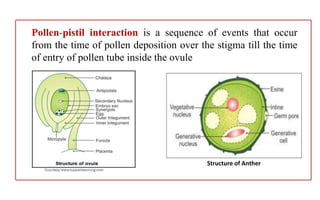
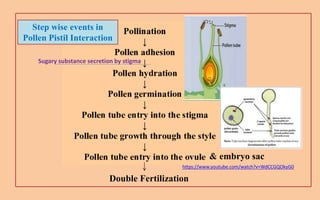
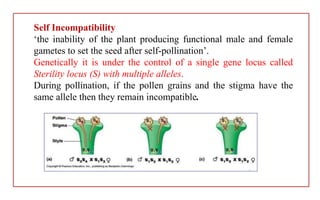
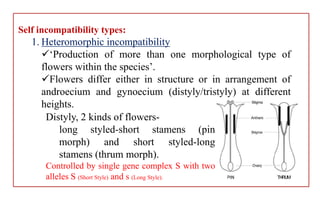
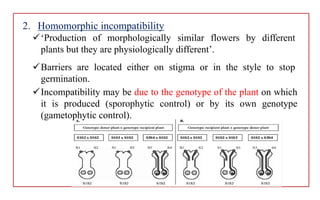
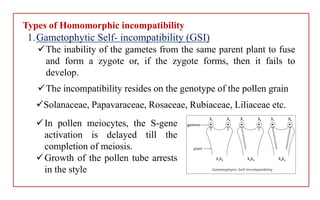
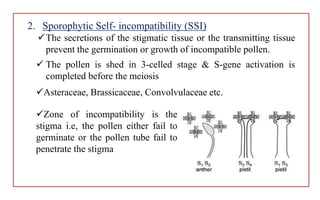
The document discusses pollen-pistil interaction, detailing the sequence of events from pollen deposition to fertilization, including concepts of sexual compatibility and incompatibility. It defines self-incompatibility, its genetic control, and types such as heteromorphic and homomorphic incompatibility, as well as their mechanisms. Additionally, it explores methods for overcoming incompatibility, emphasizing the importance of self-incompatibility in maintaining genetic diversity and plant vigor.