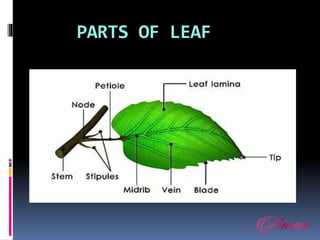
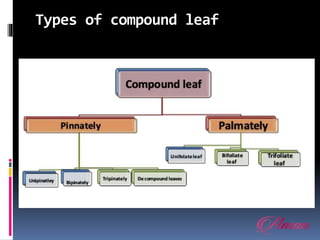
The leaf is the main organ of plants responsible for photosynthesis. It comes in different shapes and sizes and contains chlorophyll which gives it a green color. The main parts of a leaf include the petiole, leaf base, and leaf blade. Veins in the leaf blade can be arranged in reticulate or parallel patterns. Leaves are either simple with one leaf blade or compound with multiple leaflets. Compound leaves can be pinnately or palmately arranged. The key functions of leaves are to produce oxygen, food for the plant via photosynthesis, and reduce soil erosion.