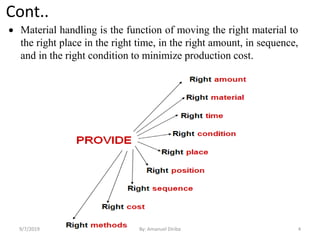
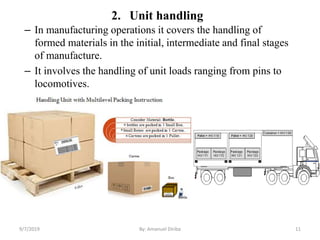
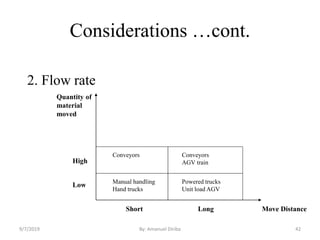
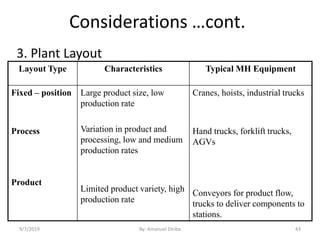
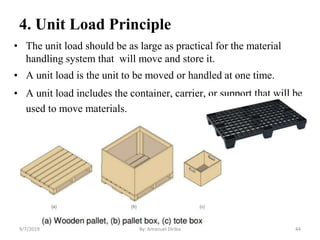
This document provides an introduction and overview of materials handling equipment. It defines materials handling, outlines its importance and limitations, and discusses how materials are classified and the applications of materials handling equipment. It also covers key design considerations for materials handling systems including material characteristics, flow rate, plant layout, and the unit load principle. The document aims to introduce the basics of materials handling equipment and systems.