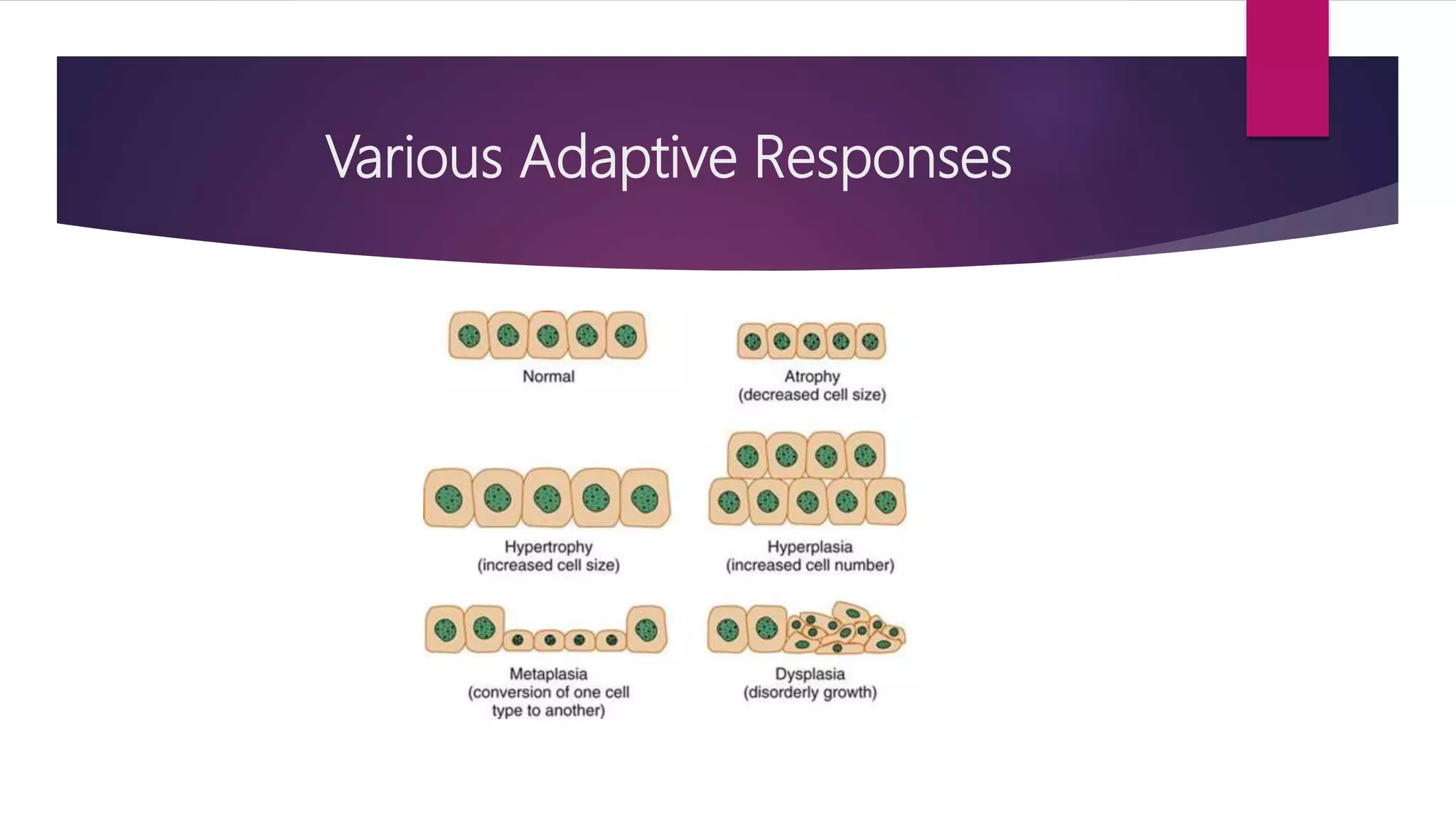
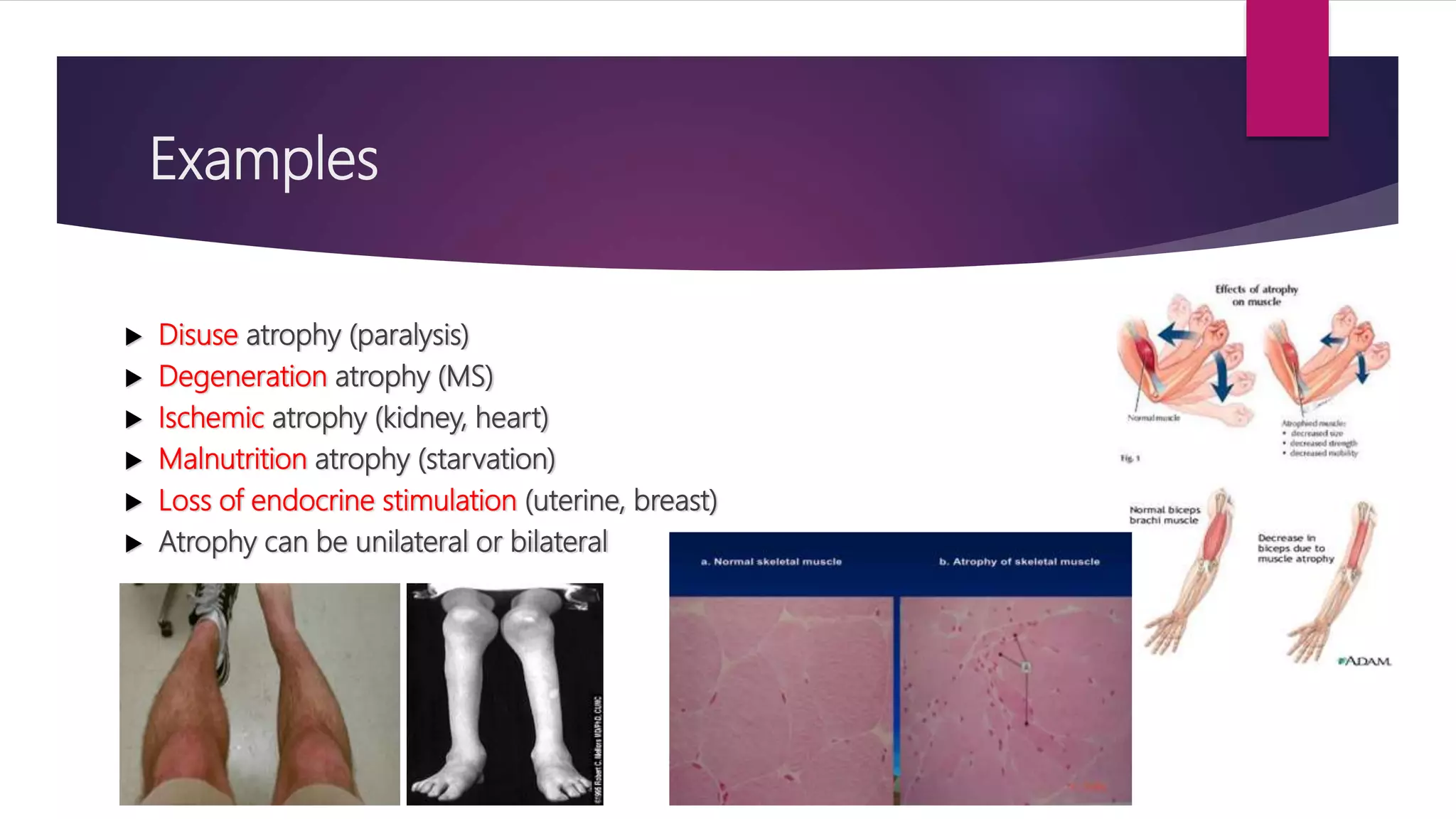
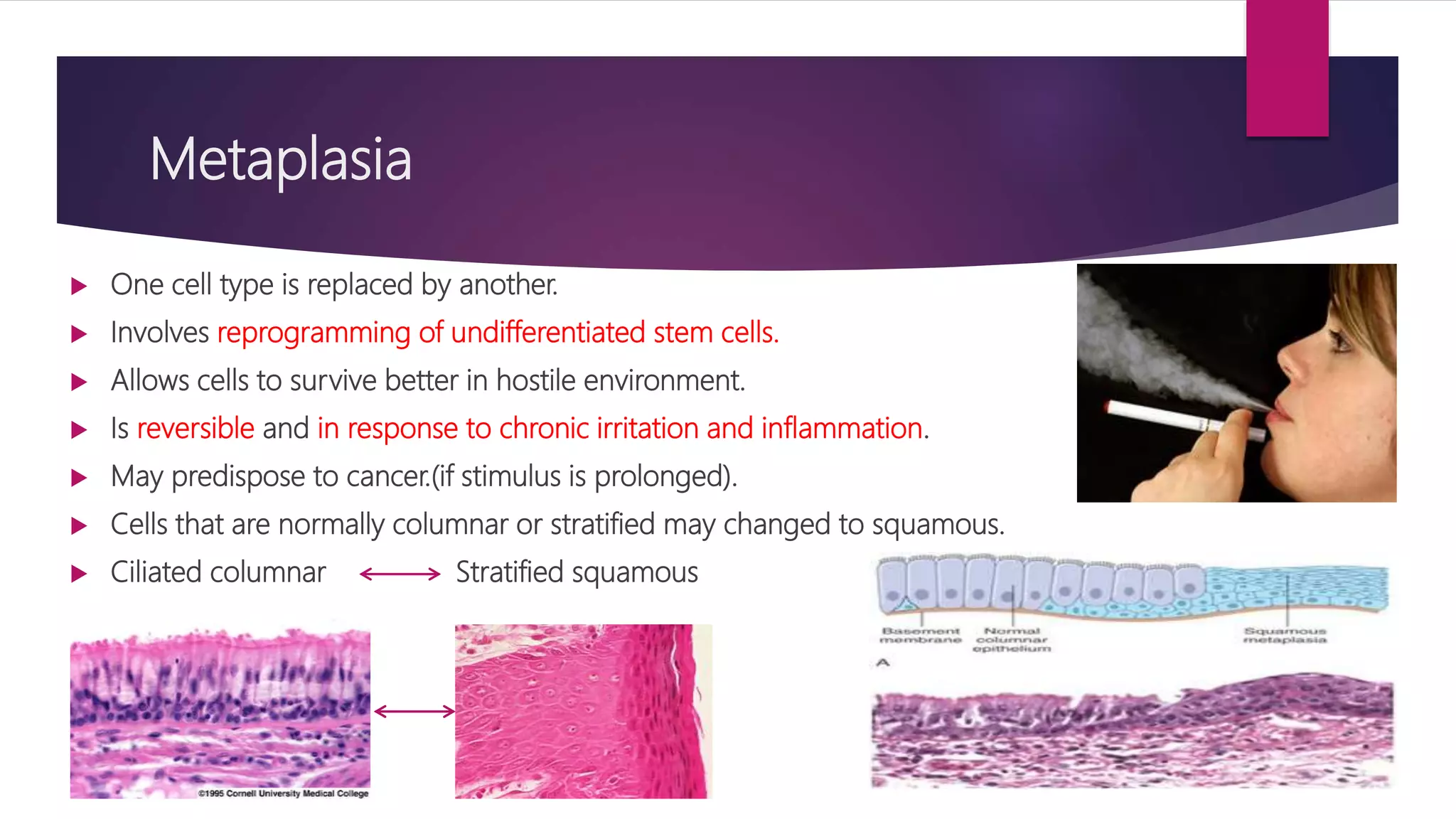
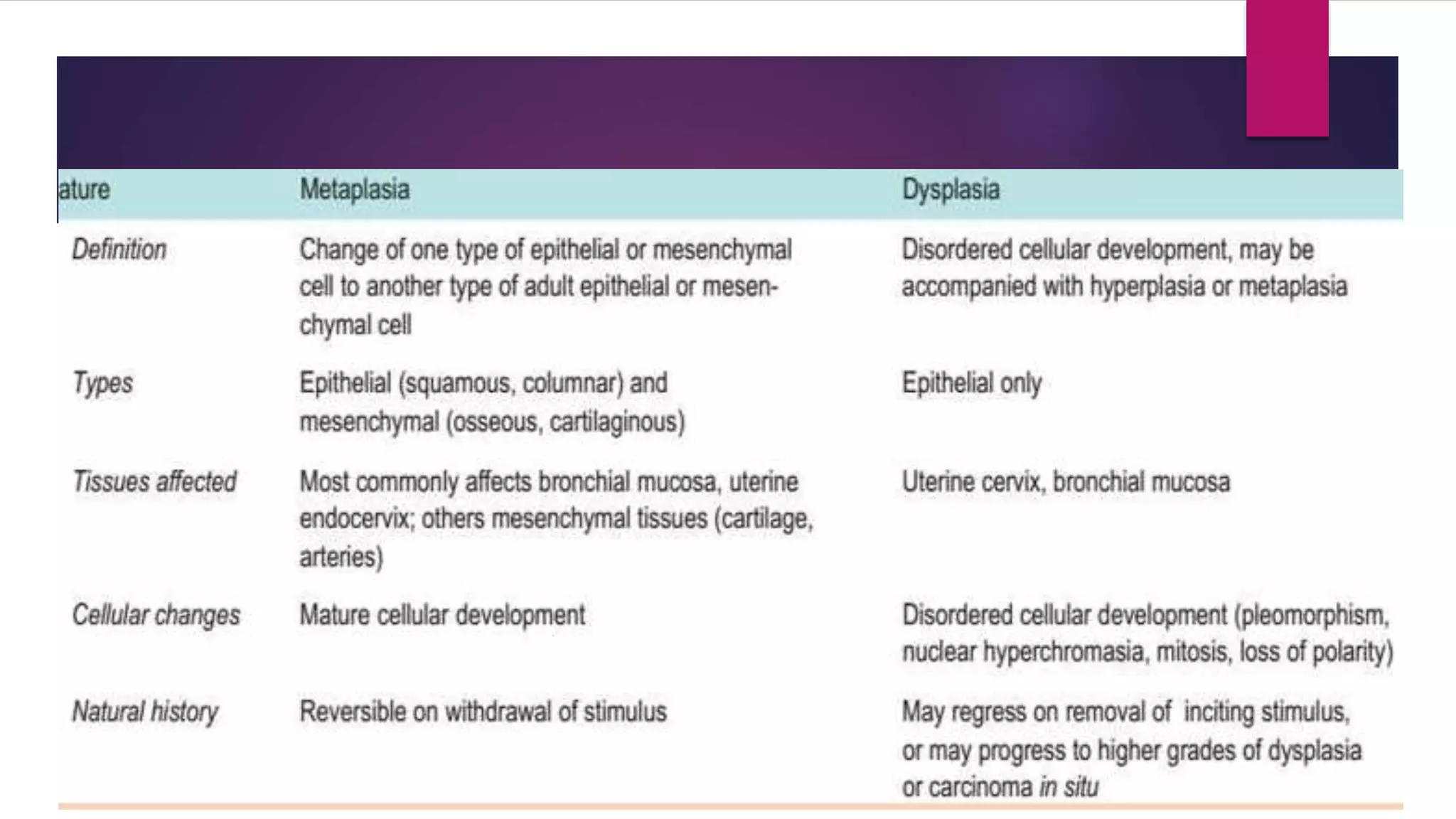
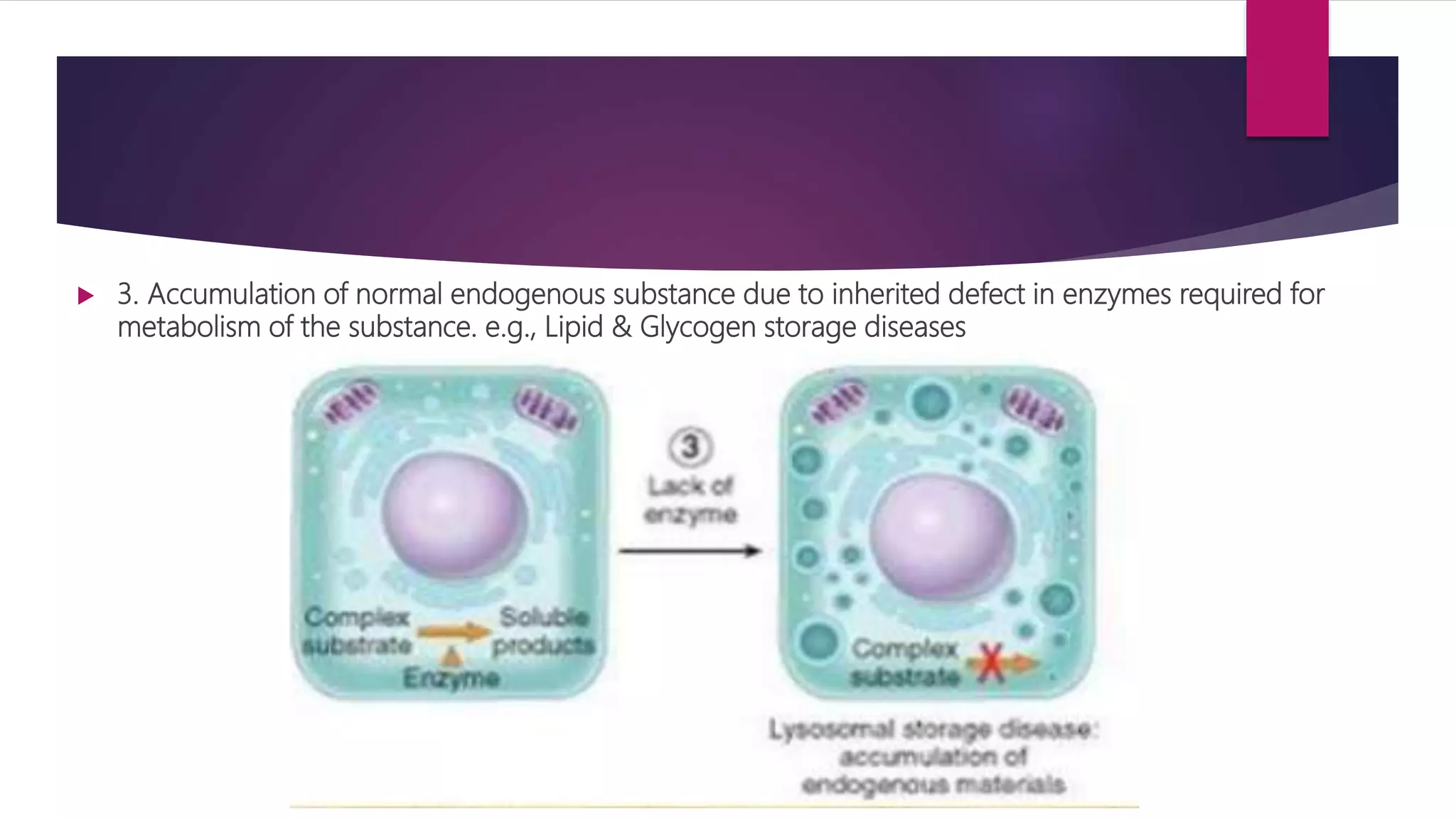
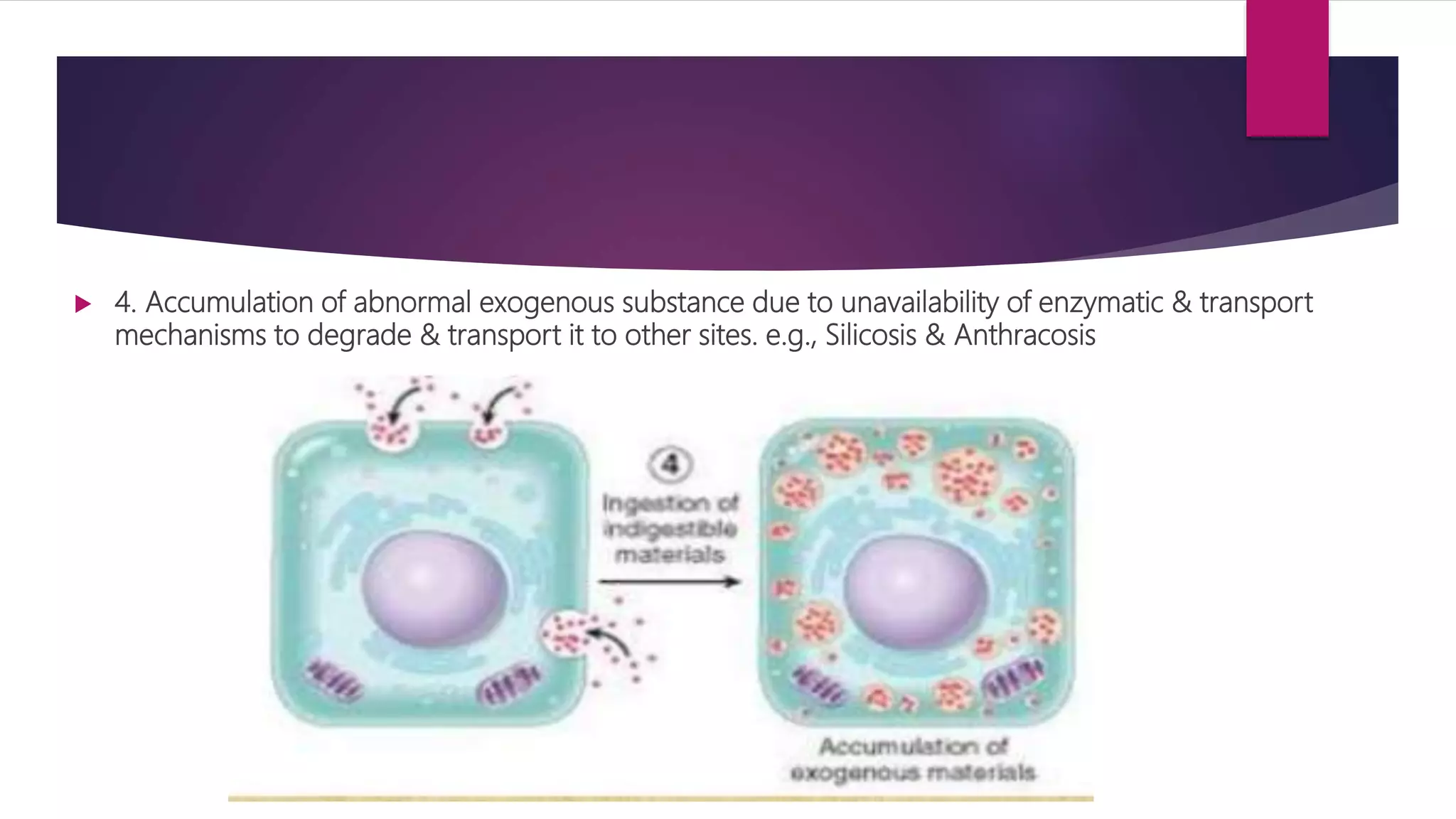
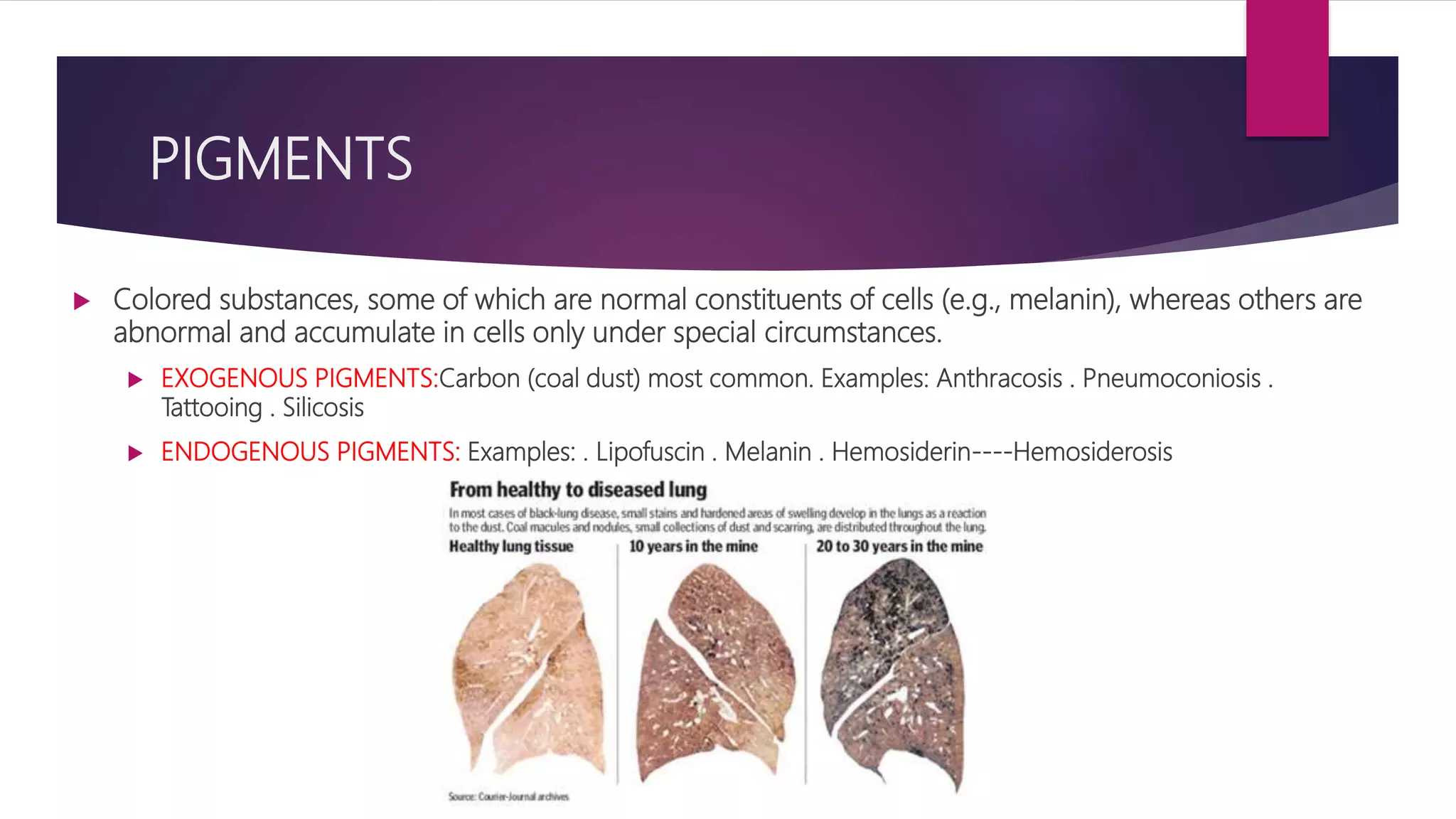
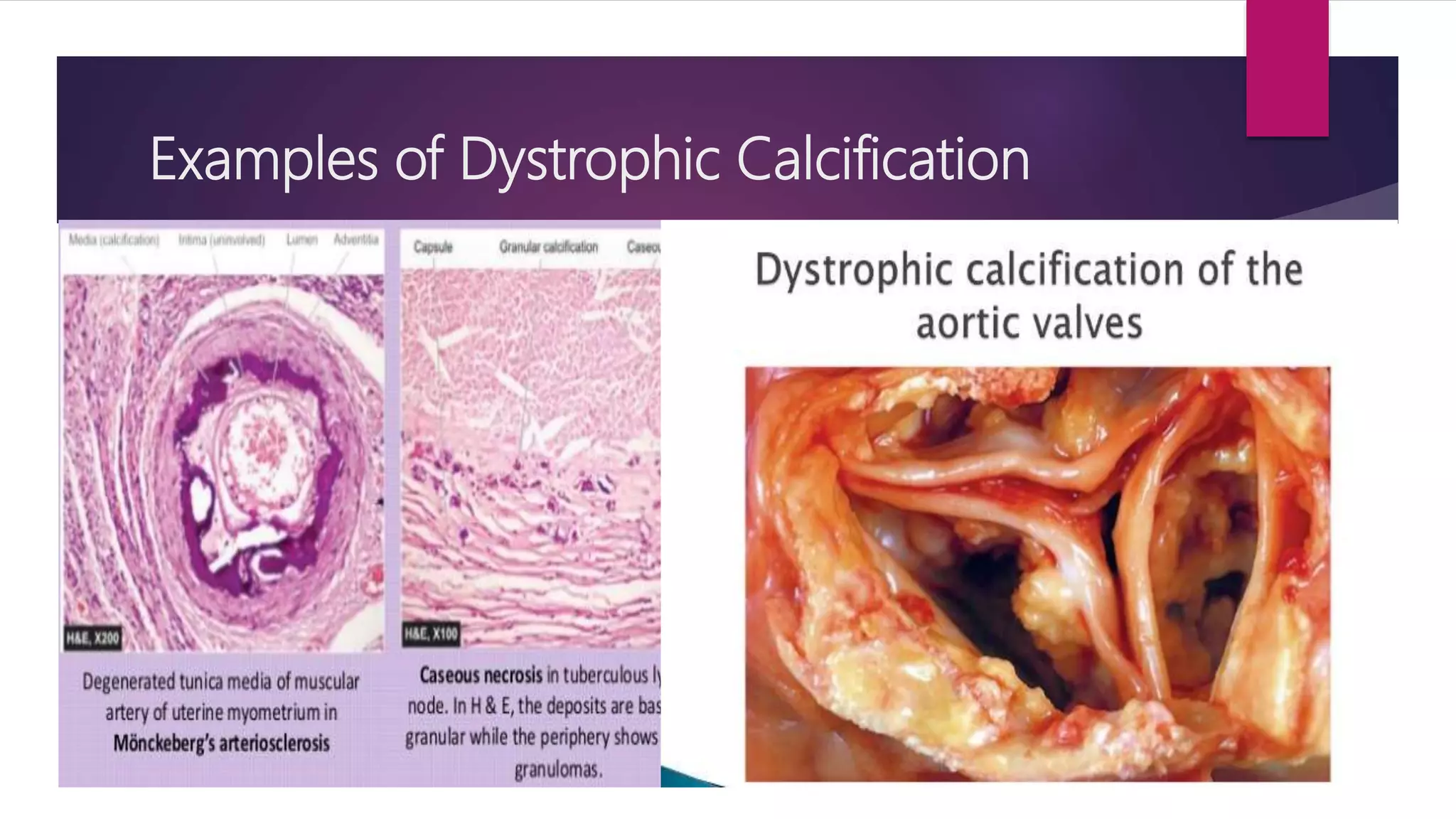
The document discusses various cellular adaptations in response to environmental changes including atrophy, hypertrophy, hyperplasia, metaplasia, dysplasia, and anaplasia. It also discusses intracellular accumulations of substances such as lipids, proteins, glycogen, pigments, and calcium deposits. Atrophy is a decrease in cell size while hypertrophy is an increase in cell size. Hyperplasia is an increase in cell number. Metaplasia, dysplasia and anaplasia refer to changes in cell type. Accumulations can occur due to excess production or defects in metabolism. Common accumulations include lipids in fatty liver, proteins in renal tubules, and iron as hemosiderin.