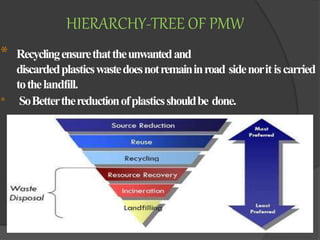
Plastics have made significant contributions across many fields like agriculture, medicine, transportation, and manufacturing. They are widely used due to properties like light weight, durability, and low price. Plastics can be categorized based on their recyclability and size. Improper plastic waste disposal pollutes the marine environment. New technologies are being developed and implemented for plastic waste management like recycling, incineration, use in road construction, and co-processing in cement kilns. Education programs are needed to promote better plastic waste disposal practices and reduce environmental pollution.