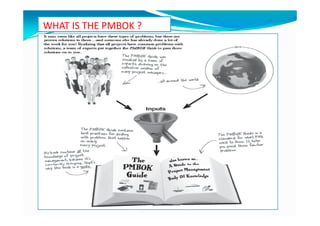
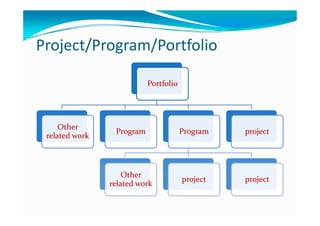
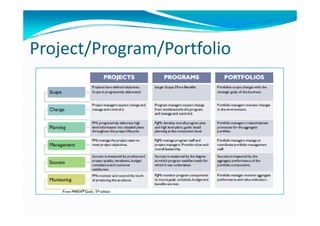
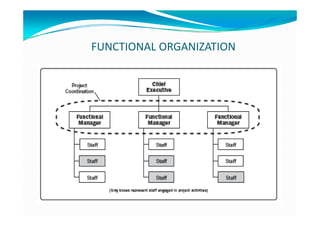
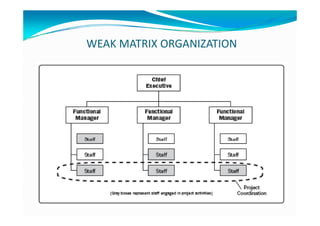
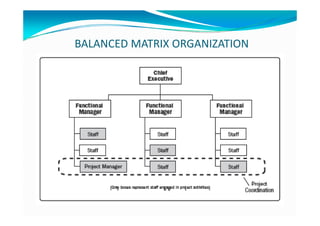
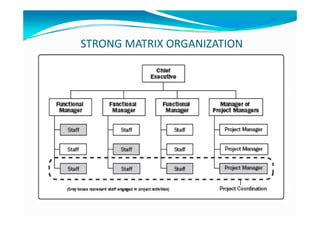
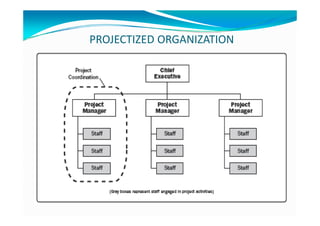
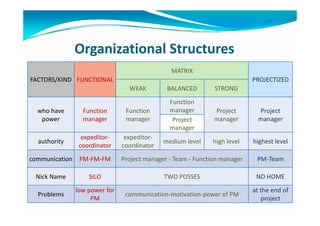
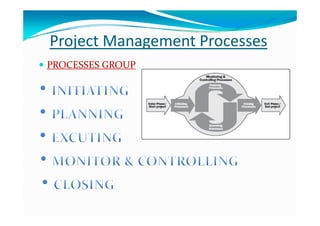
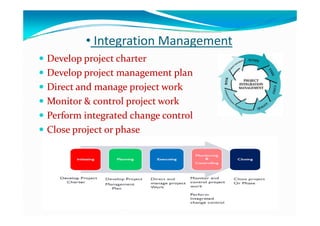
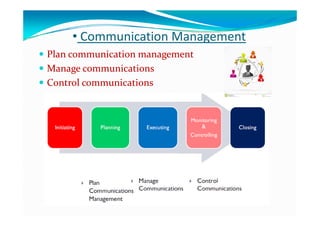
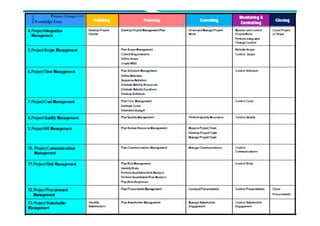
The document provides an overview of project management certification (PMP) and related concepts. It discusses that the PMP is issued by PMI and requires passing an exam on the contents of the PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge). The PMBOK defines standard processes, terminology and guidelines for project management. It also summarizes the differences between projects, programs and operations, and outlines some key aspects of project management including integration, scope, time, cost and quality management processes.