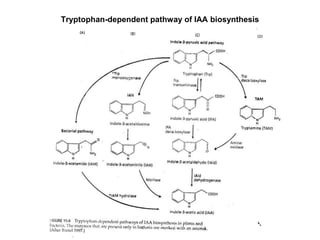
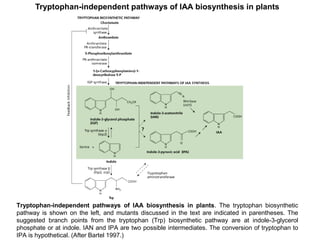
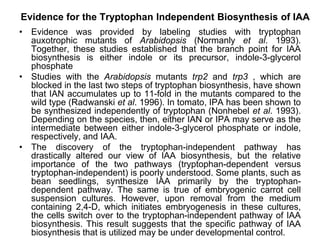
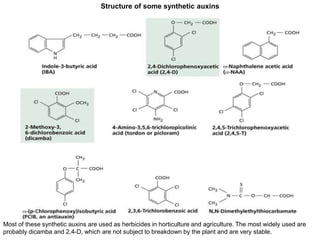
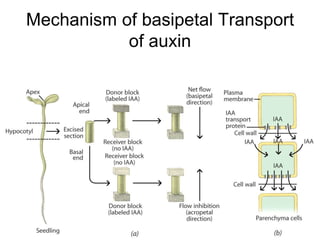
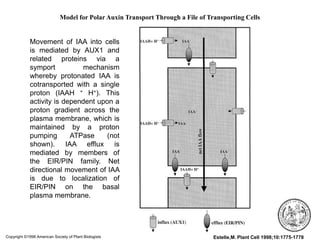
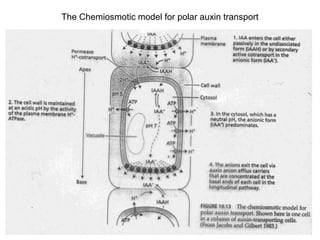
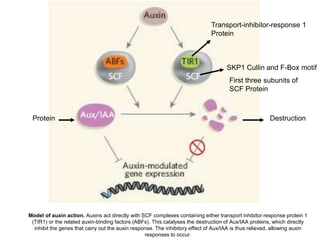
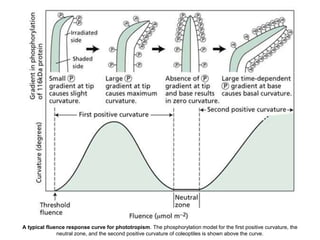
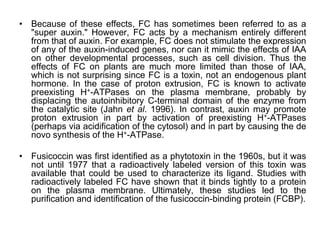
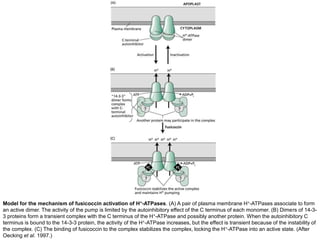
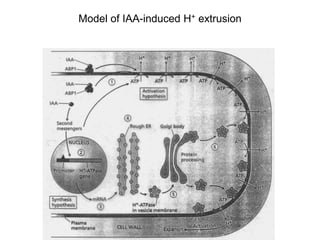
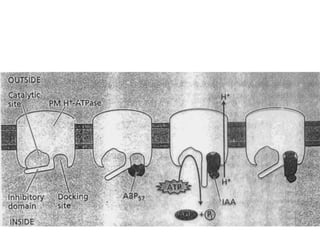
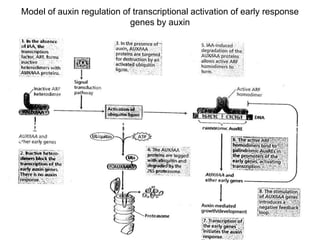
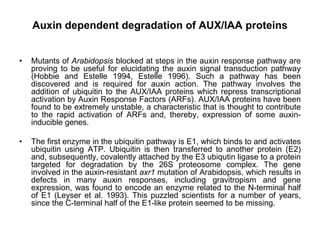
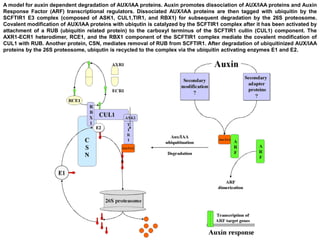
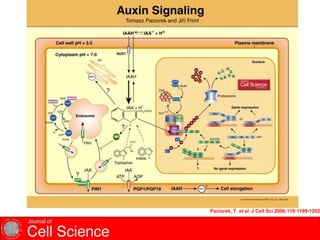
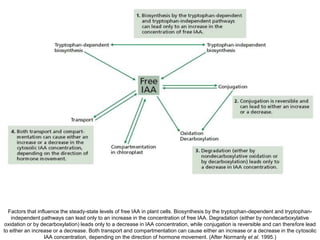
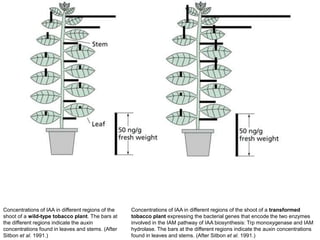
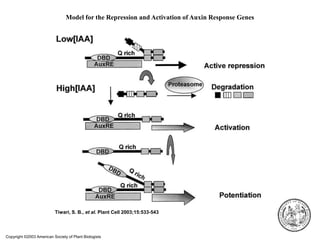
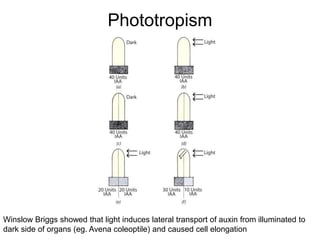
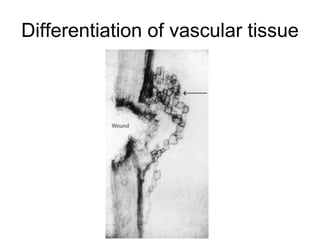
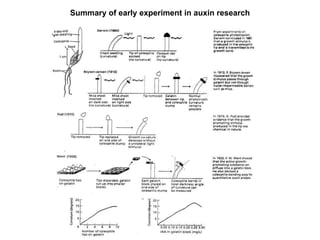
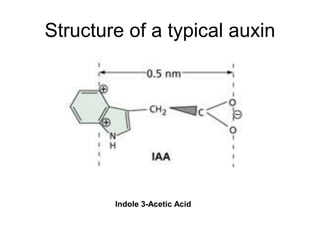
Auxins are plant hormones that stimulate growth. They were the first hormone discovered and are important regulators of many growth processes. Auxins stimulate cell division, elongation, apical dominance, root initiation, flowering, and breaking bud dormancy. Their mechanism of action involves activating transcription of auxin response genes. Auxins are transported polarly through plants via influx and efflux carriers, establishing concentration gradients that direct growth. The most common native auxin is indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), but plants can synthesize IAA via tryptophan-dependent and -independent pathways.






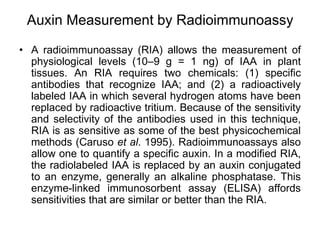
![Radioimmunoassay for the amount of auxin in a plant tissue extract. In the preparation of auxin antibodies, IAA is first conjugated to
a large protein and injected into a mouse or rabbit. The animal produces antibodies to all of the antigenic determinants on the protein,
including the IAA. The anti-IAA antibodies can then be purified for use in the RIA. Unlabeled antigen (IAA) competes with a known
amount of radioactively labeled antigen—e.g., [14C]IAA—for binding to antibodies. The more unlabeled antigen present, the less
radioactivity from the radioactive antigen will be found in the antibody precipitate.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/002auxins-230829043041-46ed2899/85/002-Auxins-ppt-13-320.jpg)