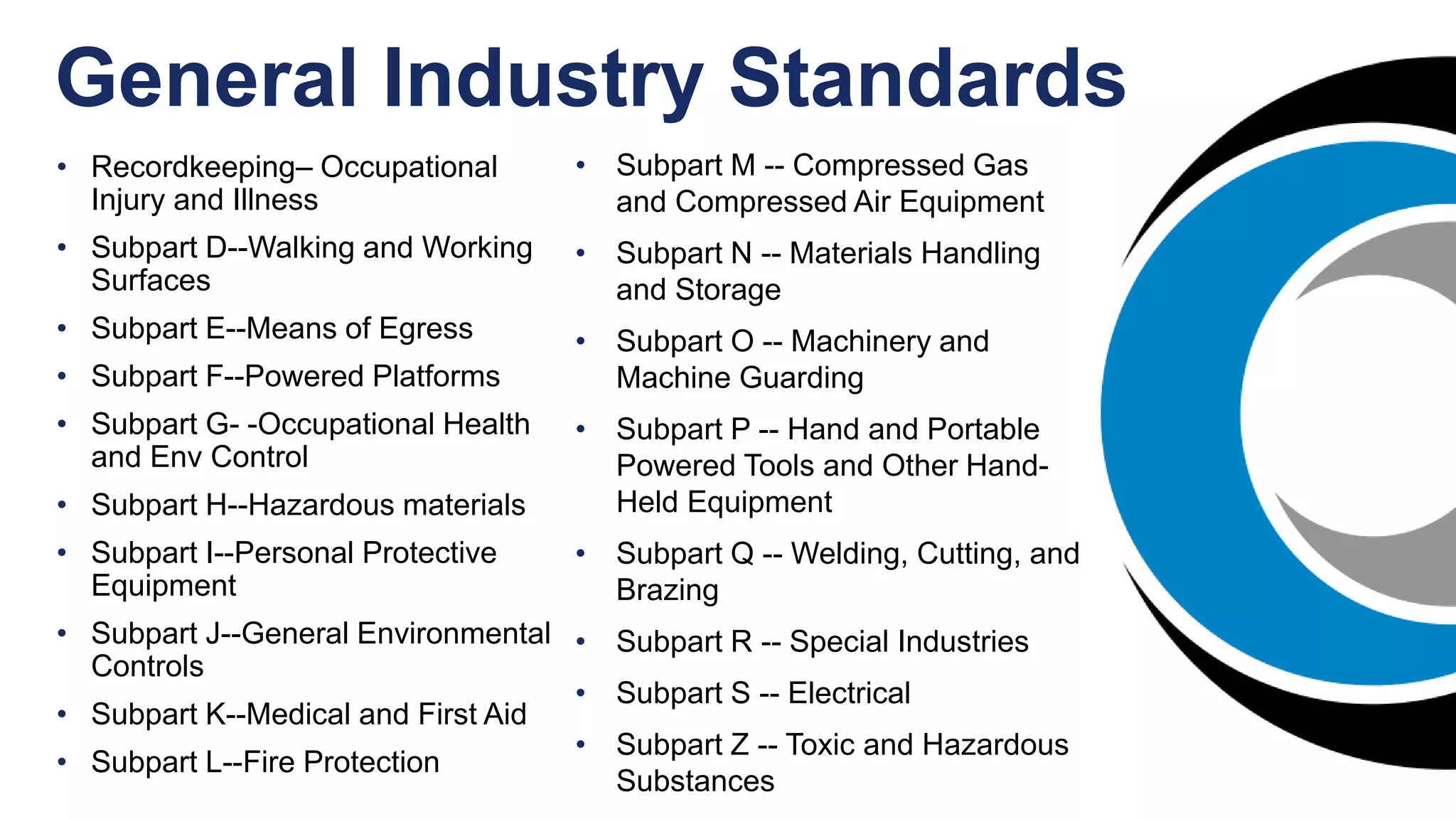
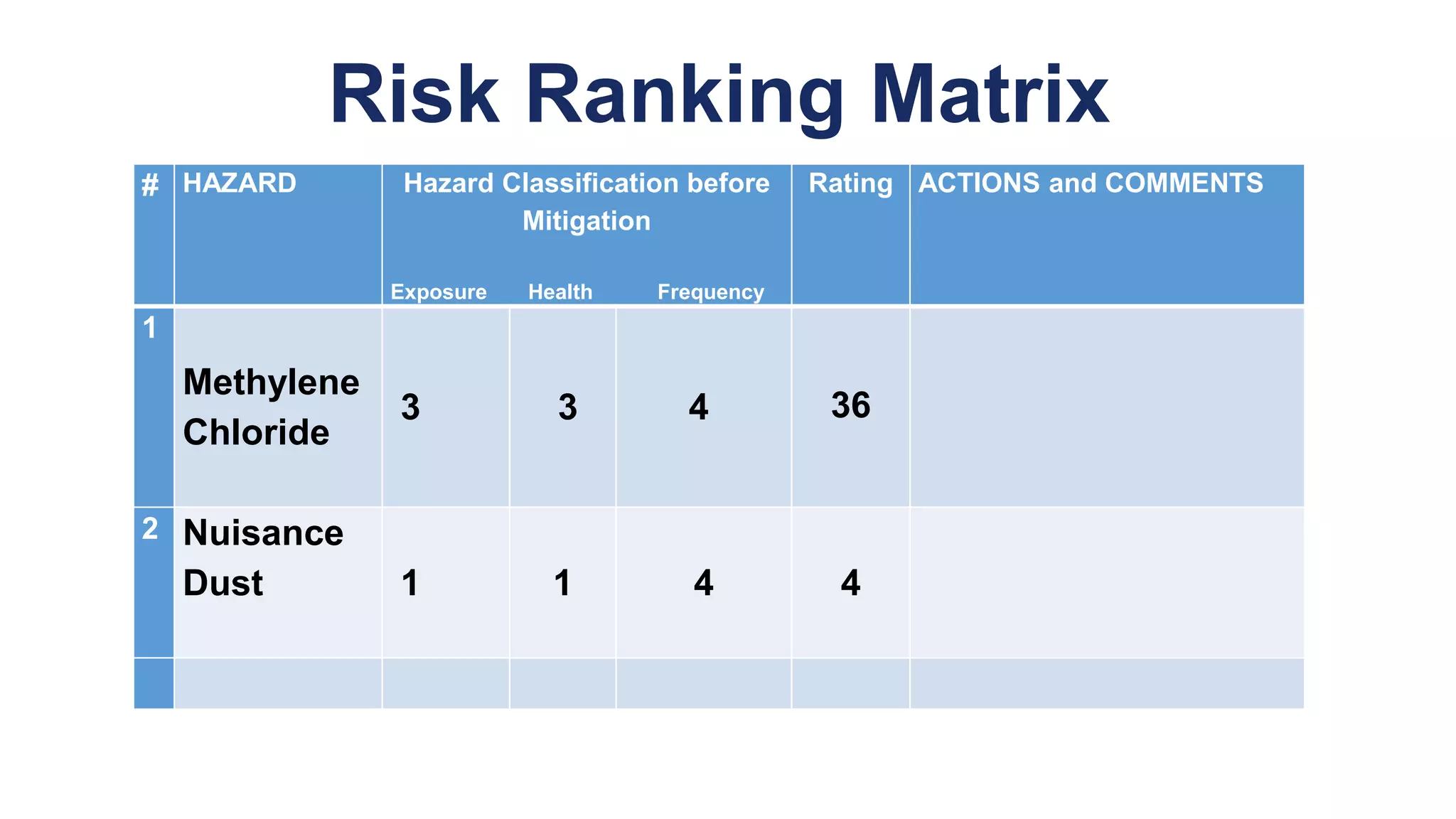
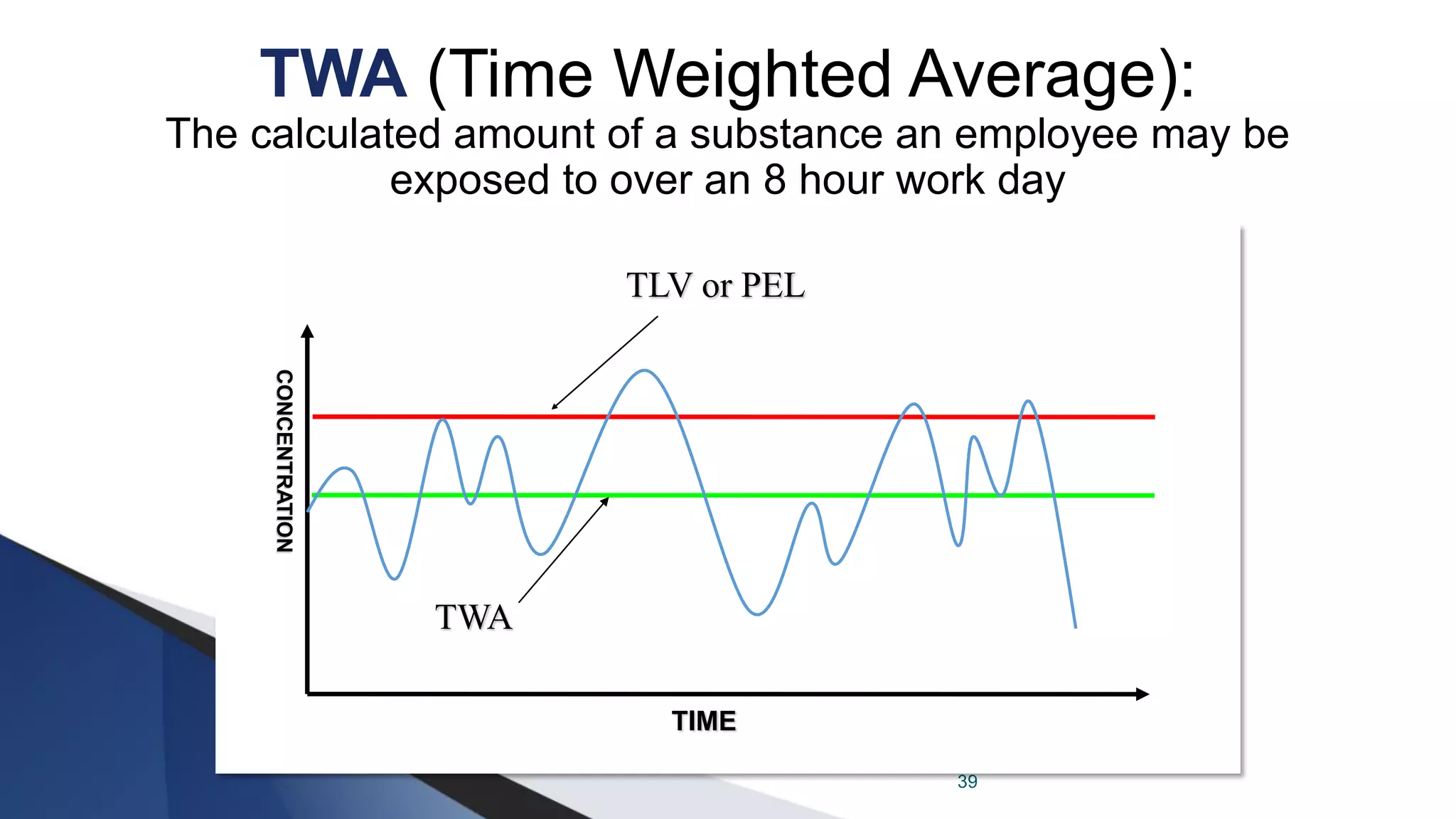
The document outlines the planning and execution of an industrial hygiene program, emphasizing its importance for worker health and compliance with regulations. It details essential elements of such a program, roles and responsibilities of involved parties, and the need for effective chemical exposure monitoring. The presentation encourages a proactive risk-based approach to identify and mitigate workplace hazards.