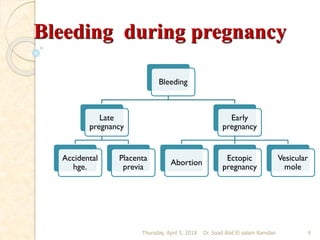
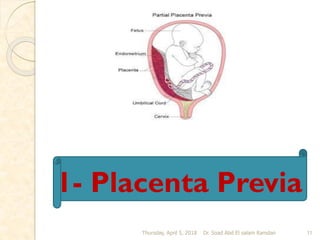
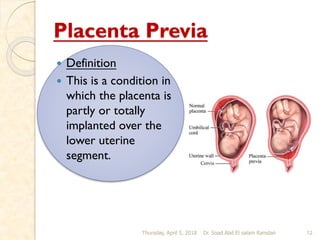
This document discusses bleeding during pregnancy, specifically focusing on bleeding in late pregnancy known as ante partum hemorrhage. It describes the main causes of ante partum hemorrhage as placenta previa and abruptio placenta. Placenta previa is defined as an abnormally positioned placenta that covers all or part of the cervical os, and can cause inevitable bleeding. The document outlines the prevalence, causes, degrees, diagnosis, and management of placenta previa. Nursing care for women with placenta previa focuses on careful assessment and monitoring of maternal and fetal status, with the goals of preventing complications and delivering a healthy infant.













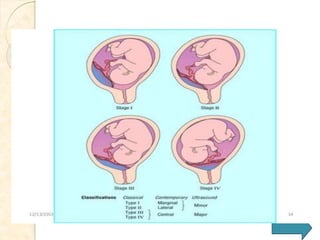
![Degrees:-
◘ Placenta previa
lateralis: [type I]
The lower part of
the placenta is
implanted over the
lower uterine
segment, but does
not reach the
internal os.
◘ Placenta previa
marginalis: [type II]
Part of the placenta
is implanted over the
lower uterine
segment and its
margin reaches the
internal os, but does
not cover it
completely.
Thursday, April 5, 2018 Dr. Soad Abd El salam Ramdan 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/placentaprevia-180405230431/85/Placenta-previa-17-320.jpg)
![◘ Incomplete central
placenta previa: [type
III]
The placenta covers the
closed or incompletely
dilated internal os
eccentrically, but with
further dilatation.The
placenta does not cover
it completely when it is
closed, but covers it
incompletely when the
os is dilated.
◘ Complete central
placenta previa: [type
IV]
The whole placenta is
implanted over the
lower uterine segment,
with the internal os
located at the center of
the placenta.Thus, the
placenta covers the
internal os completely
even when it is fully
dilated.
Thursday, April 5, 2018 Dr. Soad Abd El salam Ramdan 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/placentaprevia-180405230431/85/Placenta-previa-18-320.jpg)