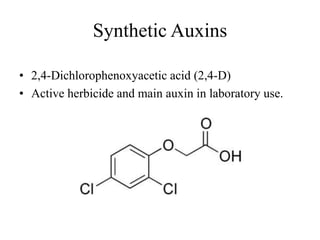
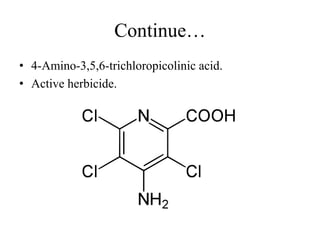
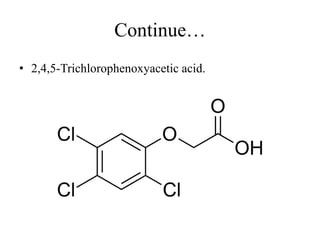
Auxins are a class of plant hormones that play a key role in coordinating plant growth and development. The first auxin discovered was indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), which is produced in plant shoots and promotes growth by inhibiting lateral bud development. Auxins govern plant form and architecture by controlling the growth of roots, shoots, leaves and other organs. They allow plants to bend towards light via differential cell elongation. Auxins have many physiological effects including stimulating root growth, fruit development, cell enlargement and division.