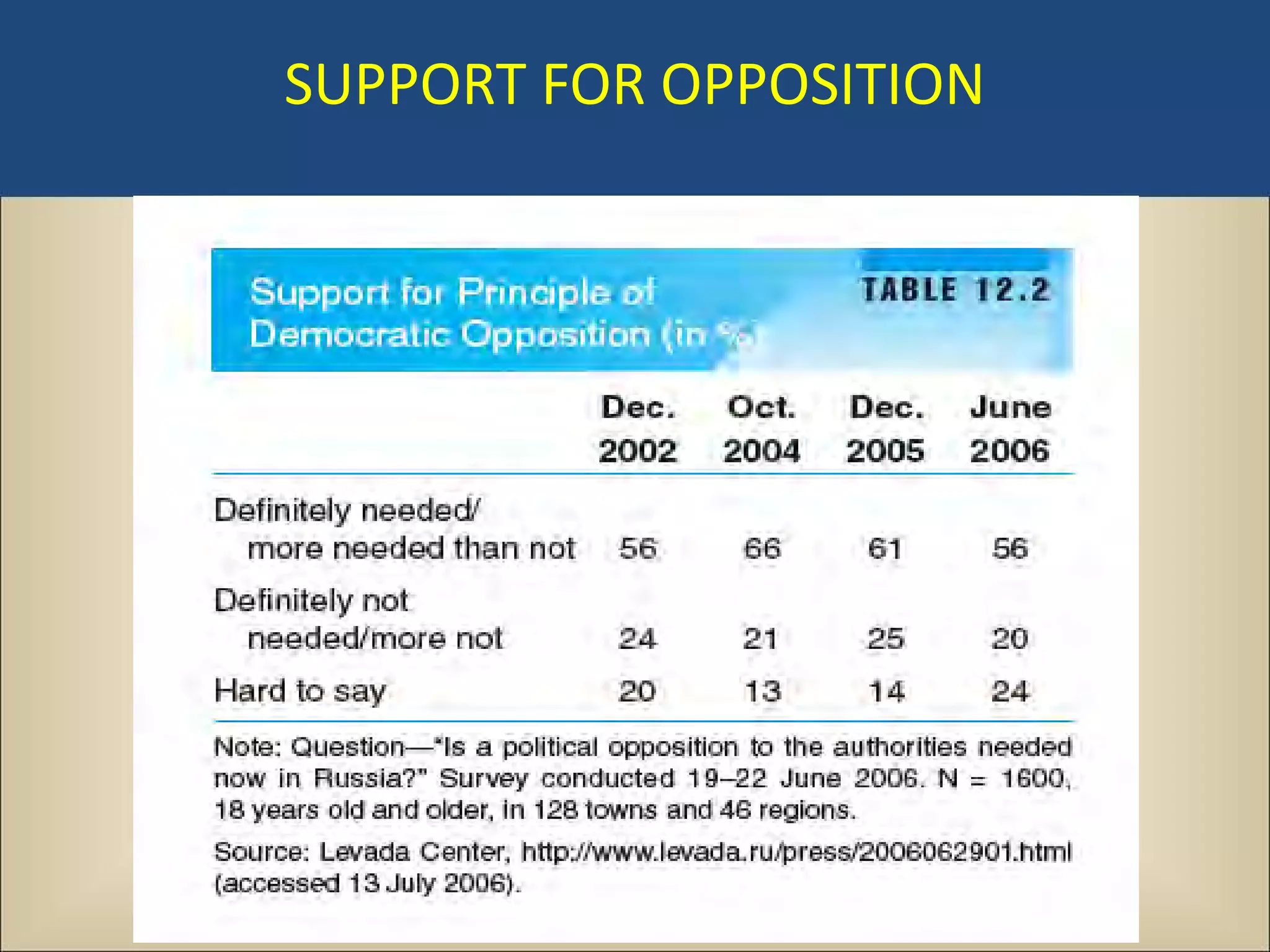
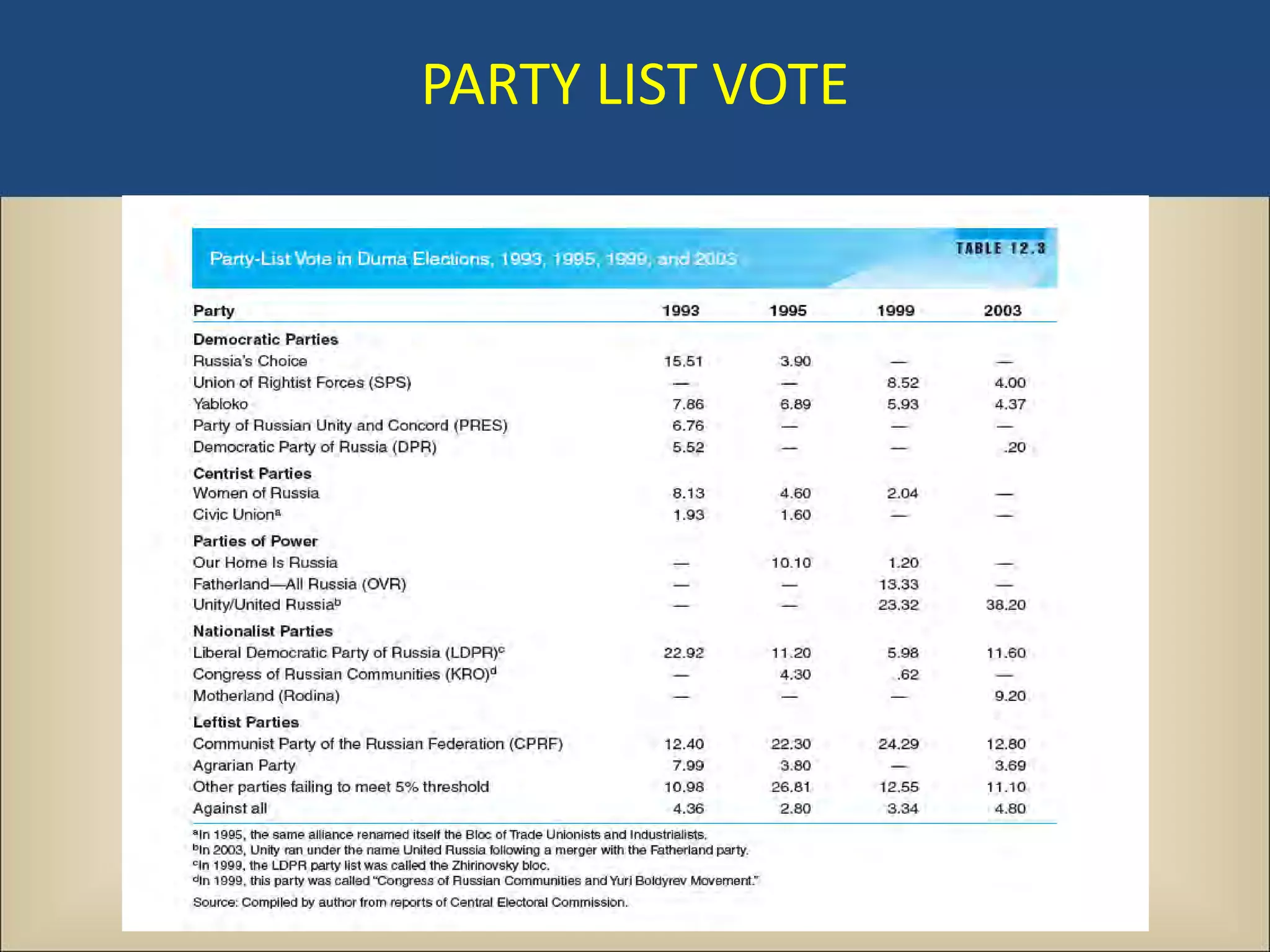
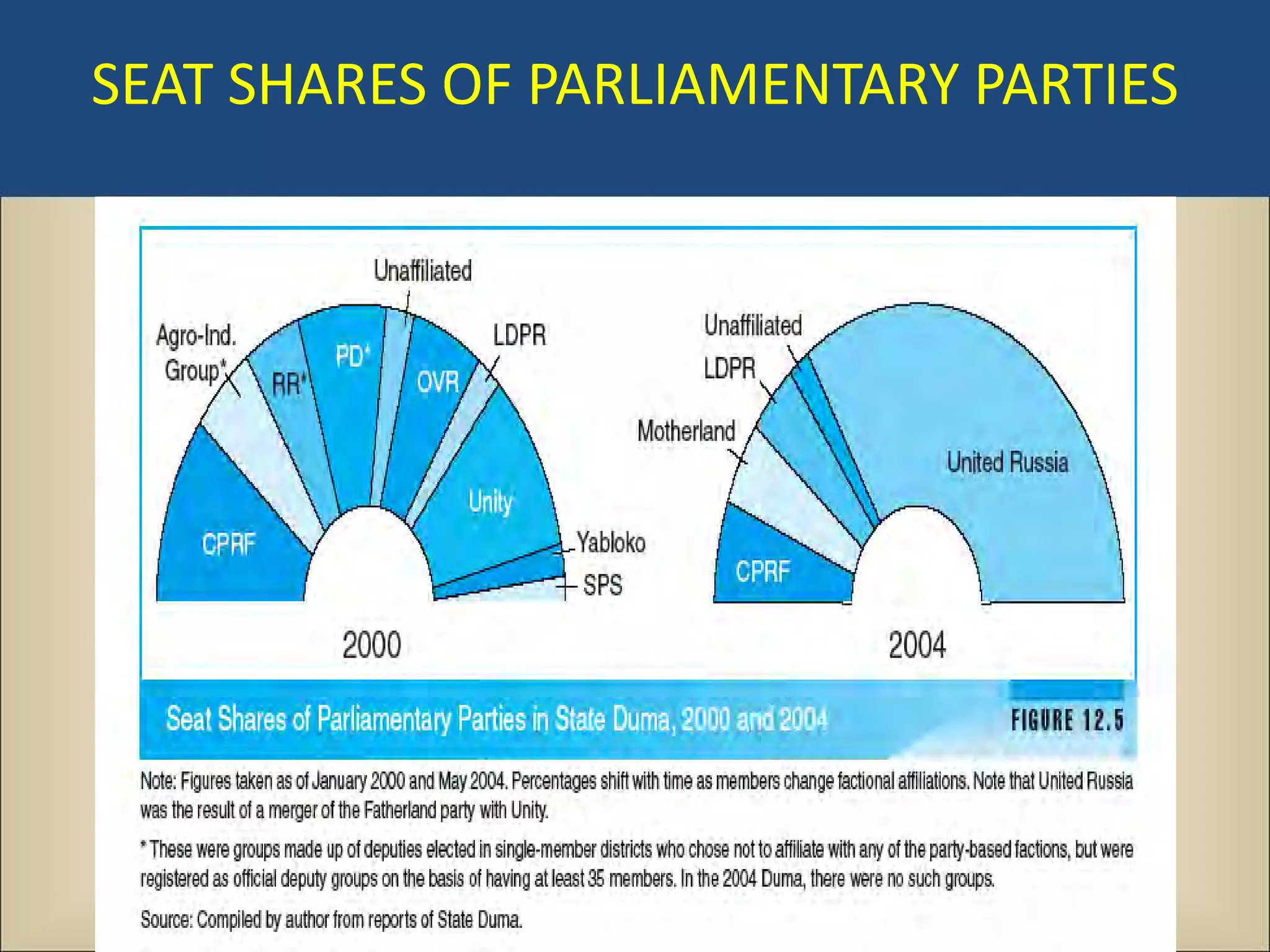
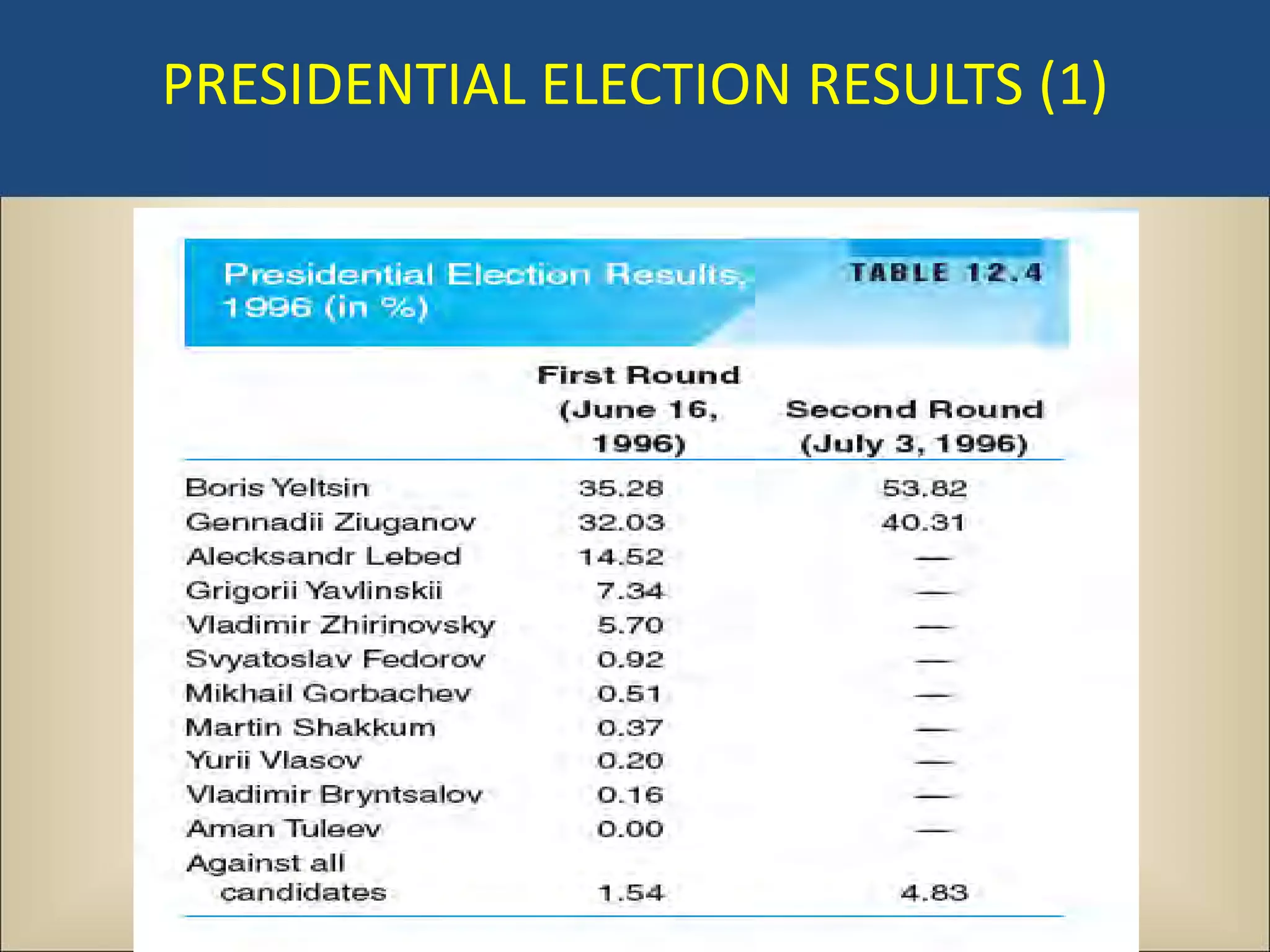
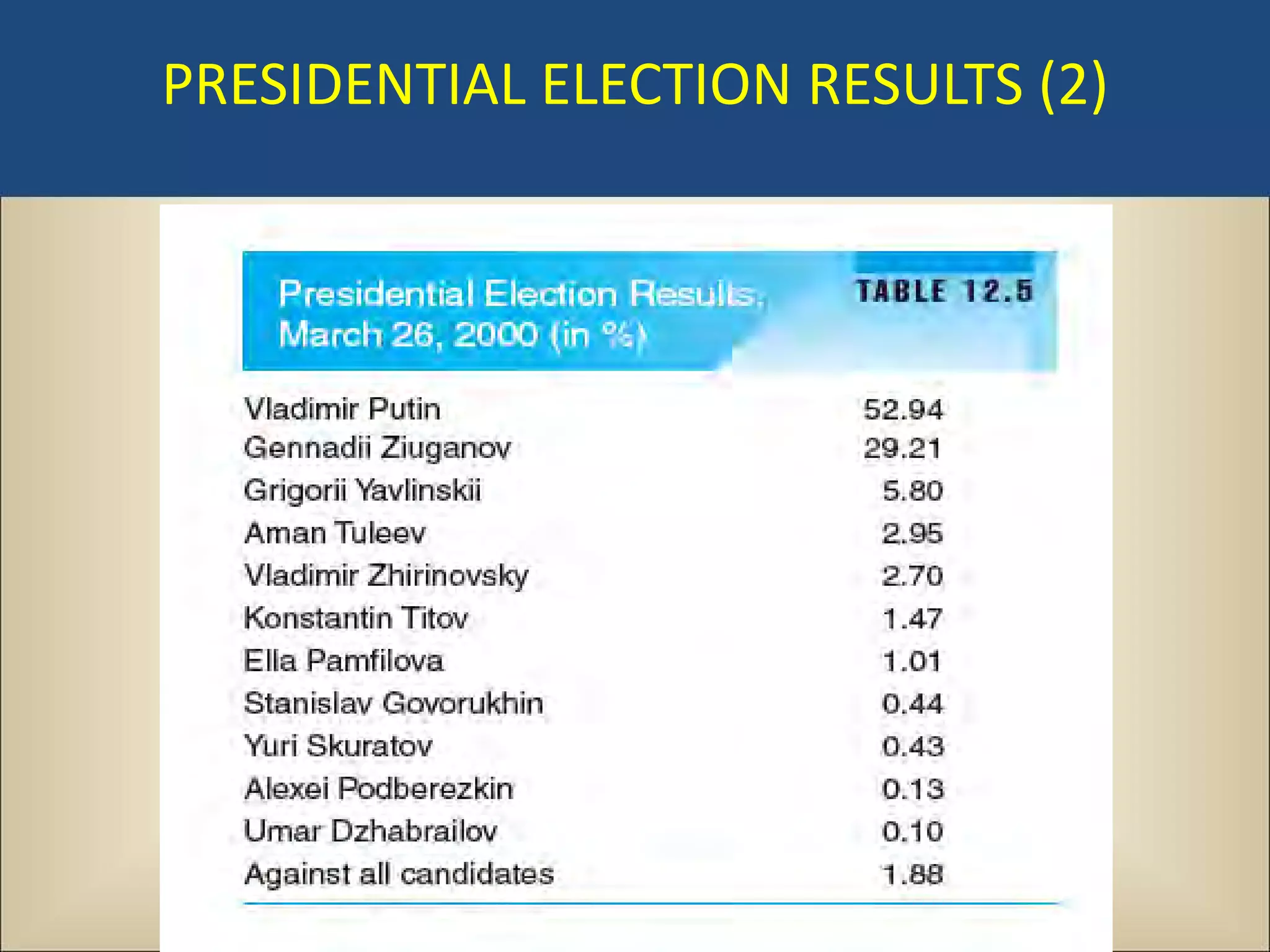
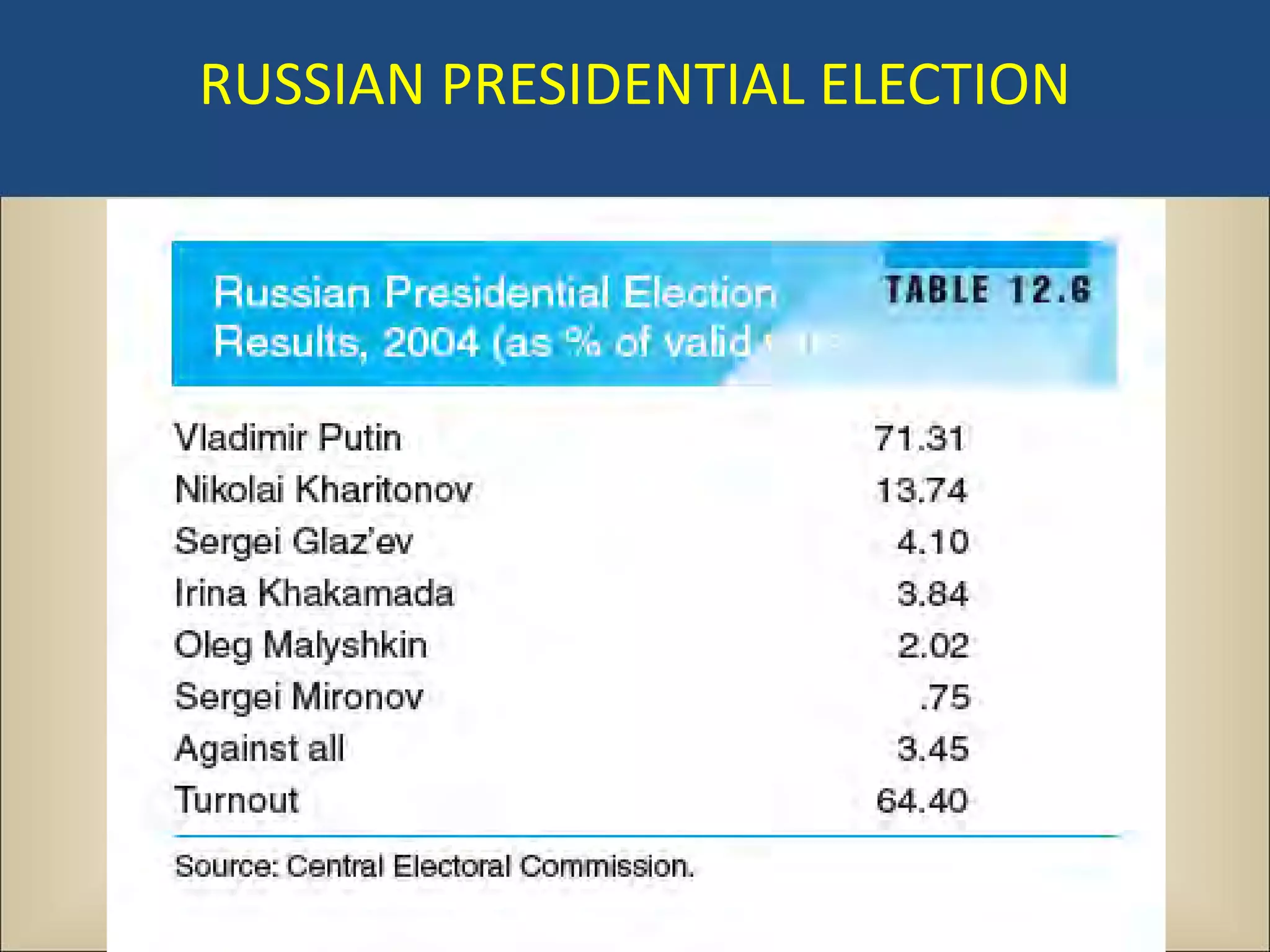
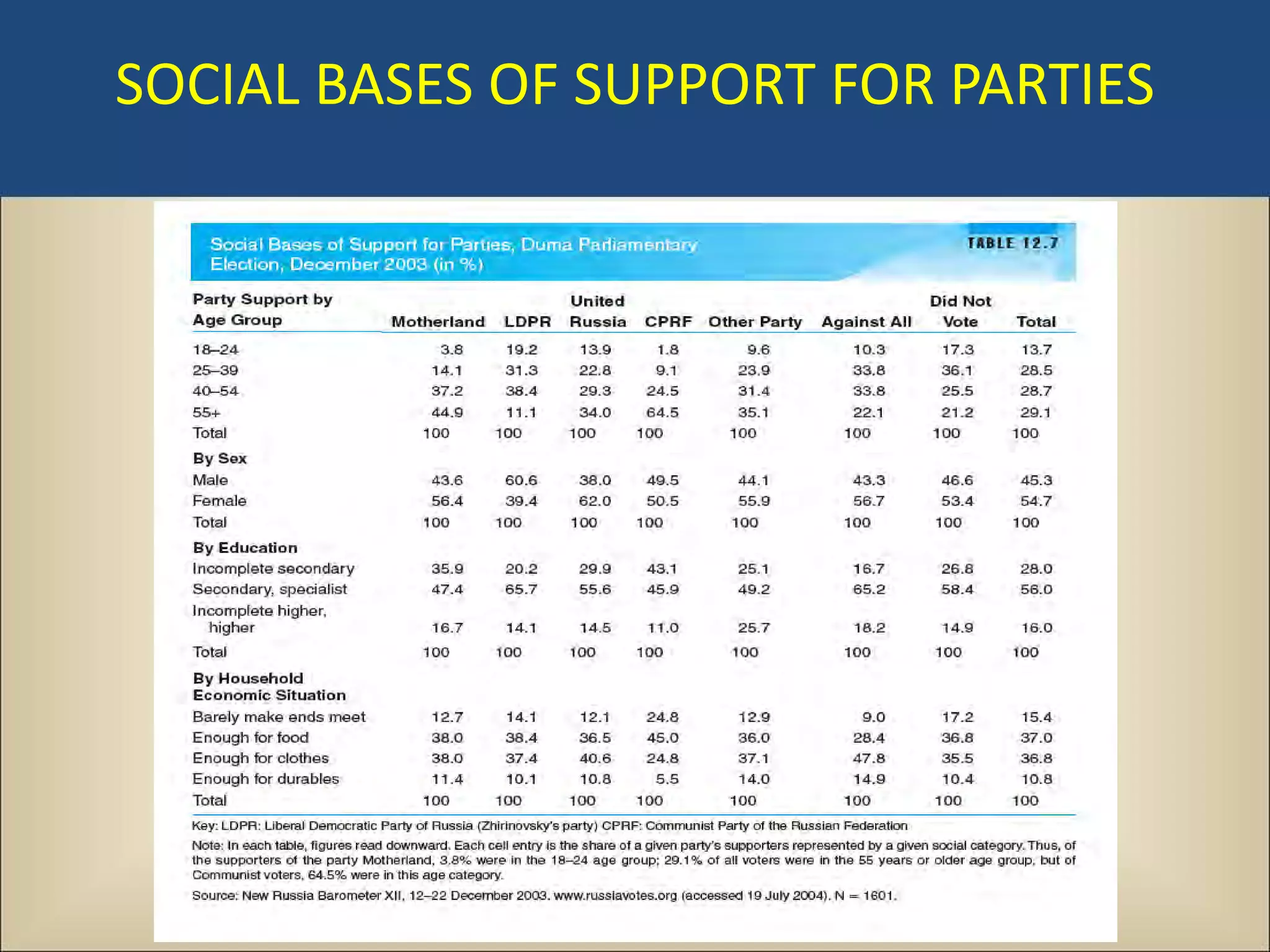
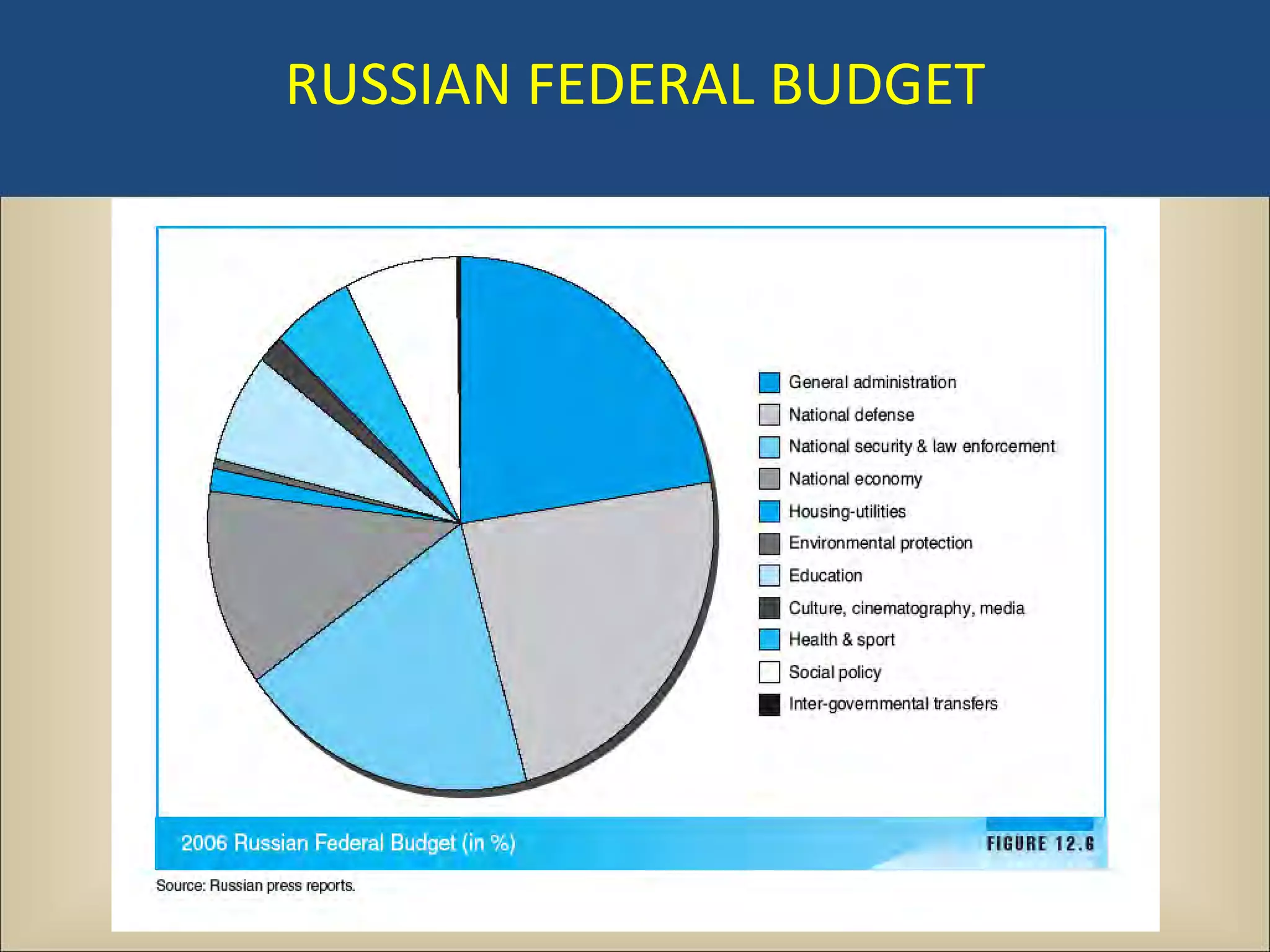
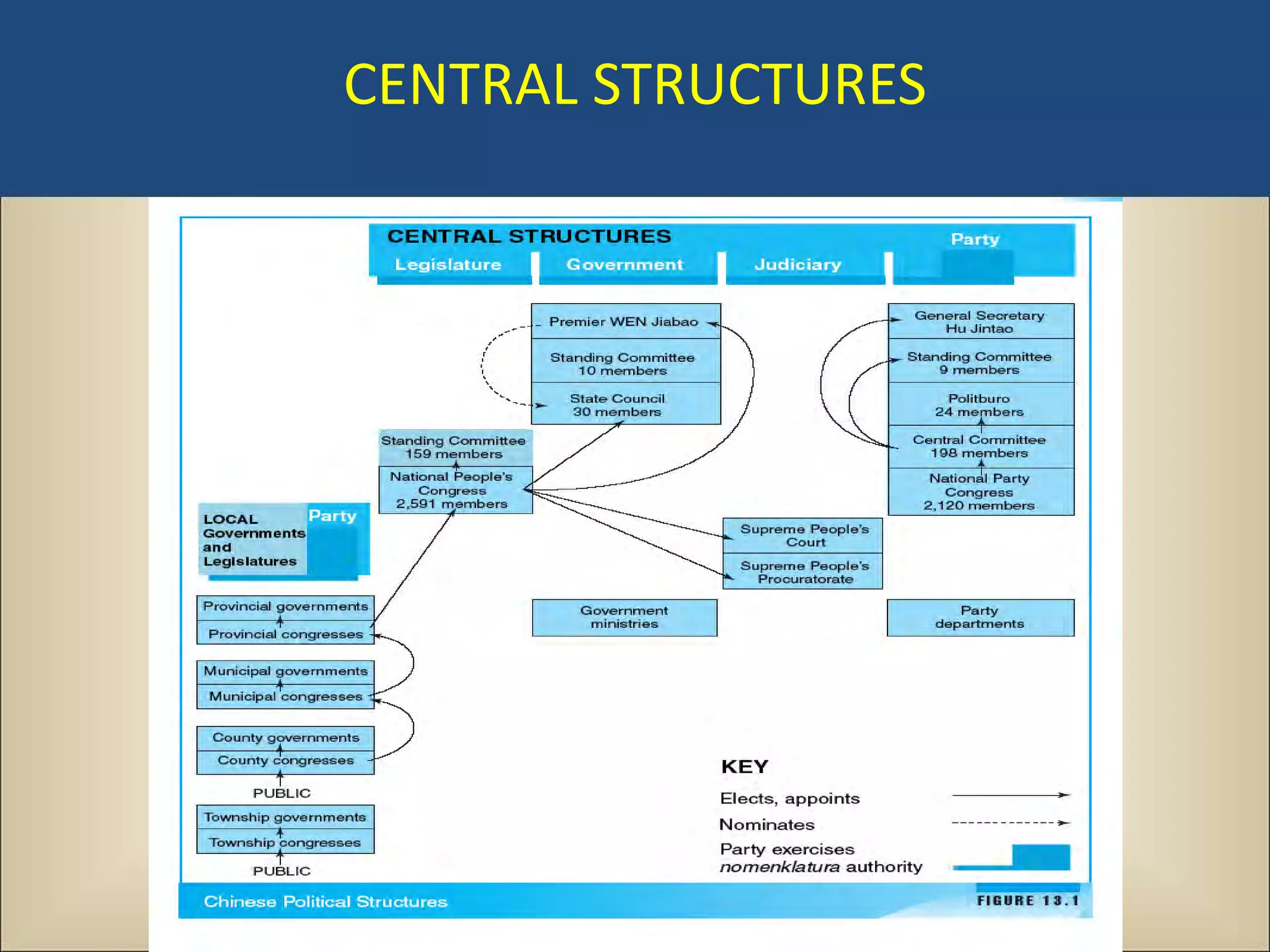
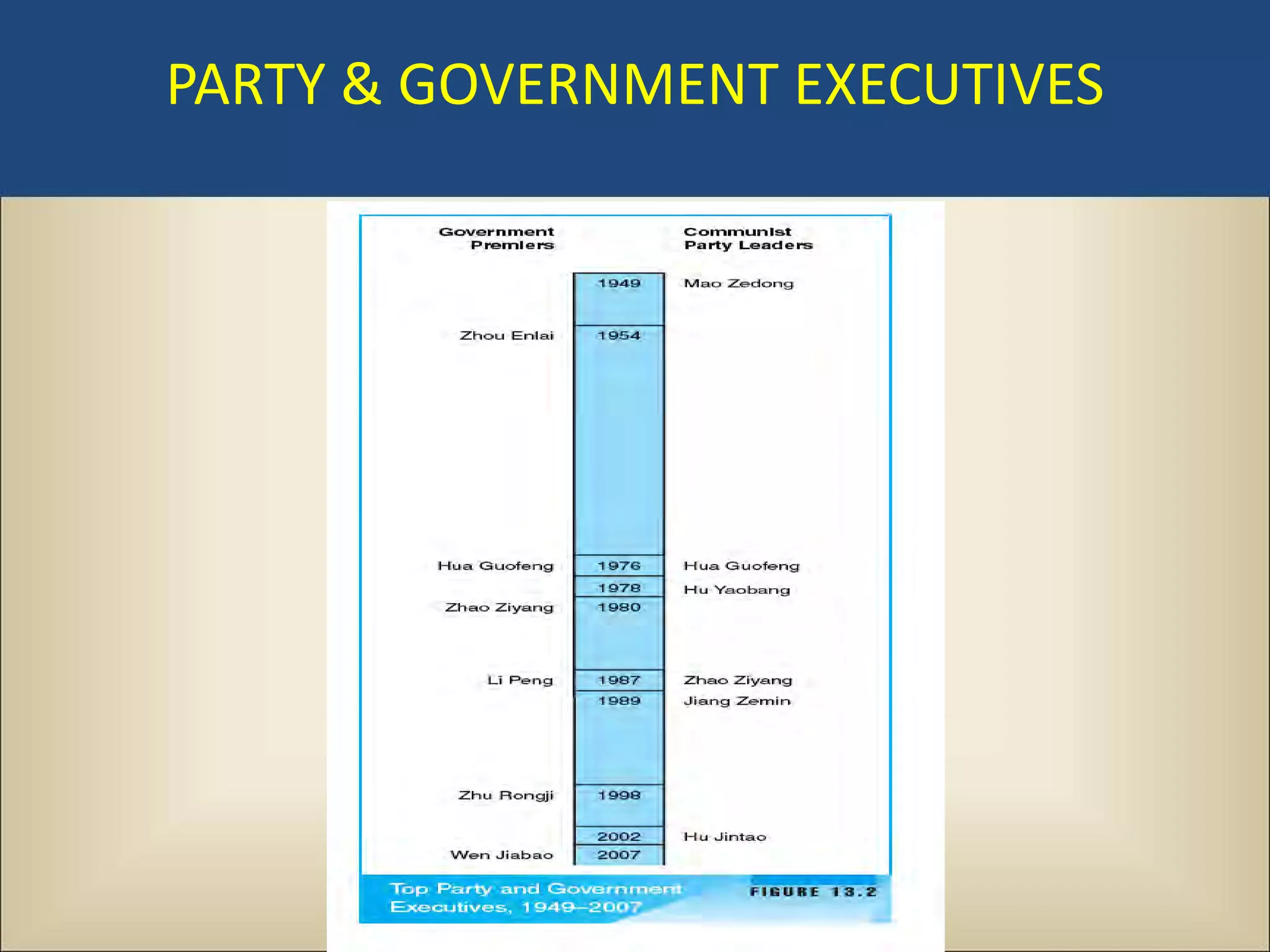
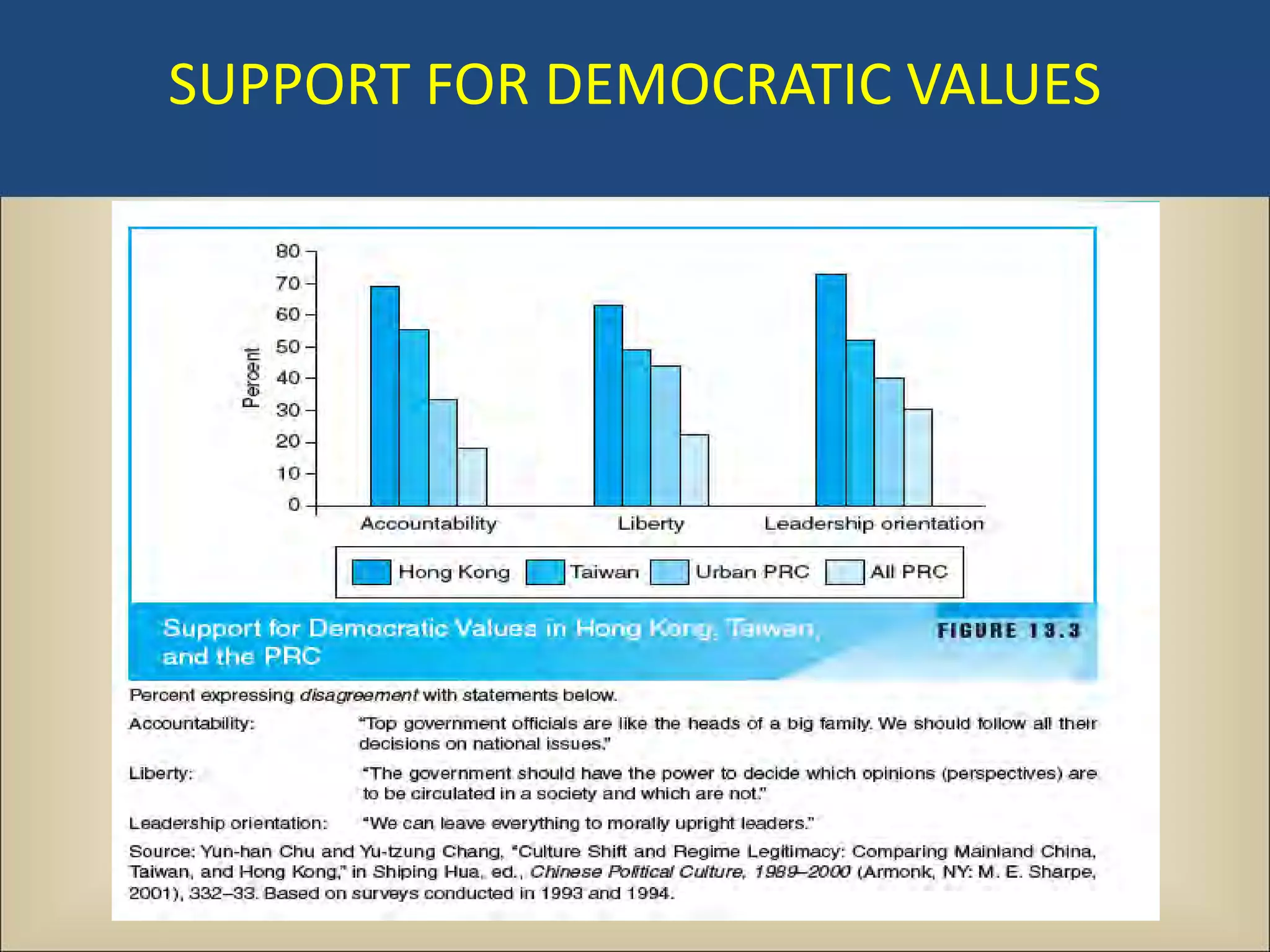
The document outlines a political science lecture on modern world governments focusing on Russia and China, detailing their historical contexts, current policy challenges, and political structures. It highlights Russia's attempts to rebuild state power under Putin, addressing issues like corruption, demographics, and political culture, while China's challenges include economic growth, political corruption, and social conditions within its party-state structure. Both countries show complex relationships between state authority and citizen participation, alongside issues of accountability and governance.