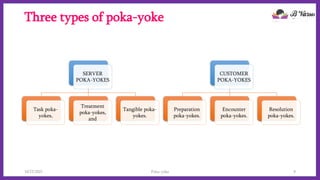
Poka-yoke is a Japanese quality control technique designed to prevent human errors in various processes by implementing mechanisms that help operators avoid mistakes and defects. Originating from Toyota, it encompasses principles such as elimination, prevention, detection, and others to enhance productivity and reduce errors across industries. The technique includes various types of poka-yoke systems tailored to specific tasks and customer interactions, ultimately benefiting businesses by improving profitability and efficiency.