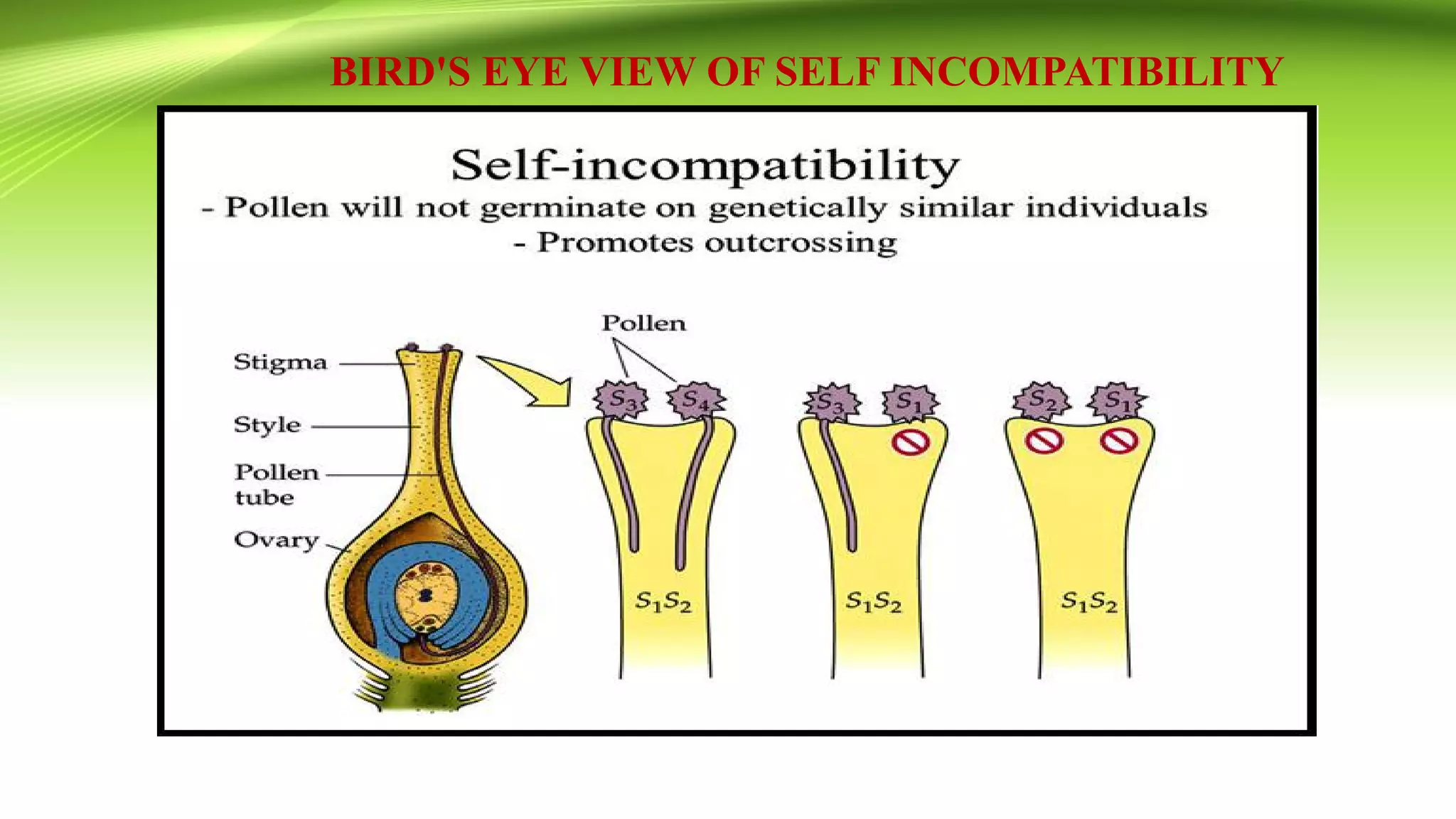
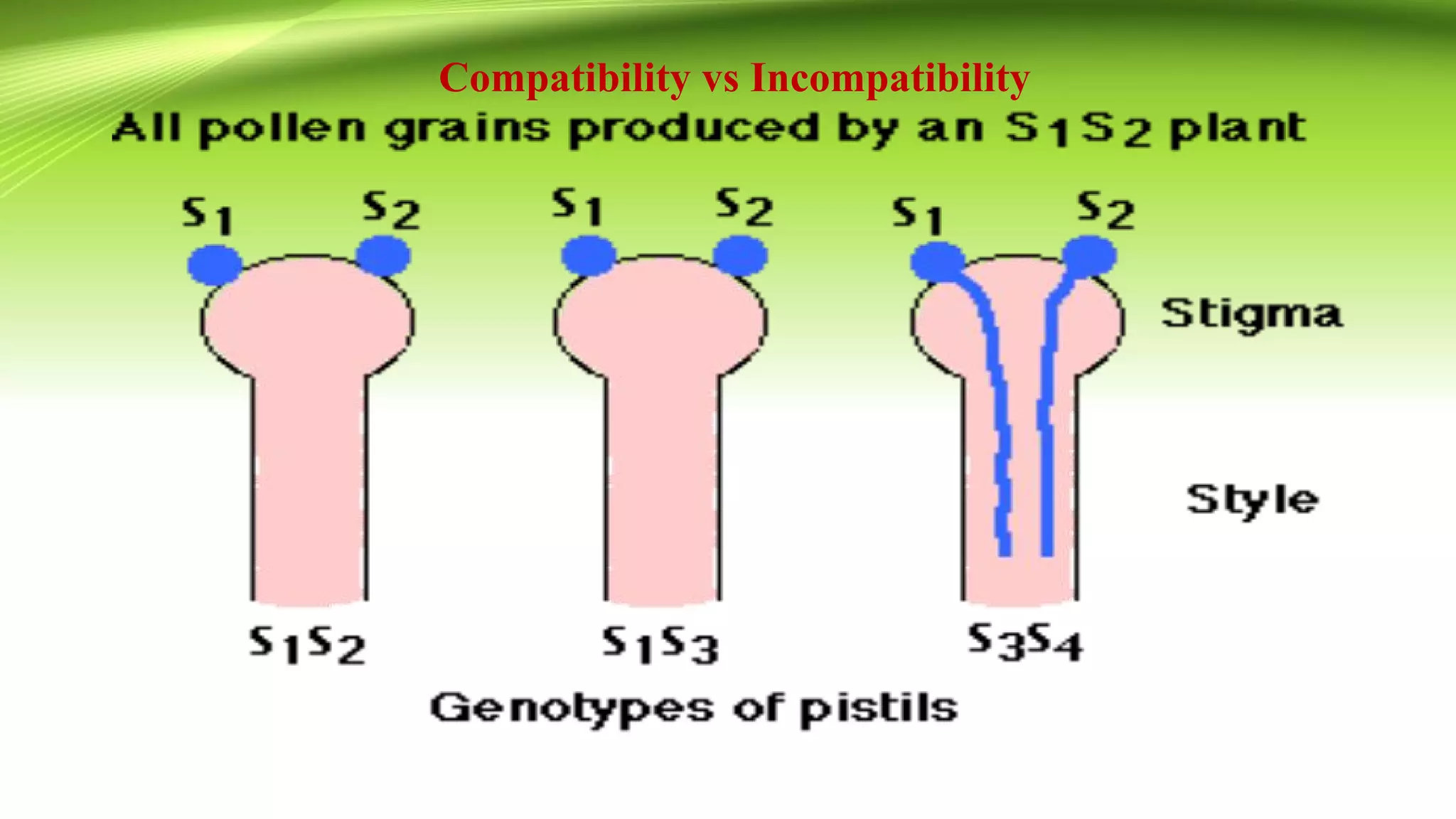
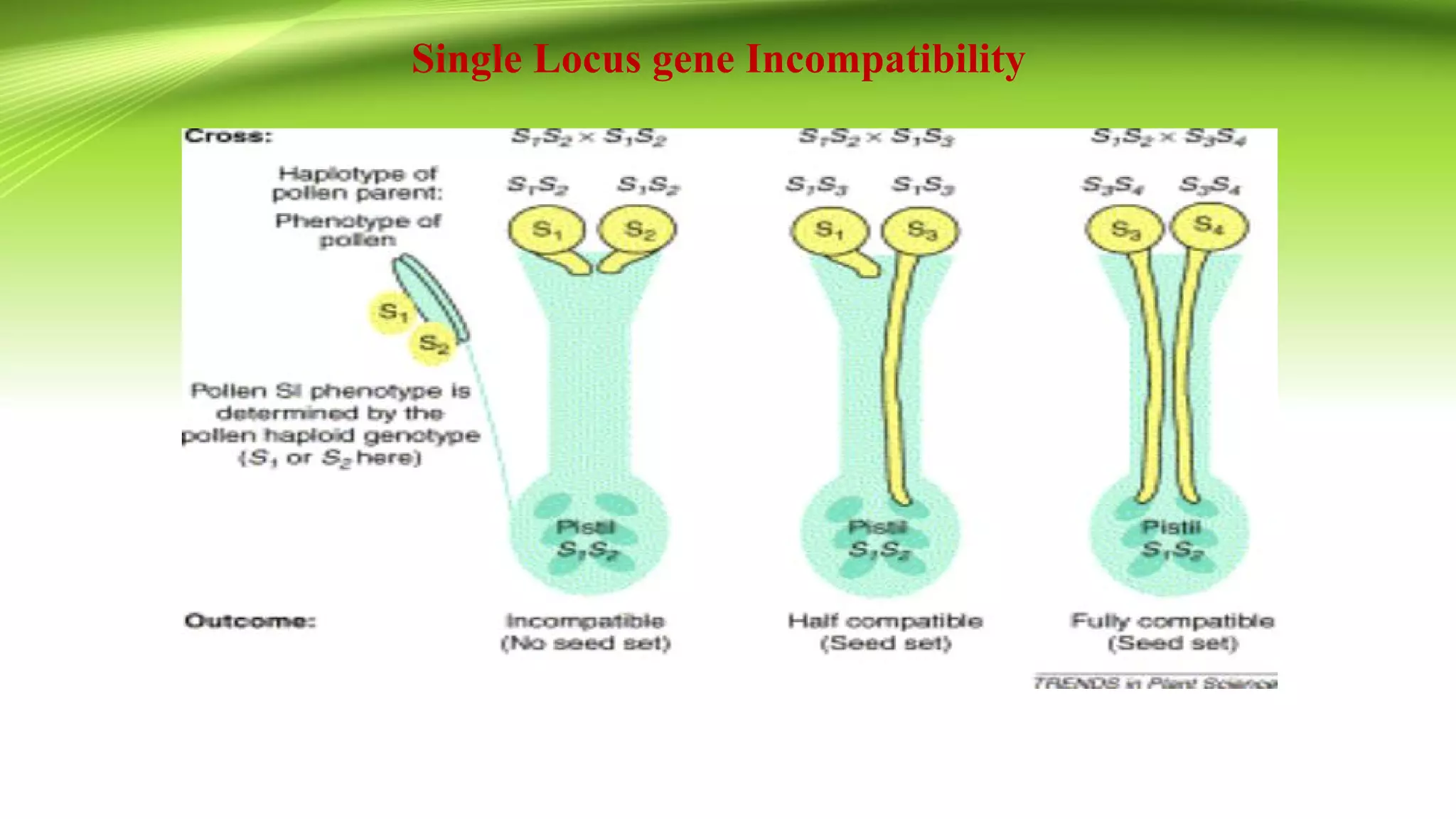
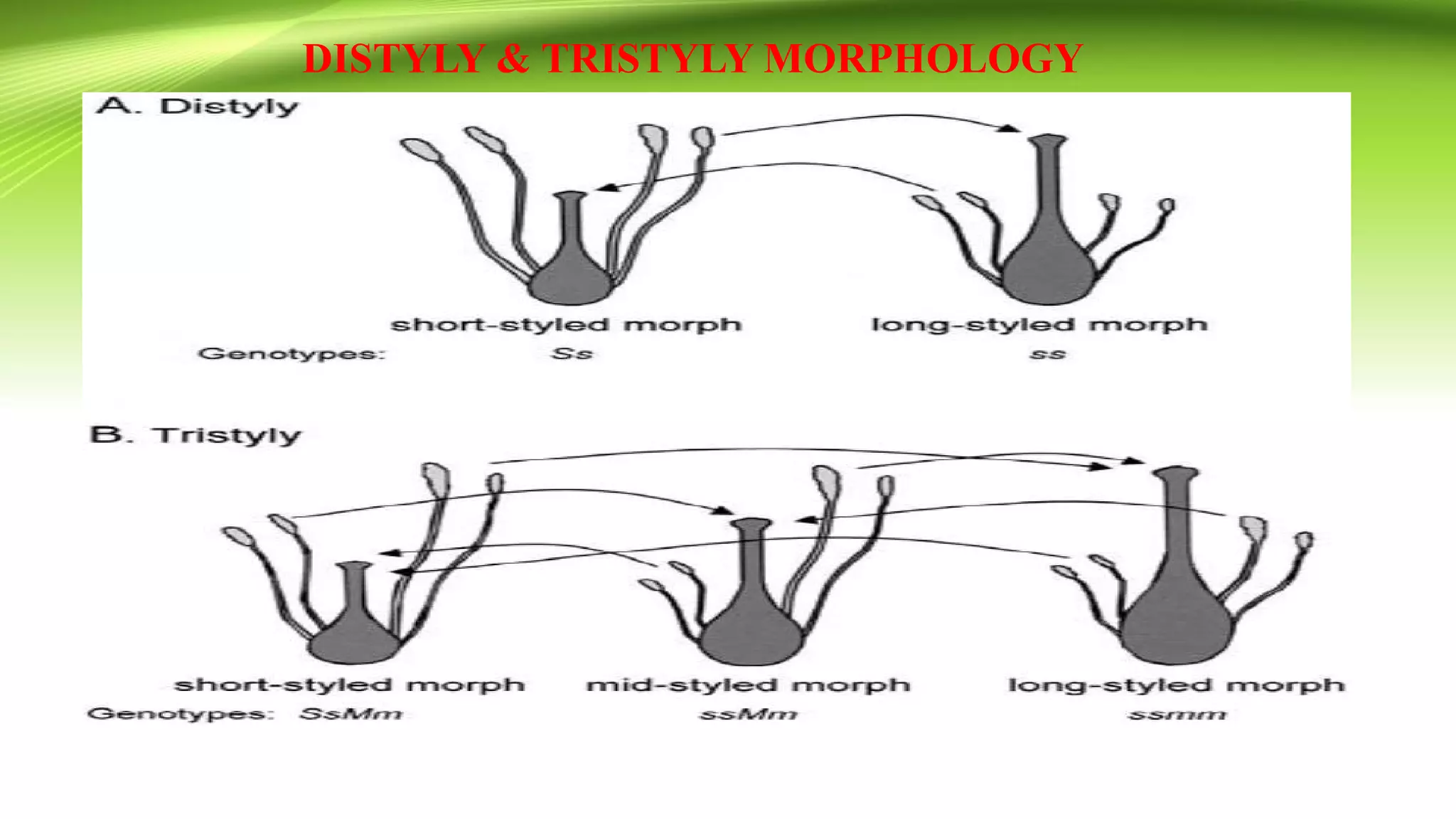
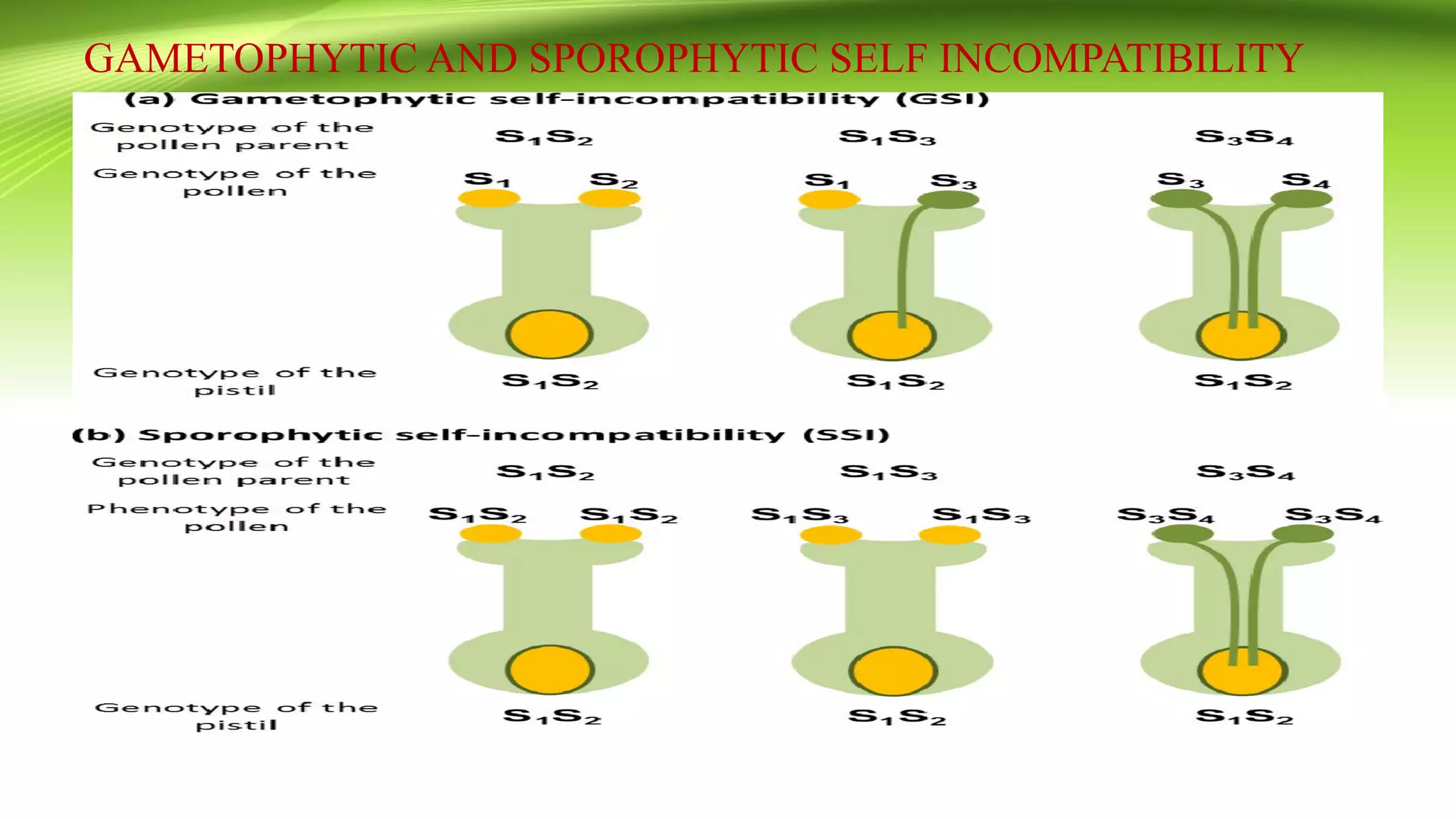
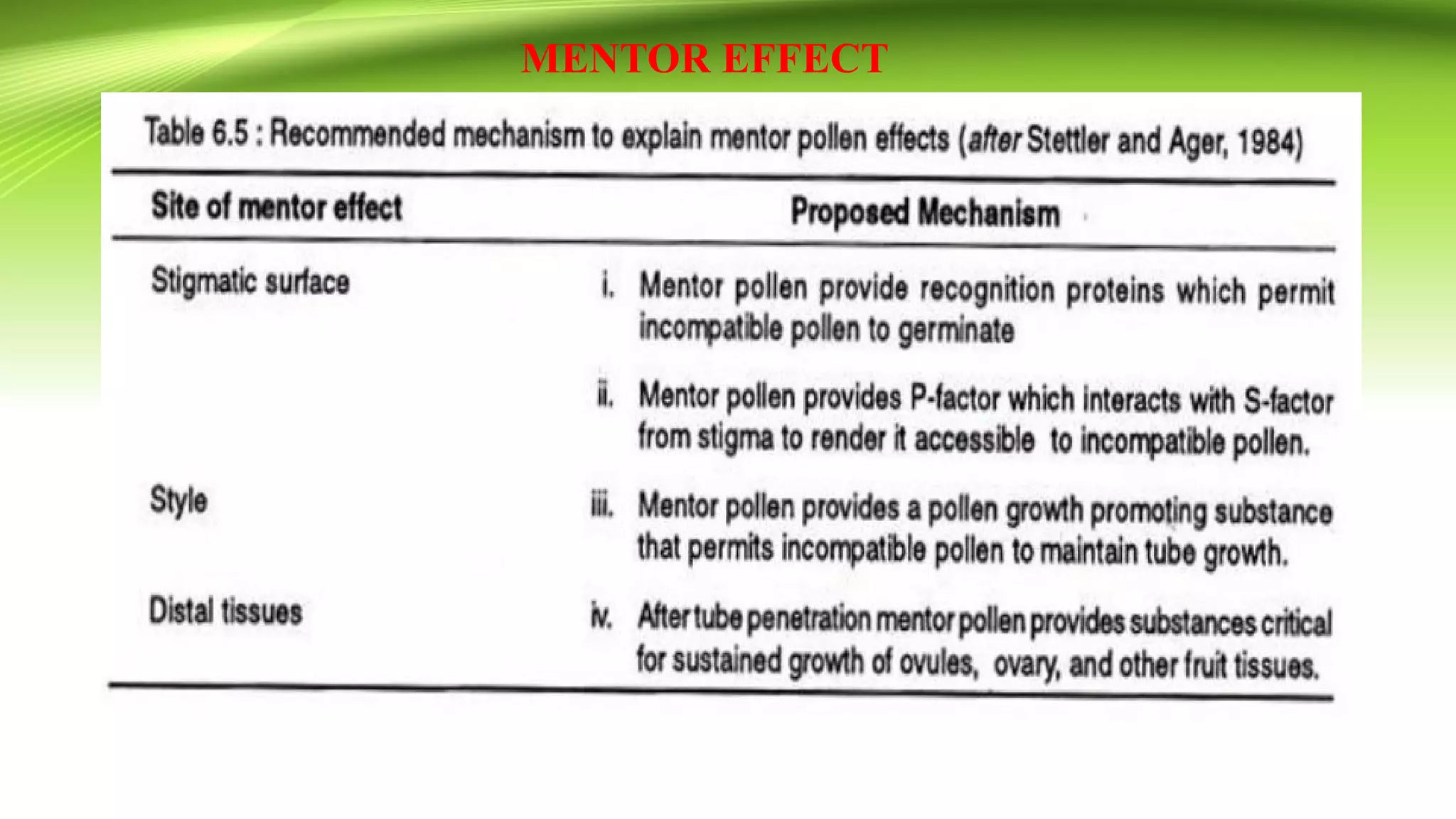
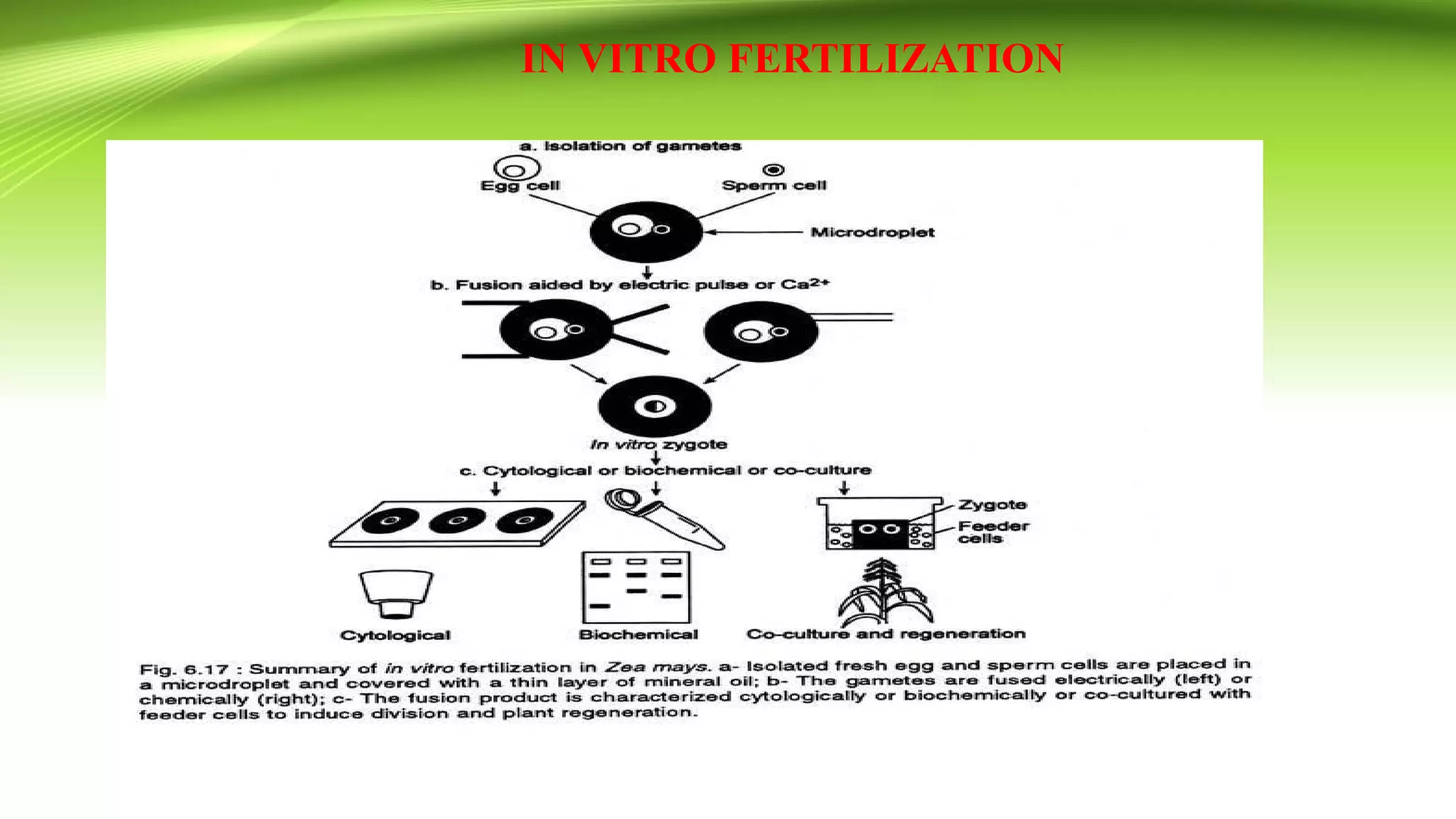
The document discusses self-incompatibility in flowering plants, a genetic mechanism that prevents self-fertilization to encourage outcrossing and maintain genetic diversity. It describes various types of self-incompatibility, including gametophytic and sporophytic systems, as well as methods to overcome these reproductive barriers. The significance of understanding self-incompatibility is emphasized in the context of agricultural breeding and crop production enhancements.