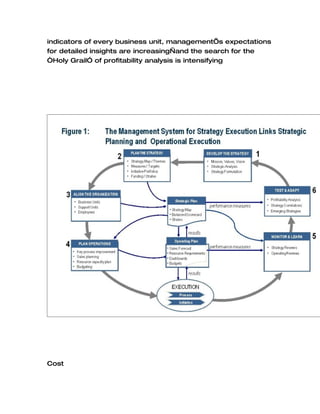
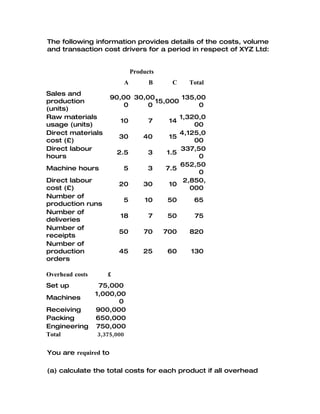
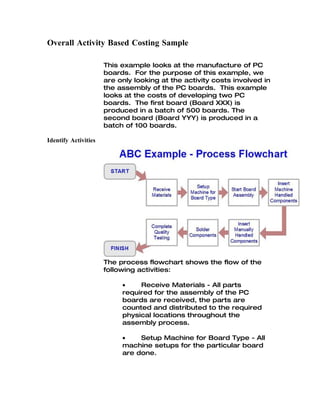
Activity-based costing (ABC) is a costing model that assigns indirect costs to products based on actual consumption, enabling organizations to identify unprofitable products and make informed pricing decisions. Developed from traditional costing methods in the 1970s and 1980s, ABC focuses on cost drivers to improve accuracy in cost allocation and has applications beyond manufacturing, including financial institutions. Despite its utility, ABC can be complex and costly, leading to the emergence of lean accounting methods that seek to streamline cost control.