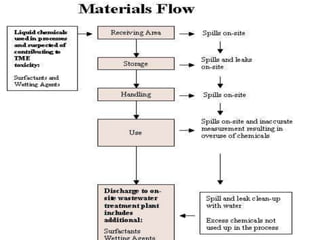
This document discusses material handling systems and equipment. It provides definitions of material handling and outlines the goals of effective material handling. Key types of material handling equipment are described, including pallet racks, automated storage and retrieval systems, conveyors, industrial trucks, and bulk handling equipment. The roles of material handling systems in flexible manufacturing are also summarized. Advantages like improved efficiency and disadvantages like additional costs are highlighted.